Interim executives bring targeted expertise and immediate leadership to organizations facing transitional phases, while founders possess deep visionary insight and a long-term commitment driving a company from inception. Interim leaders focus on stabilizing operations and executing strategic plans quickly, whereas founders concentrate on innovation, culture-building, and sustained growth. Discover how combining interim leadership with founder vision can optimize your management strategy.
Why it is important
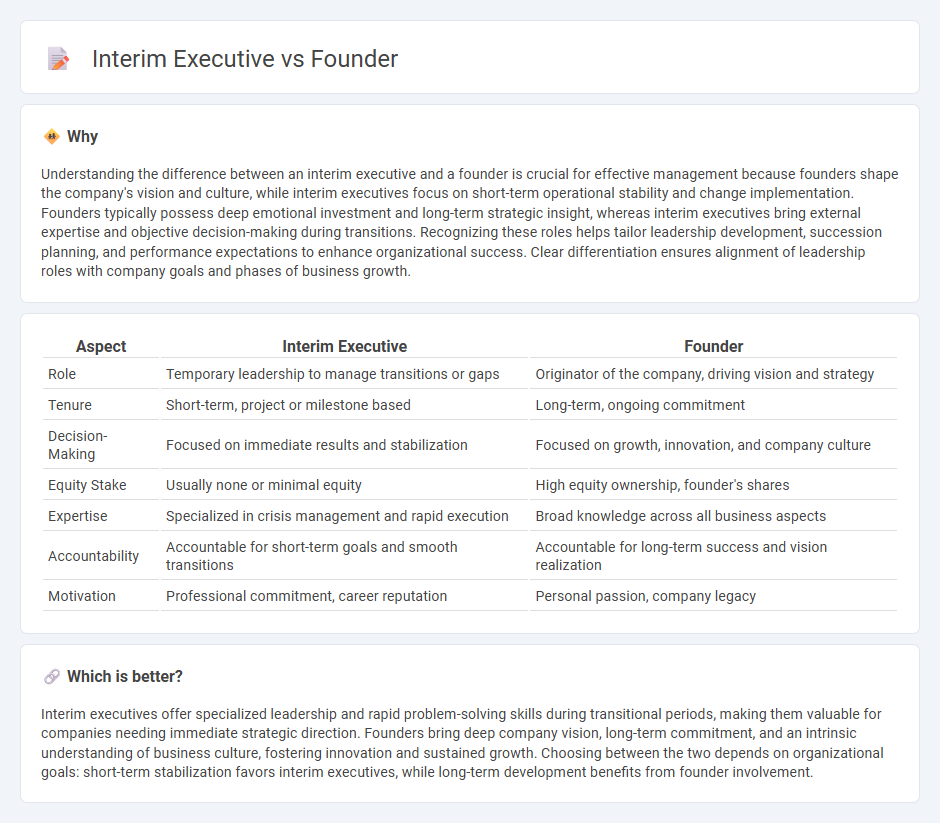
Understanding the difference between an interim executive and a founder is crucial for effective management because founders shape the company's vision and culture, while interim executives focus on short-term operational stability and change implementation. Founders typically possess deep emotional investment and long-term strategic insight, whereas interim executives bring external expertise and objective decision-making during transitions. Recognizing these roles helps tailor leadership development, succession planning, and performance expectations to enhance organizational success. Clear differentiation ensures alignment of leadership roles with company goals and phases of business growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Interim Executive | Founder |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Temporary leadership to manage transitions or gaps | Originator of the company, driving vision and strategy |
| Tenure | Short-term, project or milestone based | Long-term, ongoing commitment |
| Decision-Making | Focused on immediate results and stabilization | Focused on growth, innovation, and company culture |
| Equity Stake | Usually none or minimal equity | High equity ownership, founder's shares |
| Expertise | Specialized in crisis management and rapid execution | Broad knowledge across all business aspects |
| Accountability | Accountable for short-term goals and smooth transitions | Accountable for long-term success and vision realization |
| Motivation | Professional commitment, career reputation | Personal passion, company legacy |
Which is better?
Interim executives offer specialized leadership and rapid problem-solving skills during transitional periods, making them valuable for companies needing immediate strategic direction. Founders bring deep company vision, long-term commitment, and an intrinsic understanding of business culture, fostering innovation and sustained growth. Choosing between the two depends on organizational goals: short-term stabilization favors interim executives, while long-term development benefits from founder involvement.
Connection
Interim executives often collaborate closely with founders to provide strategic leadership during transitional phases or rapid growth periods, leveraging their expertise to stabilize operations and implement scalable processes. Founders benefit from interim executives' objective perspective and seasoned management skills, facilitating sustainable business development and preparing the company for long-term success. This connection enables seamless knowledge transfer and continuity, ensuring the founder's vision is realized while addressing immediate organizational needs.
Key Terms
Ownership
Founders inherently possess full ownership and decision-making authority within a company, embedding deep commitment and long-term vision into their leadership. Interim executives are typically appointed temporarily to provide specialized expertise or stabilize operations without holding ownership stakes. Explore the fundamental distinctions in leadership roles and ownership to understand their unique impacts on business growth.
Authority
A founder typically holds inherent authority derived from establishing the company and shaping its vision, often wielding long-term strategic control. Interim executives possess temporary authority, granted to lead through transitional phases, bringing specialized expertise without permanent decision-making power. Explore how these distinct roles influence organizational dynamics and leadership effectiveness.
Duration
Founders typically engage with their startups over an extended period, often from inception through various growth stages, establishing long-term vision and company culture. Interim executives, however, serve temporarily to address specific challenges or transitions, their tenure usually spanning a few months to a year. Explore further to understand how duration impacts leadership roles and business outcomes.
Source and External Links
The Founder - A 2016 film about Ray Kroc's role in transforming McDonald's into a global fast-food chain.
The Founder on Wikipedia - A biographical drama film detailing Ray Kroc's involvement in McDonald's history.
Founder Definition - The definition of a founder as a person who establishes or starts something.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com