Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical management with decentralized authority and self-organizing teams, empowering employees to make decisions within defined roles. Network organizations emphasize flexible, interconnected relationships across teams, fostering collaboration and rapid information flow without rigid structures. Explore how these innovative management models transform organizational agility and employee engagement.
Why it is important
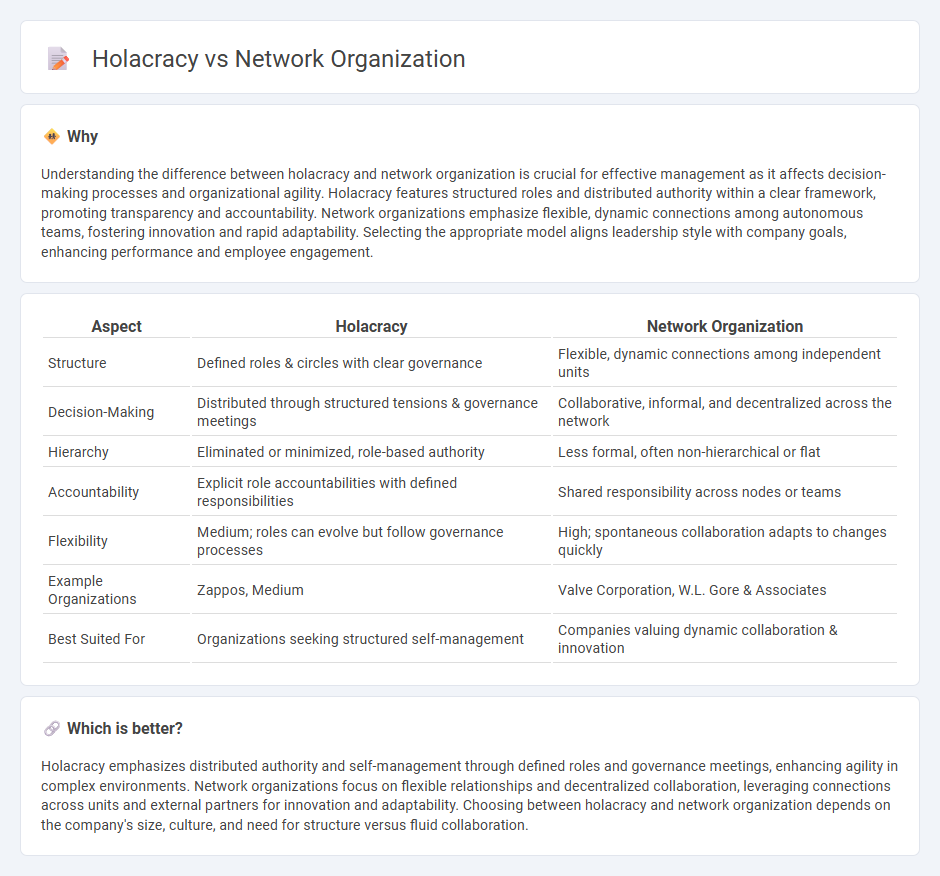
Understanding the difference between holacracy and network organization is crucial for effective management as it affects decision-making processes and organizational agility. Holacracy features structured roles and distributed authority within a clear framework, promoting transparency and accountability. Network organizations emphasize flexible, dynamic connections among autonomous teams, fostering innovation and rapid adaptability. Selecting the appropriate model aligns leadership style with company goals, enhancing performance and employee engagement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Holacracy | Network Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Defined roles & circles with clear governance | Flexible, dynamic connections among independent units |
| Decision-Making | Distributed through structured tensions & governance meetings | Collaborative, informal, and decentralized across the network |
| Hierarchy | Eliminated or minimized, role-based authority | Less formal, often non-hierarchical or flat |
| Accountability | Explicit role accountabilities with defined responsibilities | Shared responsibility across nodes or teams |
| Flexibility | Medium; roles can evolve but follow governance processes | High; spontaneous collaboration adapts to changes quickly |
| Example Organizations | Zappos, Medium | Valve Corporation, W.L. Gore & Associates |
| Best Suited For | Organizations seeking structured self-management | Companies valuing dynamic collaboration & innovation |
Which is better?
Holacracy emphasizes distributed authority and self-management through defined roles and governance meetings, enhancing agility in complex environments. Network organizations focus on flexible relationships and decentralized collaboration, leveraging connections across units and external partners for innovation and adaptability. Choosing between holacracy and network organization depends on the company's size, culture, and need for structure versus fluid collaboration.
Connection
Holacracy and network organization share a decentralized approach that distributes authority across self-managed teams, enhancing agility and transparency in management. Both frameworks emphasize dynamic roles over rigid hierarchies, enabling rapid decision-making aligned with organizational goals. This connection fosters collaboration and innovation by empowering individuals within a fluid, interconnected structure.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Network organization emphasizes decentralized decision-making through interconnected nodes that enhance flexibility and innovation, allowing teams to operate autonomously with minimal hierarchical constraints. Holacracy implements decentralization by distributing authority across self-organizing teams called circles, each with clear roles and governance processes to ensure agility and accountability. Explore how these decentralized frameworks transform management and drive organizational efficiency.
Self-Management
Network organizations emphasize decentralized decision-making and fluid roles to foster agility, whereas holacracy formalizes self-management through structured governance processes and defined circles. Both models prioritize autonomy and distributed authority but holacracy provides explicit frameworks for role accountability and conflict resolution. Explore the key differences and practical applications of these self-management systems to enhance organizational effectiveness.
Roles
Network organizations distribute decision-making through interconnected nodes, emphasizing flexible, informal roles that adapt to project needs, fostering collaboration and innovation. Holacracy implements a structured system of clearly defined roles and accountabilities within self-organizing circles, ensuring transparency and dynamic governance. Explore how role definitions impact organizational agility and employee empowerment to discover the best fit for your company's culture.
Source and External Links
What Is Network Organization? [+ Examples] - This resource explains the concept of network organizations, their types, and how they operate in a decentralized manner compared to traditional hierarchical structures.
Project Management in Network Organizations - This article discusses how network organizations can gain a competitive advantage through complex adaptive systems and collaboration without central hierarchical control.
Network-centric organization - This page describes a network-centric organization as a governance pattern that empowers knowledge workers through collaboration in small teams to leverage information and increase competitive advantage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com