Intelligent automation integrates artificial intelligence with robotic process automation (RPA) to enhance decision-making and handle complex tasks beyond repetitive rule-based processes. RPA focuses on automating routine, structured workflows through software robots, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Explore how combining these technologies revolutionizes management practices and drives operational excellence.
Why it is important
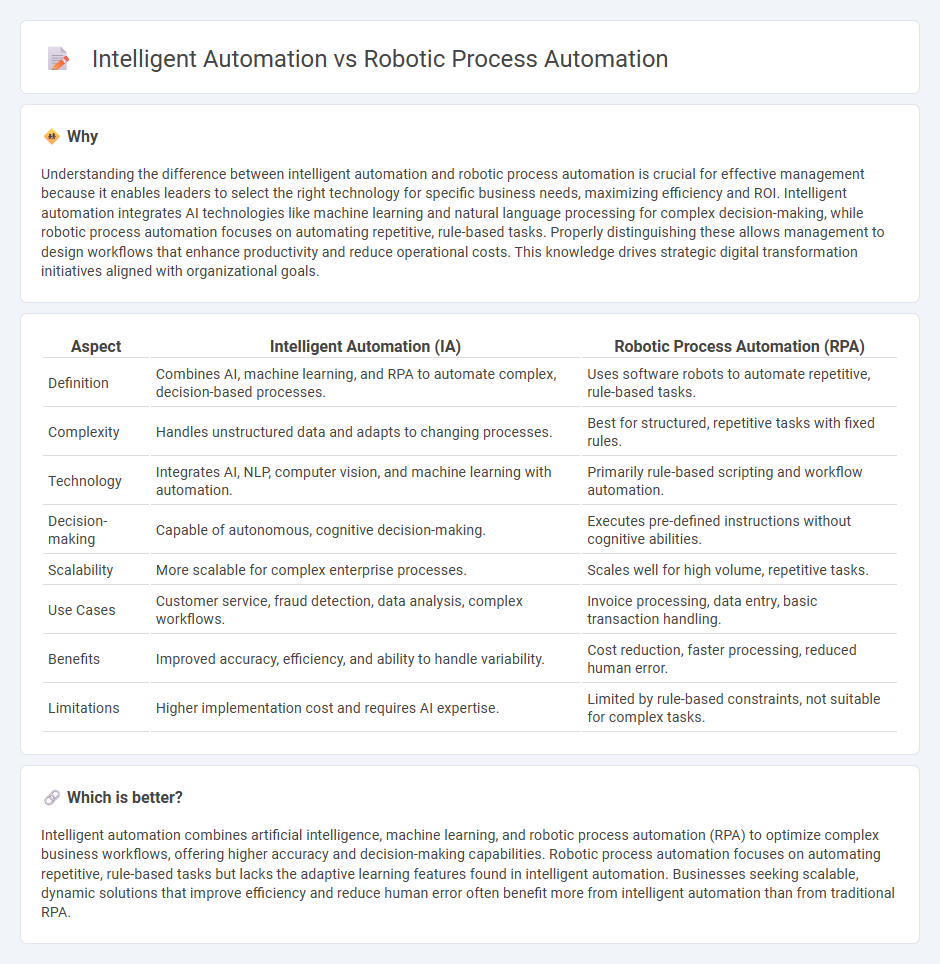
Understanding the difference between intelligent automation and robotic process automation is crucial for effective management because it enables leaders to select the right technology for specific business needs, maximizing efficiency and ROI. Intelligent automation integrates AI technologies like machine learning and natural language processing for complex decision-making, while robotic process automation focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. Properly distinguishing these allows management to design workflows that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. This knowledge drives strategic digital transformation initiatives aligned with organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Intelligent Automation (IA) | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines AI, machine learning, and RPA to automate complex, decision-based processes. | Uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. |
| Complexity | Handles unstructured data and adapts to changing processes. | Best for structured, repetitive tasks with fixed rules. |
| Technology | Integrates AI, NLP, computer vision, and machine learning with automation. | Primarily rule-based scripting and workflow automation. |
| Decision-making | Capable of autonomous, cognitive decision-making. | Executes pre-defined instructions without cognitive abilities. |
| Scalability | More scalable for complex enterprise processes. | Scales well for high volume, repetitive tasks. |
| Use Cases | Customer service, fraud detection, data analysis, complex workflows. | Invoice processing, data entry, basic transaction handling. |
| Benefits | Improved accuracy, efficiency, and ability to handle variability. | Cost reduction, faster processing, reduced human error. |
| Limitations | Higher implementation cost and requires AI expertise. | Limited by rule-based constraints, not suitable for complex tasks. |
Which is better?
Intelligent automation combines artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to optimize complex business workflows, offering higher accuracy and decision-making capabilities. Robotic process automation focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks but lacks the adaptive learning features found in intelligent automation. Businesses seeking scalable, dynamic solutions that improve efficiency and reduce human error often benefit more from intelligent automation than from traditional RPA.
Connection
Intelligent automation integrates artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing with robotic process automation (RPA) to enhance workflow efficiency and decision-making. RPA handles repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human actions, while intelligent automation extends these capabilities by enabling cognitive functions and adaptive responses. This synergy improves operational management by reducing errors, accelerating processes, and enabling scalable automation solutions.
Key Terms
Rule-based Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) specializes in rule-based automation by executing repetitive, structured tasks through predefined rules without the need for human intervention. Unlike Intelligent Automation, which integrates AI capabilities for decision-making and adaptability, RPA strictly follows clear, programmed workflows to enhance operational efficiency. Explore more about how rule-based automation can streamline your business processes and improve accuracy.
Machine Learning
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates rule-based, repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions, while Intelligent Automation (IA) integrates Machine Learning (ML) to enable systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on data patterns. ML enhances IA by processing unstructured data, improving accuracy, and enabling predictive analytics beyond the capabilities of traditional RPA. Explore how combining RPA with ML-driven IA can transform business processes for enhanced efficiency and innovation.
Cognitive Capabilities
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) primarily executes rule-based tasks with structured data, while Intelligent Automation (IA) incorporates cognitive capabilities such as natural language processing, machine learning, and decision-making to handle unstructured data and complex workflows. IA enhances automation by enabling systems to learn from interactions and adapt processes, leading to improved accuracy and efficiency in dynamic business environments. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how cognitive capabilities transform automation strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - RPA is a business process automation technology using software robots to perform repetitive human tasks by emulating human interactions across multiple systems, combining APIs and user interfaces, and evolving into intelligent automation by incorporating AI subfields like machine learning and natural language processing.
What is Robotic Process Automation - RPA Software - RPA software robots automate workflows by mimicking human digital interactions, improving efficiency, reducing errors, cutting costs, and freeing employees from mundane tasks, making organizations more flexible and productive.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) - RPA uses bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks such as document processing, invoice management, customer service, HR onboarding, and supply chain operations, thereby increasing accuracy, speed, and productivity across industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com