Resenteeism occurs when employees remain physically present at work but disengage mentally, resulting in reduced productivity and morale. Job withdrawal encompasses a broader range of behaviors including absenteeism, lateness, and eventual resignation, reflecting dissatisfaction and disconnection from organizational goals. Explore how understanding these dynamics can improve management strategies and employee retention.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between presenteeism and job withdrawal is crucial for effective management because presenteeism, where employees are physically present but unproductive, impacts overall performance and health, while job withdrawal indicates disengagement and potential turnover risks. Recognizing these behaviors helps managers implement targeted interventions to boost productivity and retain talent. Accurately diagnosing these issues enables better resource allocation and supports employee well-being. This knowledge ultimately improves organizational efficiency and reduces costs associated with absenteeism and turnover.
Comparison Table
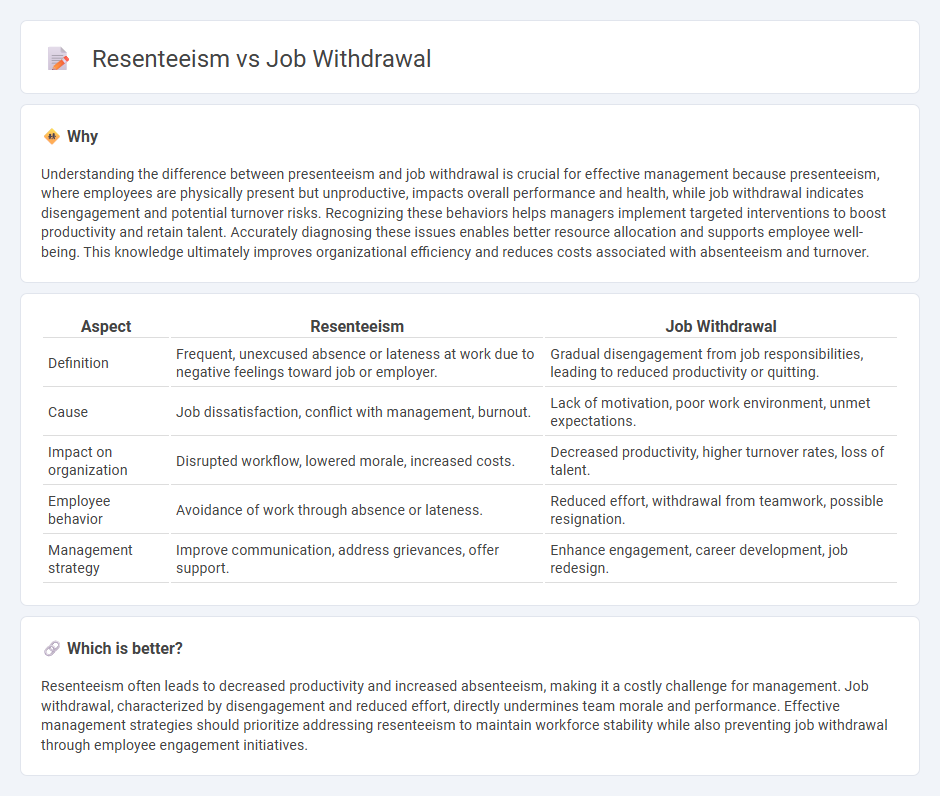
| Aspect | Resenteeism | Job Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Frequent, unexcused absence or lateness at work due to negative feelings toward job or employer. | Gradual disengagement from job responsibilities, leading to reduced productivity or quitting. |
| Cause | Job dissatisfaction, conflict with management, burnout. | Lack of motivation, poor work environment, unmet expectations. |
| Impact on organization | Disrupted workflow, lowered morale, increased costs. | Decreased productivity, higher turnover rates, loss of talent. |
| Employee behavior | Avoidance of work through absence or lateness. | Reduced effort, withdrawal from teamwork, possible resignation. |
| Management strategy | Improve communication, address grievances, offer support. | Enhance engagement, career development, job redesign. |
Which is better?
Resenteeism often leads to decreased productivity and increased absenteeism, making it a costly challenge for management. Job withdrawal, characterized by disengagement and reduced effort, directly undermines team morale and performance. Effective management strategies should prioritize addressing resenteeism to maintain workforce stability while also preventing job withdrawal through employee engagement initiatives.
Connection
Resenteeism reflects an employee's negative emotional response to workplace stress, which directly contributes to job withdrawal behaviors such as reduced effort, absenteeism, and eventual turnover. Studies in organizational psychology indicate that higher levels of resentment lead to decreased job satisfaction and increased intentions to quit. Effective management strategies targeting employee engagement and workplace fairness can mitigate resentful attitudes, reducing job withdrawal and improving retention.
Key Terms
Disengagement
Job withdrawal and presenteeism both signify forms of workplace disengagement, but manifest differently; job withdrawal involves employees physically or psychologically distancing themselves from work, often by absenteeism or reduced effort, while presenteeism describes attending work despite health issues, leading to decreased productivity. Disengagement in job withdrawal is more overt through absence, whereas presenteeism conceals disengagement through presenteeism-related factors like stress or burnout. Explore deeper insights into managing disengagement and improving employee engagement strategies.
Turnover
Turnover is significantly impacted by both job withdrawal behaviors and presenteeism, as employees disengage mentally or physically while still present at work, often leading to eventual resignation. Job withdrawal encompasses actions such as reducing effort, lateness, and absenteeism, which correlate strongly with increased turnover rates, while presenteeism--attending work while unwell--can decrease productivity and escalate burnout, further driving employee exit. Explore deeper insights into how managing withdrawal and presenteeism can strategically reduce turnover and improve organizational retention.
Dissatisfaction
Job withdrawal manifests as employees physically distancing themselves from work through absenteeism or tardiness, often driven by dissatisfaction with job roles or organizational culture. Resenteeism involves employees being physically present but mentally disengaged, leading to reduced productivity and increased errors, primarily fueled by underlying dissatisfaction and unresolved grievances. Explore how addressing dissatisfaction can mitigate both job withdrawal and presenteeism to enhance workplace well-being and performance.
Source and External Links
How to Write a Letter of Withdrawal to an Employer - This article provides guidance on writing a letter to withdraw from a job application, including templates and examples based on various reasons such as accepting another job offer or relocating.
Reason Why Employers Withdraw a Job Offer - The article explains scenarios under which employers can withdraw job offers, including breaches in the employment agreement and the need to send a withdrawal letter to applicants.
Guide: How To Withdraw an Application - This guide offers tips and templates for withdrawing a job application professionally, including reasons such as accepting another offer or realizing the job isn't a good fit.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com