Management strategies differ significantly between deskless and knowledge workforces due to varying work environments and communication needs. Deskless employees often require mobile tools and real-time updates for on-the-ground tasks, while knowledge workers depend on collaborative software and information-sharing platforms to perform analytical and creative functions. Explore effective management techniques tailored to both workforce types to enhance productivity and engagement.
Why it is important
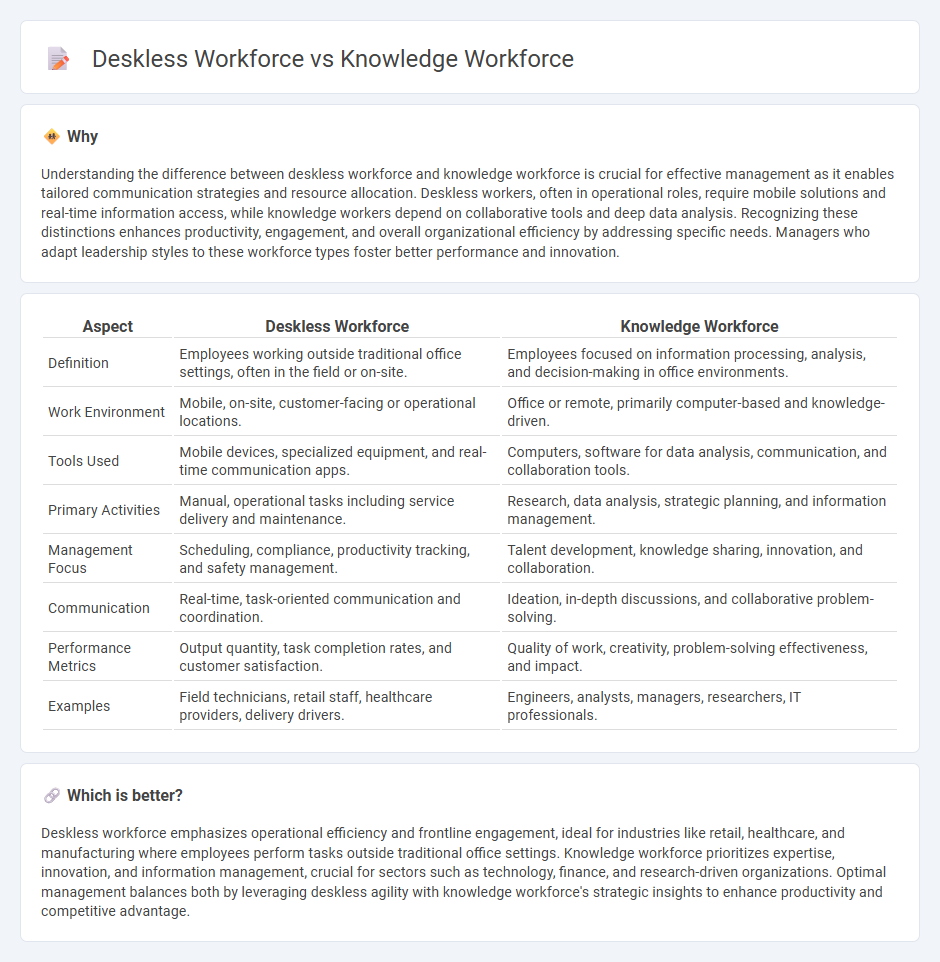
Understanding the difference between deskless workforce and knowledge workforce is crucial for effective management as it enables tailored communication strategies and resource allocation. Deskless workers, often in operational roles, require mobile solutions and real-time information access, while knowledge workers depend on collaborative tools and deep data analysis. Recognizing these distinctions enhances productivity, engagement, and overall organizational efficiency by addressing specific needs. Managers who adapt leadership styles to these workforce types foster better performance and innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deskless Workforce | Knowledge Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees working outside traditional office settings, often in the field or on-site. | Employees focused on information processing, analysis, and decision-making in office environments. |
| Work Environment | Mobile, on-site, customer-facing or operational locations. | Office or remote, primarily computer-based and knowledge-driven. |
| Tools Used | Mobile devices, specialized equipment, and real-time communication apps. | Computers, software for data analysis, communication, and collaboration tools. |
| Primary Activities | Manual, operational tasks including service delivery and maintenance. | Research, data analysis, strategic planning, and information management. |
| Management Focus | Scheduling, compliance, productivity tracking, and safety management. | Talent development, knowledge sharing, innovation, and collaboration. |
| Communication | Real-time, task-oriented communication and coordination. | Ideation, in-depth discussions, and collaborative problem-solving. |
| Performance Metrics | Output quantity, task completion rates, and customer satisfaction. | Quality of work, creativity, problem-solving effectiveness, and impact. |
| Examples | Field technicians, retail staff, healthcare providers, delivery drivers. | Engineers, analysts, managers, researchers, IT professionals. |
Which is better?
Deskless workforce emphasizes operational efficiency and frontline engagement, ideal for industries like retail, healthcare, and manufacturing where employees perform tasks outside traditional office settings. Knowledge workforce prioritizes expertise, innovation, and information management, crucial for sectors such as technology, finance, and research-driven organizations. Optimal management balances both by leveraging deskless agility with knowledge workforce's strategic insights to enhance productivity and competitive advantage.
Connection
The connection between deskless and knowledge workforces lies in the seamless flow of real-time information and collaboration tools that empower frontline employees to access critical data and insights. Integrating mobile technology and cloud-based platforms bridges the gap, enhancing productivity and decision-making across operational and strategic levels. This interconnected ecosystem drives organizational agility by aligning hands-on execution with expertise-driven knowledge management.
Key Terms
Remote Work
The knowledge workforce primarily consists of employees who leverage specialized skills and information in roles that often enable remote work through digital communication tools and cloud-based platforms. In contrast, the deskless workforce includes frontline workers typically engaged in physical tasks at various locations, such as retail, healthcare, or field services, where remote work is less feasible but mobile technology adoption is growing. Explore more insights on how remote work dynamics impact both workforce categories.
Mobility
The knowledge workforce relies heavily on digital tools and cloud-based platforms to access and share information seamlessly, enhancing collaboration regardless of location. In contrast, the deskless workforce depends on mobile devices and real-time data applications to execute tasks efficiently in dynamic, on-site environments. Explore the latest mobility solutions driving productivity in both workforce segments.
Collaboration
Collaboration within the knowledge workforce relies heavily on digital tools and platforms that facilitate information sharing among highly skilled professionals, enabling efficient problem-solving and innovation. In contrast, the deskless workforce depends on mobile communication and real-time coordination to manage tasks across various locations, often requiring lightweight, user-friendly collaboration apps. Explore detailed strategies to optimize collaboration in both workforce types for enhanced productivity and engagement.
Source and External Links
What is a Knowledge Worker? | IBM - Knowledge workers are professionals who create value using their expertise, critical thinking, and interpersonal skills, often overseeing daily tasks of information workers.
Knowledge Workers - Definition, What They Do, Who - Knowledge workers apply theoretical and analytical knowledge gained through formal training to develop products and services, often requiring advanced degrees.
What Is a Knowledge Worker and What Do They Do? (With Types) - Knowledge workers solve problems by retrieving, sharing, teaching, and applying information, undertaking tasks like overseeing budgets and strategizing plans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com