Hybrid management combines delegation and oversight, allowing leaders to balance autonomy with guidance, enhancing team productivity and innovation. Micromanagement, characterized by excessive control and constant monitoring, often stifles creativity and reduces employee morale. Discover the key differences between these management styles to optimize your leadership approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between hybrid management and micromanagement is crucial for fostering employee autonomy and improving productivity. Hybrid management balances strategic oversight with employee empowerment, while micromanagement restricts autonomy by excessively controlling tasks. Properly distinguishing these styles helps leaders adapt their approach to enhance team motivation and project outcomes. Effective management drives organizational success by aligning leadership style with workforce needs and business goals.
Comparison Table
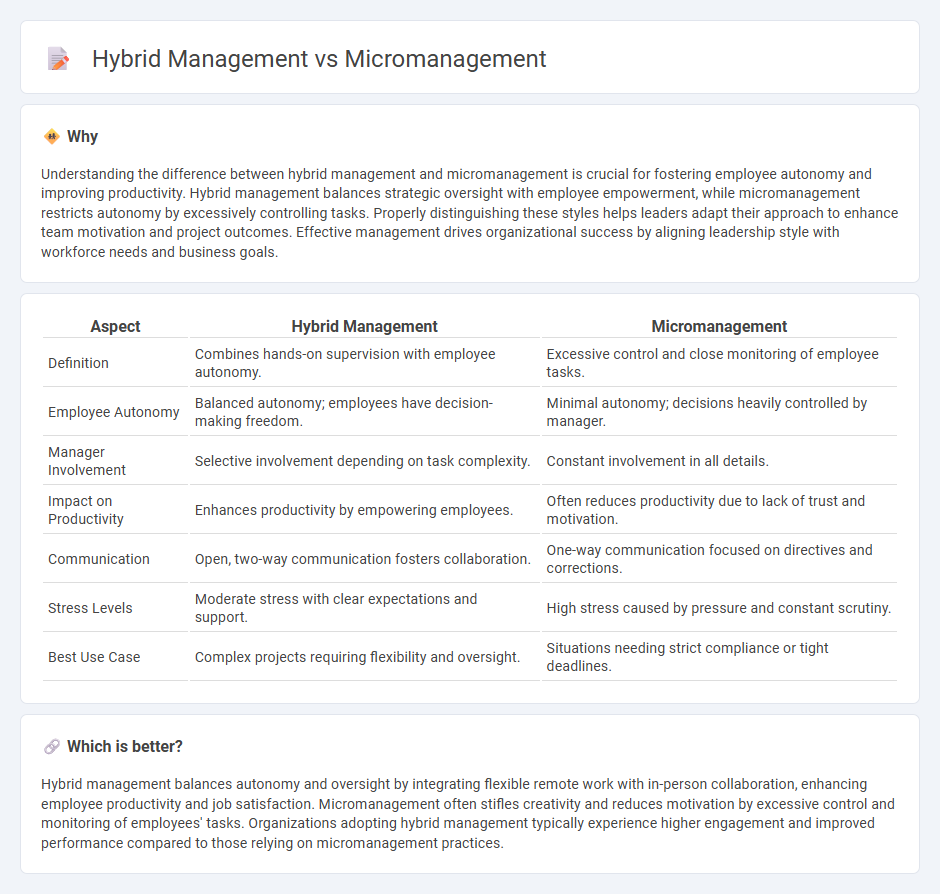
| Aspect | Hybrid Management | Micromanagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines hands-on supervision with employee autonomy. | Excessive control and close monitoring of employee tasks. |
| Employee Autonomy | Balanced autonomy; employees have decision-making freedom. | Minimal autonomy; decisions heavily controlled by manager. |
| Manager Involvement | Selective involvement depending on task complexity. | Constant involvement in all details. |
| Impact on Productivity | Enhances productivity by empowering employees. | Often reduces productivity due to lack of trust and motivation. |
| Communication | Open, two-way communication fosters collaboration. | One-way communication focused on directives and corrections. |
| Stress Levels | Moderate stress with clear expectations and support. | High stress caused by pressure and constant scrutiny. |
| Best Use Case | Complex projects requiring flexibility and oversight. | Situations needing strict compliance or tight deadlines. |
Which is better?
Hybrid management balances autonomy and oversight by integrating flexible remote work with in-person collaboration, enhancing employee productivity and job satisfaction. Micromanagement often stifles creativity and reduces motivation by excessive control and monitoring of employees' tasks. Organizations adopting hybrid management typically experience higher engagement and improved performance compared to those relying on micromanagement practices.
Connection
Hybrid management combines remote and on-site leadership techniques, often leading to increased reliance on micromanagement to monitor employee performance across different locations. Micromanagement in hybrid environments can stem from managers' desire to maintain control and ensure productivity despite physical distance. Effective hybrid management requires balancing oversight with autonomy to prevent micromanagement from hindering team morale and innovation.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Micromanagement restricts employee autonomy by closely monitoring every task, often leading to decreased motivation and innovation. Hybrid management balances oversight with flexibility, granting employees the freedom to make decisions while maintaining alignment with organizational goals. Explore how shifting from micromanagement to hybrid management can enhance autonomy and drive business success.
Flexibility
Micromanagement involves strict control and frequent oversight, limiting employee autonomy and reducing organizational flexibility. Hybrid management balances direct supervision with independent workflows, promoting adaptability and fostering a more resilient work environment. Explore the benefits of hybrid management to enhance your team's flexibility and performance.
Oversight
Micromanagement involves excessive oversight where supervisors control every detail, often stifling employee autonomy and innovation. Hybrid management balances oversight with delegation, allowing managers to monitor progress while empowering teams to make decisions and adapt to changing conditions. Explore how implementing hybrid management can improve productivity and employee satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Micromanagement - Wikipedia - Micromanagement is a management style characterized by excessive control and attention to details, often leading to a lack of trust and freedom in the workplace.
Micromanagement Meaning and How to Deal With It - Coursera - This article explains micromanagement as a style that involves excessive scrutiny and control over teams, stifling creativity and independent thought.
Is All Micromanagement Bad? Here's How the Best Startup Leaders Use It - The article discusses how some leaders view micromanagement as a shortcut that can be useful if used sparingly and appropriately, emphasizing the importance of regular feedback.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com