Quiet firing occurs when employers subtly reduce responsibilities or opportunities, leading to employee disengagement and decreased productivity. Burnout manifests as physical and emotional exhaustion caused by prolonged workplace stress, significantly impacting performance and well-being. Explore more to understand how effective management strategies can address and prevent both issues.
Why it is important
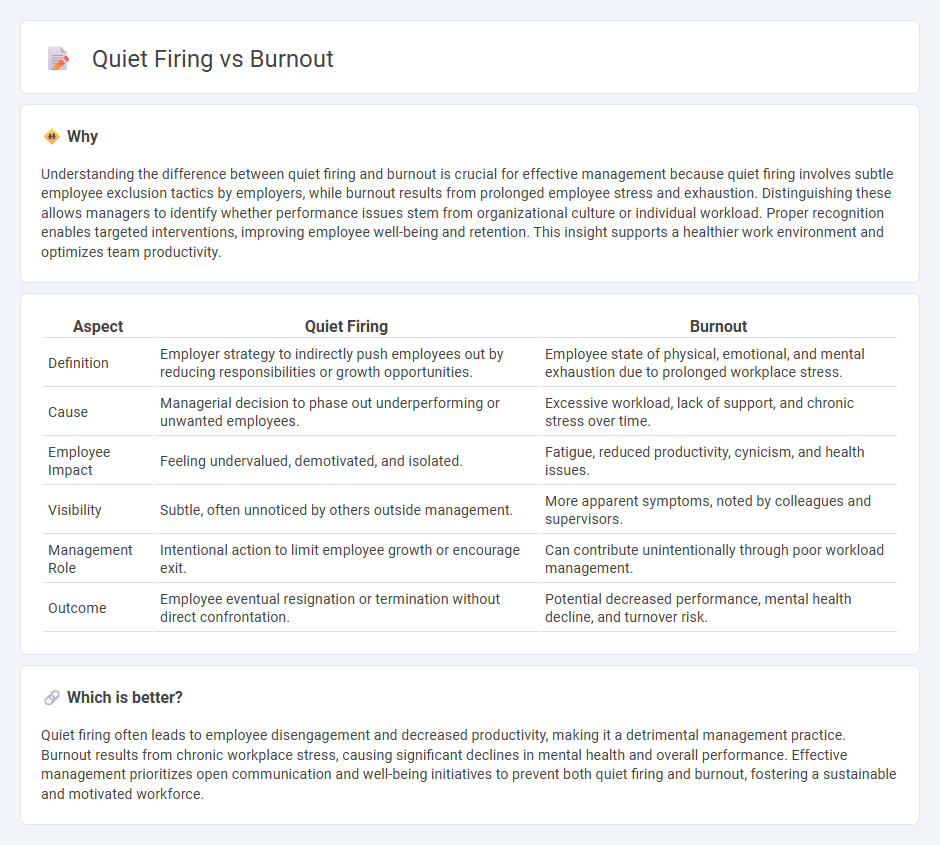
Understanding the difference between quiet firing and burnout is crucial for effective management because quiet firing involves subtle employee exclusion tactics by employers, while burnout results from prolonged employee stress and exhaustion. Distinguishing these allows managers to identify whether performance issues stem from organizational culture or individual workload. Proper recognition enables targeted interventions, improving employee well-being and retention. This insight supports a healthier work environment and optimizes team productivity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Firing | Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employer strategy to indirectly push employees out by reducing responsibilities or growth opportunities. | Employee state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion due to prolonged workplace stress. |
| Cause | Managerial decision to phase out underperforming or unwanted employees. | Excessive workload, lack of support, and chronic stress over time. |
| Employee Impact | Feeling undervalued, demotivated, and isolated. | Fatigue, reduced productivity, cynicism, and health issues. |
| Visibility | Subtle, often unnoticed by others outside management. | More apparent symptoms, noted by colleagues and supervisors. |
| Management Role | Intentional action to limit employee growth or encourage exit. | Can contribute unintentionally through poor workload management. |
| Outcome | Employee eventual resignation or termination without direct confrontation. | Potential decreased performance, mental health decline, and turnover risk. |
Which is better?
Quiet firing often leads to employee disengagement and decreased productivity, making it a detrimental management practice. Burnout results from chronic workplace stress, causing significant declines in mental health and overall performance. Effective management prioritizes open communication and well-being initiatives to prevent both quiet firing and burnout, fostering a sustainable and motivated workforce.
Connection
Quiet firing, characterized by subtle marginalization tactics such as reduced responsibilities or exclusion from key projects, often leads to employee burnout by increasing stress and diminishing engagement. Burnout results from prolonged exposure to workplace neglect and unacknowledged workloads, negatively impacting productivity and mental health. Effective management strategies focusing on transparent communication and employee support can mitigate the risks associated with quiet firing and subsequent burnout.
Key Terms
Employee Wellbeing
Employee wellbeing is crucial in addressing burnout, characterized by chronic workplace stress leading to exhaustion, reduced performance, and disengagement. Quiet firing, a subtle form of employee neglect where employers limit growth opportunities and support, can exacerbate burnout symptoms and harm mental health. Explore effective strategies to enhance workplace wellbeing and prevent burnout by understanding these phenomena in depth.
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture plays a critical role in differentiating burnout from quiet firing; burnout often stems from excessive workload, lack of support, and unrealistic expectations within a high-pressure environment, while quiet firing reflects subtle signals from management to encourage an employee's self-departure through task reduction or exclusion. Toxic cultures that neglect transparency and employee well-being exacerbate both burnout and quiet firing, undermining trust and morale. Explore further how fostering a healthy organizational culture can prevent these detrimental workplace phenomena.
Performance Management
Burnout in performance management often results from chronic workplace stress leading to exhaustion and reduced productivity, whereas quiet firing involves subtle managerial tactics to encourage employees to leave without formal termination. Both impact employee engagement and retention, requiring proactive strategies such as regular feedback, clear expectations, and support systems to address underlying issues. Explore effective performance management techniques to prevent burnout and recognize quiet firing behaviors.
Source and External Links
Burnout phenomenon: neurophysiological factors, clinical... - This article discusses burnout as a state of emotional exhaustion, physical fatigue, and cognitive weariness caused by long-term stressors.
Burnout: Symptoms, Treatment, and Coping Strategy Tips - Provides a comprehensive guide to burnout, including symptoms, stages, and strategies for recovery.
Job burnout: How to spot it and take action - Offers insights into recognizing and addressing job burnout, including symptoms and effects on health.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com