Psychological safety fosters an environment where employees feel secure to express ideas and take risks without fear of negative consequences, directly influencing teamwork and innovation. Organizational culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors shaping workplace dynamics and employee engagement. Explore how integrating psychological safety within organizational culture boosts productivity and employee satisfaction.
Why it is important
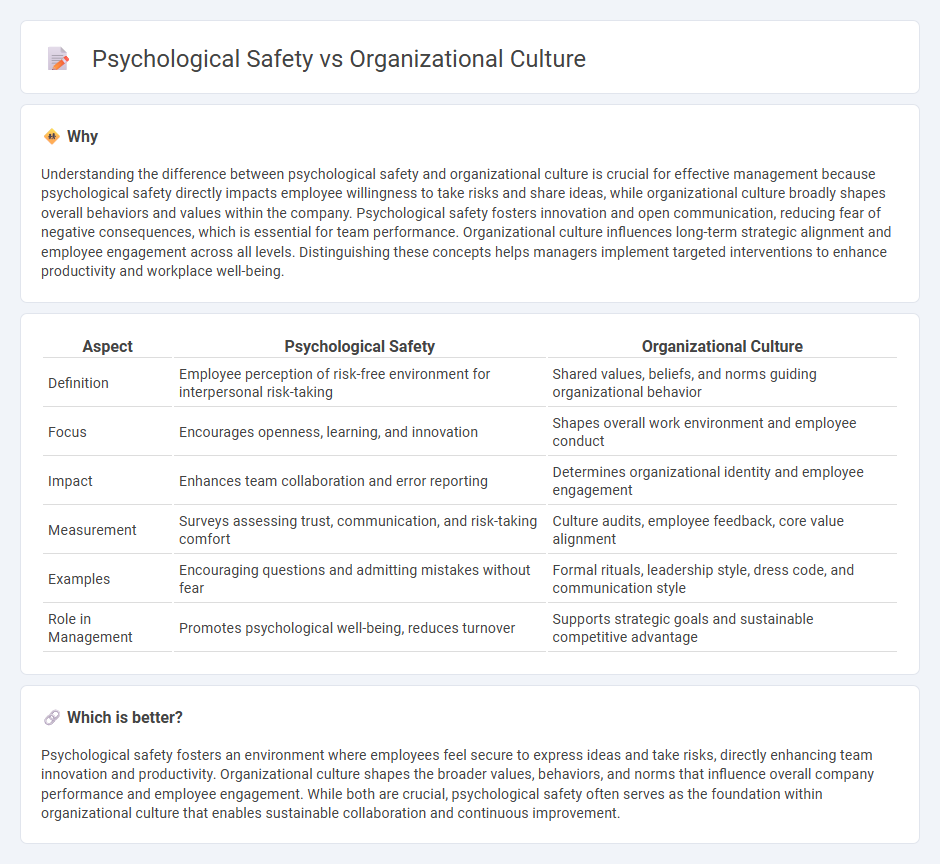
Understanding the difference between psychological safety and organizational culture is crucial for effective management because psychological safety directly impacts employee willingness to take risks and share ideas, while organizational culture broadly shapes overall behaviors and values within the company. Psychological safety fosters innovation and open communication, reducing fear of negative consequences, which is essential for team performance. Organizational culture influences long-term strategic alignment and employee engagement across all levels. Distinguishing these concepts helps managers implement targeted interventions to enhance productivity and workplace well-being.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Psychological Safety | Organizational Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee perception of risk-free environment for interpersonal risk-taking | Shared values, beliefs, and norms guiding organizational behavior |
| Focus | Encourages openness, learning, and innovation | Shapes overall work environment and employee conduct |
| Impact | Enhances team collaboration and error reporting | Determines organizational identity and employee engagement |
| Measurement | Surveys assessing trust, communication, and risk-taking comfort | Culture audits, employee feedback, core value alignment |
| Examples | Encouraging questions and admitting mistakes without fear | Formal rituals, leadership style, dress code, and communication style |
| Role in Management | Promotes psychological well-being, reduces turnover | Supports strategic goals and sustainable competitive advantage |
Which is better?
Psychological safety fosters an environment where employees feel secure to express ideas and take risks, directly enhancing team innovation and productivity. Organizational culture shapes the broader values, behaviors, and norms that influence overall company performance and employee engagement. While both are crucial, psychological safety often serves as the foundation within organizational culture that enables sustainable collaboration and continuous improvement.
Connection
Psychological safety fosters open communication, allowing employees to express ideas and concerns without fear of negative consequences, which directly shapes a collaborative and supportive organizational culture. Organizations emphasizing trust and inclusivity create environments where innovation thrives and team performance improves. Research from Google's Project Aristotle highlights psychological safety as a core factor influencing effective team dynamics within strong organizational cultures.
Key Terms
Shared Values
Organizational culture is defined by shared values that shape employee behavior, guiding decision-making and fostering a cohesive work environment. Psychological safety hinges on these shared values, promoting open communication and trust, allowing employees to take risks without fear of negative consequences. Explore how aligning organizational culture with psychological safety can enhance team collaboration and innovation.
Trust
Organizational culture shapes the collective values and behaviors that influence trust among employees, while psychological safety specifically fosters an environment where individuals feel safe to take interpersonal risks without fear of negative consequences. Trust in organizational culture promotes open communication and collaboration, creating a foundation for psychological safety to thrive. Explore deeper insights into how trust interlinks these concepts to drive employee engagement and innovation.
Open Communication
Organizational culture that promotes open communication fosters trust, collaboration, and transparency among employees, directly enhancing psychological safety by encouraging individuals to share ideas and concerns without fear of judgment or reprisal. Psychological safety, a critical component of high-performing teams, thrives in environments where open dialogue is not only accepted but actively encouraged, leading to increased innovation and engagement. Explore further how cultivating open communication within your organizational culture can boost psychological safety and drive business success.
Source and External Links
The 4 Types of Organizational Culture & How to Design Change - This article discusses the four main types of organizational culture--adhocracy, clan, hierarchy, and market--and how they influence a company's work environment.
Organizational Culture: Definition, Importance, and Development - This resource defines organizational culture and outlines its importance, highlighting the role of leaders in shaping culture and the six dimensions of organizational culture.
Organizational Culture: Definition and Types - This webpage explains organizational culture as the shared values and practices within an organization, focusing on the four main types defined by Quinn and Cameron: clan, adhocracy, market, and hierarchy cultures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com