Toxic positivity undermines effective management by dismissing legitimate concerns and discouraging honest feedback, while critical thinking promotes realistic problem-solving and informed decision-making. Emphasizing critical thinking in leadership fosters a culture of transparency, resilience, and continuous improvement. Explore more to understand how balancing positivity with critical thinking enhances management success.
Why it is important
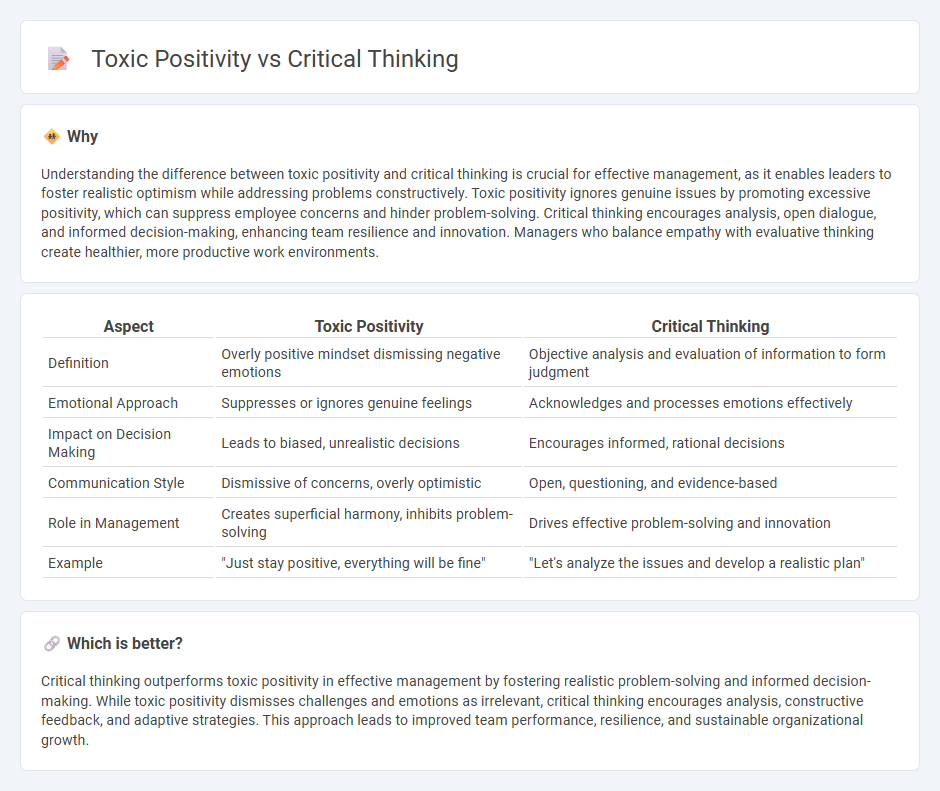
Understanding the difference between toxic positivity and critical thinking is crucial for effective management, as it enables leaders to foster realistic optimism while addressing problems constructively. Toxic positivity ignores genuine issues by promoting excessive positivity, which can suppress employee concerns and hinder problem-solving. Critical thinking encourages analysis, open dialogue, and informed decision-making, enhancing team resilience and innovation. Managers who balance empathy with evaluative thinking create healthier, more productive work environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Toxic Positivity | Critical Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overly positive mindset dismissing negative emotions | Objective analysis and evaluation of information to form judgment |
| Emotional Approach | Suppresses or ignores genuine feelings | Acknowledges and processes emotions effectively |
| Impact on Decision Making | Leads to biased, unrealistic decisions | Encourages informed, rational decisions |
| Communication Style | Dismissive of concerns, overly optimistic | Open, questioning, and evidence-based |
| Role in Management | Creates superficial harmony, inhibits problem-solving | Drives effective problem-solving and innovation |
| Example | "Just stay positive, everything will be fine" | "Let's analyze the issues and develop a realistic plan" |
Which is better?
Critical thinking outperforms toxic positivity in effective management by fostering realistic problem-solving and informed decision-making. While toxic positivity dismisses challenges and emotions as irrelevant, critical thinking encourages analysis, constructive feedback, and adaptive strategies. This approach leads to improved team performance, resilience, and sustainable organizational growth.
Connection
Toxic positivity undermines critical thinking by promoting an unrealistic insistence on positive emotions, which can suppress honest evaluation and problem-solving. Critical thinking requires acknowledging and analyzing negative emotions or challenges to make informed decisions and foster genuine growth. Recognizing toxic positivity allows managers to create environments where constructive feedback and realistic perspectives drive effective leadership and organizational success.
Key Terms
Objective Analysis
Critical thinking involves objective analysis by evaluating facts and evidence without bias, enabling rational decision-making and problem-solving. Toxic positivity, by contrast, dismisses genuine emotions and critical perspectives, promoting an unrealistic and overly optimistic outlook that undermines authentic understanding. Explore more to understand how balancing critical thinking with healthy positivity enhances mental resilience.
Authentic Feedback
Critical thinking involves analyzing information objectively and providing authentic feedback based on evidence and reason, fostering growth and improvement. Toxic positivity, on the other hand, discourages genuine critique by promoting an overly optimistic outlook that ignores challenges and valid concerns. Explore effective strategies for balancing honest feedback with positive encouragement to enhance communication skills.
Emotional Intelligence
Critical thinking sharpens emotional intelligence by fostering self-awareness and realistic self-appraisal, while toxic positivity undermines emotional intelligence by dismissing genuine feelings and promoting forced optimism. Both approaches impact how individuals process emotions, with critical thinking encouraging balanced emotional responses and toxic positivity leading to emotional suppression. Discover how enhancing emotional intelligence through critical thinking can improve mental well-being and relationships.
Source and External Links
Critical Thinking - Wikipedia - Critical thinking involves analyzing facts, evidence, and arguments to make informed choices by applying rational and skeptical analysis.
What is Critical Thinking? - Monash University - Critical thinking is a process of questioning, analyzing, interpreting, evaluating, and making judgments based on reliable information.
Defining Critical Thinking - The Critical Thinking Community - Critical thinking is self-guided, disciplined thinking that aims to reason at the highest quality in a fair-minded way, examining various elements of thought.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com