Employee ghosting occurs when workers suddenly stop communicating and fail to show up for work without notice, leaving employers uncertain about their status. Job abandonment is characterized by an extended absence, typically beyond a company's policy threshold, leading employers to consider the employee as having voluntarily resigned. Explore the key differences and implications of these behaviors to enhance management strategies.
Why it is important
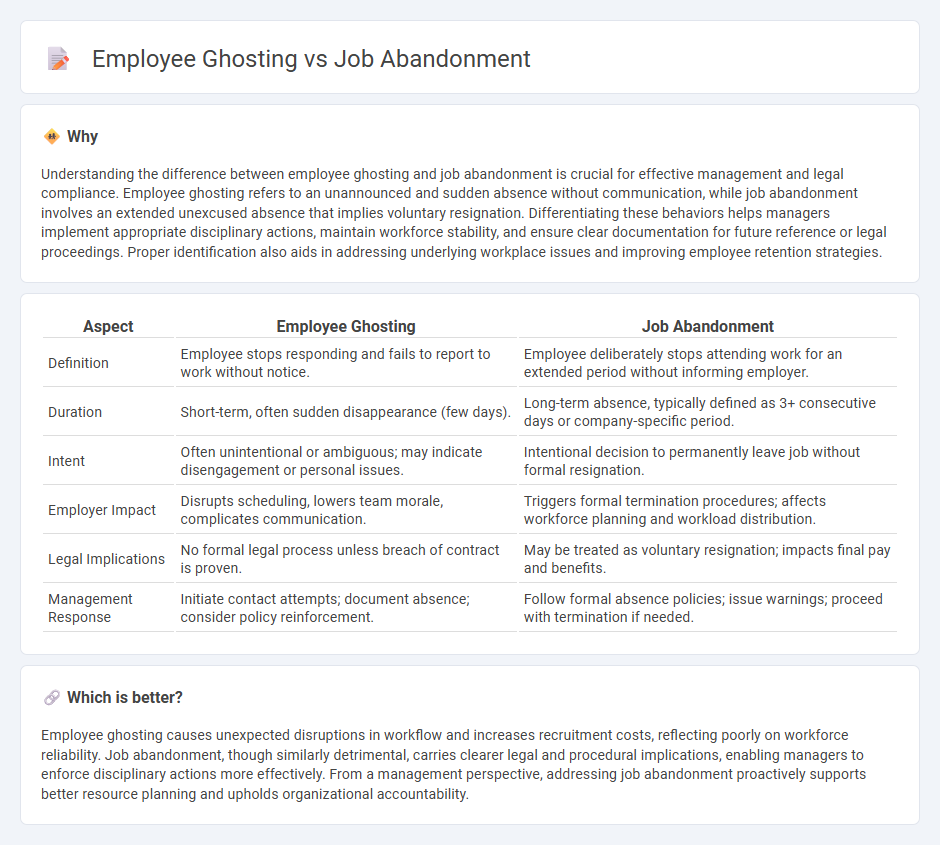
Understanding the difference between employee ghosting and job abandonment is crucial for effective management and legal compliance. Employee ghosting refers to an unannounced and sudden absence without communication, while job abandonment involves an extended unexcused absence that implies voluntary resignation. Differentiating these behaviors helps managers implement appropriate disciplinary actions, maintain workforce stability, and ensure clear documentation for future reference or legal proceedings. Proper identification also aids in addressing underlying workplace issues and improving employee retention strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Employee Ghosting | Job Abandonment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee stops responding and fails to report to work without notice. | Employee deliberately stops attending work for an extended period without informing employer. |
| Duration | Short-term, often sudden disappearance (few days). | Long-term absence, typically defined as 3+ consecutive days or company-specific period. |
| Intent | Often unintentional or ambiguous; may indicate disengagement or personal issues. | Intentional decision to permanently leave job without formal resignation. |
| Employer Impact | Disrupts scheduling, lowers team morale, complicates communication. | Triggers formal termination procedures; affects workforce planning and workload distribution. |
| Legal Implications | No formal legal process unless breach of contract is proven. | May be treated as voluntary resignation; impacts final pay and benefits. |
| Management Response | Initiate contact attempts; document absence; consider policy reinforcement. | Follow formal absence policies; issue warnings; proceed with termination if needed. |
Which is better?
Employee ghosting causes unexpected disruptions in workflow and increases recruitment costs, reflecting poorly on workforce reliability. Job abandonment, though similarly detrimental, carries clearer legal and procedural implications, enabling managers to enforce disciplinary actions more effectively. From a management perspective, addressing job abandonment proactively supports better resource planning and upholds organizational accountability.
Connection
Employee ghosting and job abandonment both disrupt organizational efficiency by creating unexpected workforce gaps that hinder project continuity and increase recruitment costs. Ghosting occurs when employees abruptly cease communication without formal resignation, while job abandonment involves unapproved, prolonged absences leading employers to consider the employee as having voluntarily left. Both phenomena challenge management's ability to maintain reliable staffing levels and necessitate the implementation of clearer exit protocols and engagement strategies.
Key Terms
Absenteeism
Job abandonment occurs when an employee fails to show up for work for an extended period without notifying their employer, signaling a formal end to their employment through absence. Employee ghosting refers to a sudden disappearance without explanation, typically during the hiring process or early employment, causing disruption and uncertainty. Explore detailed differences and impacts of absenteeism in workforce management to improve retention strategies.
Turnover
Job abandonment occurs when an employee abruptly stops showing up for work without notice, signaling a formal or informal resignation that directly impacts turnover rates by creating unexpected vacancies and increasing recruitment costs. Employee ghosting refers to the act of disappearing during the hiring process or shortly after onboarding, leading to higher turnover as employers struggle to fill roles and maintain workforce stability. Explore more to understand how these behaviors affect organizational retention strategies and operational continuity.
Communication
Job abandonment occurs when an employee stops showing up to work without notifying their employer, violating company policies and causing workflow disruptions. Employee ghosting refers to when an individual abruptly ceases all communication during the hiring process or after starting a job, leaving employers without explanations or closure. Explore key differences in communication approaches to effectively manage and prevent these workplace challenges.
Source and External Links
Job Abandonment: What is it, How it Happens & How to Handle it - Job abandonment occurs when an employee doesn't show up to work for a specified number of days without notice and with no intention of returning, and it is considered a voluntary resignation despite no formal quit notice.
Job Abandonment: Definition, Policy and Tips for Prevention - Indeed - Job abandonment is when an employee leaves their job without notice or intention to return, typically after several consecutive unauthorized absences, often linked to dissatisfaction, burnout, or better opportunities elsewhere.
Job Abandonment: Definition and How To Prevent It [Practical Guide] - Job abandonment commonly happens due to lack of commitment, communication, or because employees find better jobs, dislike their current role, or face emergencies preventing communication, with employers advised to evaluate cases carefully.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com