Zero trust leadership emphasizes rigorous verification, continuous monitoring, and adaptive trust-building to enhance security and accountability within organizations. Transactional leadership focuses on structured tasks, clear rewards, and punishments to achieve specific performance goals. Explore the key differences and benefits of both leadership styles to optimize organizational management strategies.
Why it is important
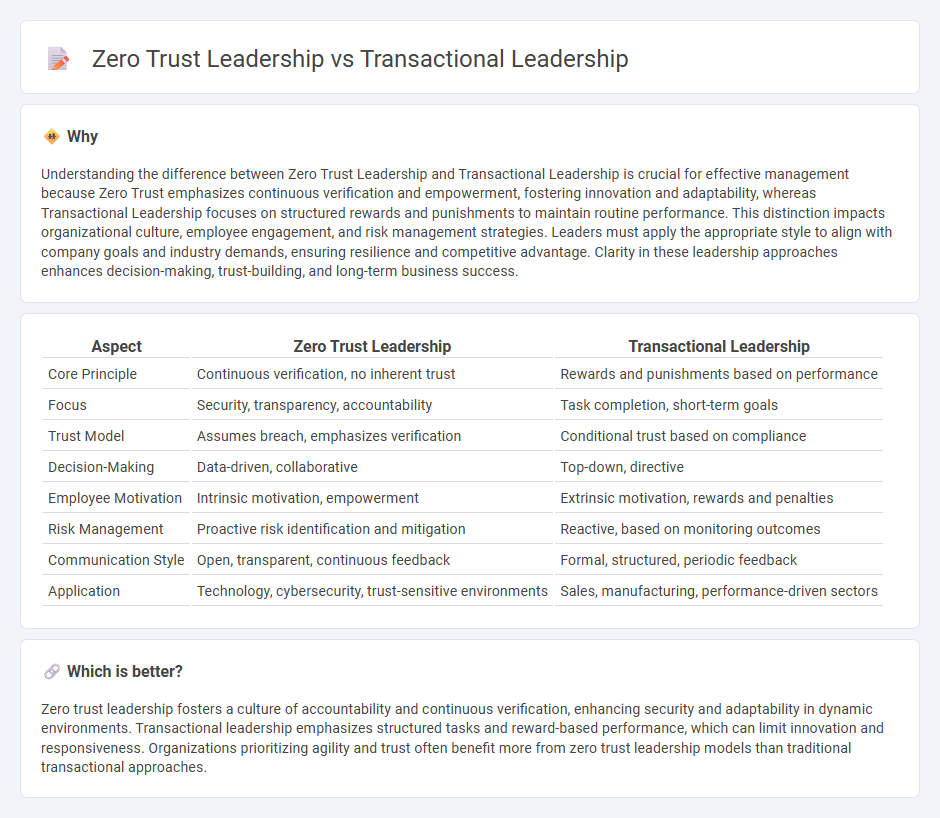
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Leadership and Transactional Leadership is crucial for effective management because Zero Trust emphasizes continuous verification and empowerment, fostering innovation and adaptability, whereas Transactional Leadership focuses on structured rewards and punishments to maintain routine performance. This distinction impacts organizational culture, employee engagement, and risk management strategies. Leaders must apply the appropriate style to align with company goals and industry demands, ensuring resilience and competitive advantage. Clarity in these leadership approaches enhances decision-making, trust-building, and long-term business success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Leadership | Transactional Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Continuous verification, no inherent trust | Rewards and punishments based on performance |
| Focus | Security, transparency, accountability | Task completion, short-term goals |
| Trust Model | Assumes breach, emphasizes verification | Conditional trust based on compliance |
| Decision-Making | Data-driven, collaborative | Top-down, directive |
| Employee Motivation | Intrinsic motivation, empowerment | Extrinsic motivation, rewards and penalties |
| Risk Management | Proactive risk identification and mitigation | Reactive, based on monitoring outcomes |
| Communication Style | Open, transparent, continuous feedback | Formal, structured, periodic feedback |
| Application | Technology, cybersecurity, trust-sensitive environments | Sales, manufacturing, performance-driven sectors |
Which is better?
Zero trust leadership fosters a culture of accountability and continuous verification, enhancing security and adaptability in dynamic environments. Transactional leadership emphasizes structured tasks and reward-based performance, which can limit innovation and responsiveness. Organizations prioritizing agility and trust often benefit more from zero trust leadership models than traditional transactional approaches.
Connection
Zero trust leadership and transactional leadership both emphasize accountability and structured processes to achieve organizational goals. Zero trust leadership ensures security and trust through constant verification, while transactional leadership focuses on clear roles, rewards, and performance monitoring. Their connection lies in fostering dependable, transparent environments where standards and expectations are rigorously maintained.
Key Terms
Authority
Transactional leadership emphasizes clear authority through structured rewards and penalties, ensuring compliance and performance within established hierarchies. Zero trust leadership challenges traditional authority by promoting continuous verification, transparency, and empowerment across all organizational levels to mitigate risks. Discover how redefining authority can transform leadership effectiveness in dynamic environments.
Trust
Transactional leadership centers on clear exchanges between leader and follower, emphasizing performance, rewards, and compliance to build trust through consistency. Zero trust leadership eliminates assumptions of inherent trust, continuously verifying actions and intentions to mitigate risks in dynamic, uncertain environments. Explore how combining these approaches can create resilient leadership strategies in today's complex organizations.
Accountability
Transactional leadership emphasizes clear structures, reward-based motivation, and strict accountability measures to ensure task completion and performance standards. Zero trust leadership prioritizes continuous verification, transparency, and decentralized control to uphold security and trust without assuming inherent reliability. Explore how integrating these leadership styles can enhance organizational accountability and resilience.
Source and External Links
What is transactional leadership? - Definition from WhatIs.com - Transactional leadership is a management style that emphasizes supervision, organization, and a system of rewards and punishments to encourage compliance with specific, measurable goals set by the leader.
Transactional leadership - Wikipedia - Transactional leadership centers on the exchange of effort for rewards, focusing on short-term goals and corrective actions when standards are not met, without fostering deeper, longer-term relationships between leaders and subordinates.
Transactional leadership | EBSCO Research Starters - Transactional leaders rely on authority and control, enforcing rules and maintaining the status quo by rewarding compliance and penalizing failures, making it effective for structured environments but often resulting in low job satisfaction and retention.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com