Shadow boards consist of emerging leaders who provide fresh perspectives to senior management, focusing on innovation and organizational agility. Consultative committees include experienced advisors offering strategic guidance and oversight to support executive decisions. Explore further to understand how these governance models enhance leadership effectiveness and corporate resilience.
Why it is important
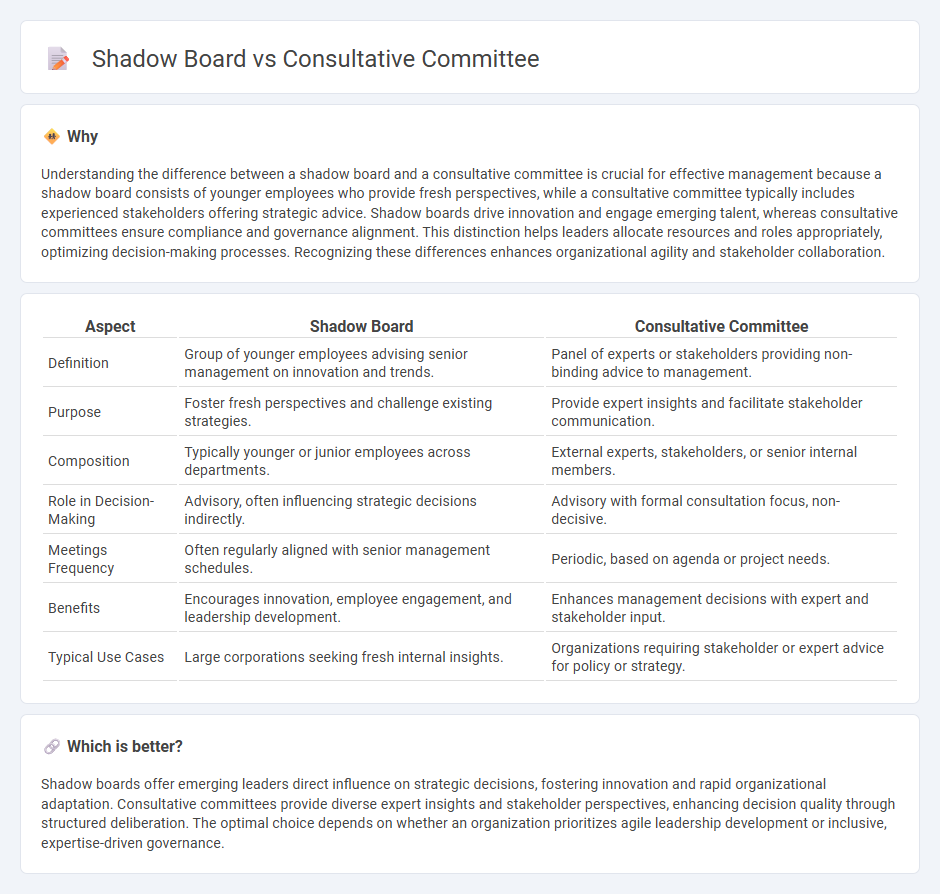
Understanding the difference between a shadow board and a consultative committee is crucial for effective management because a shadow board consists of younger employees who provide fresh perspectives, while a consultative committee typically includes experienced stakeholders offering strategic advice. Shadow boards drive innovation and engage emerging talent, whereas consultative committees ensure compliance and governance alignment. This distinction helps leaders allocate resources and roles appropriately, optimizing decision-making processes. Recognizing these differences enhances organizational agility and stakeholder collaboration.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shadow Board | Consultative Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of younger employees advising senior management on innovation and trends. | Panel of experts or stakeholders providing non-binding advice to management. |
| Purpose | Foster fresh perspectives and challenge existing strategies. | Provide expert insights and facilitate stakeholder communication. |
| Composition | Typically younger or junior employees across departments. | External experts, stakeholders, or senior internal members. |
| Role in Decision-Making | Advisory, often influencing strategic decisions indirectly. | Advisory with formal consultation focus, non-decisive. |
| Meetings Frequency | Often regularly aligned with senior management schedules. | Periodic, based on agenda or project needs. |
| Benefits | Encourages innovation, employee engagement, and leadership development. | Enhances management decisions with expert and stakeholder input. |
| Typical Use Cases | Large corporations seeking fresh internal insights. | Organizations requiring stakeholder or expert advice for policy or strategy. |
Which is better?
Shadow boards offer emerging leaders direct influence on strategic decisions, fostering innovation and rapid organizational adaptation. Consultative committees provide diverse expert insights and stakeholder perspectives, enhancing decision quality through structured deliberation. The optimal choice depends on whether an organization prioritizes agile leadership development or inclusive, expertise-driven governance.
Connection
Shadow boards consist of younger employees who provide fresh perspectives to senior management, while consultative committees gather diverse stakeholder input to inform decision-making. Both entities facilitate inclusive governance by enabling collaborative dialogue and incorporating varied insights into strategic planning. Their connection lies in fostering transparency, enhancing innovation, and bridging communication between different organizational levels.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Consultative committees provide expert advice to organizational leaders but lack formal decision-making authority, influencing strategies through recommendations and feedback. Shadow boards, composed of emerging leaders or younger employees, simulate the decision-making process by collaborating on strategic initiatives, offering fresh perspectives that inform actual board decisions. Explore how integrating these structures can optimize leadership and innovation in your organization.
Organizational representation
Consultative committees foster organizational representation by including diverse stakeholders who provide expert advice and feedback, enhancing decision-making processes. Shadow boards consist of emerging leaders or younger employees who simulate board roles to offer fresh perspectives and bridge generational gaps within the company hierarchy. Explore deeper insights into how these structures impact governance and innovation in organizations.
Influence channels
Consultative committees primarily function as formal advisory bodies, facilitating direct influence through structured meetings and expert recommendations within organizational hierarchies. Shadow boards operate as dynamic, informal groups of younger or emerging leaders who provide fresh perspectives and innovative ideas, impacting decision-making processes through collaborative engagement outside traditional channels. Explore how these influence channels differ in driving organizational change and fostering leadership development.
Source and External Links
Consultative committee: Overview, definition, and example - Cobrief - A consultative committee is a group assembled to provide advice, guidance, and recommendations on specific issues or policies, serving an advisory role rather than decision-making, often involving experts or stakeholders to help inform decisions in government, business, or other sectors.
What is a Consultative Committee? - IEUSA - Consultative Committees typically include elected employee representatives and management counterparts, meeting regularly to give employees a voice in workplace matters and to facilitate communication and consultation under enterprise agreements.
CIPM Consultative Committees - BIPM - The CIPM Consultative Committees comprise international experts advising on scientific and technical matters related to metrology, helping plan research, prepare recommendations, and coordinate standards on topics like acoustics, electricity, temperature, and time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com