Employee ghosting refers to situations where employees abruptly stop showing up for work without notice, causing disruption and uncertainty. Employee turnover encompasses the broader process of employees leaving a company, whether voluntarily or involuntarily, impacting organizational stability and costs. Explore more to understand the differences and implications of these workforce challenges.
Why it is important
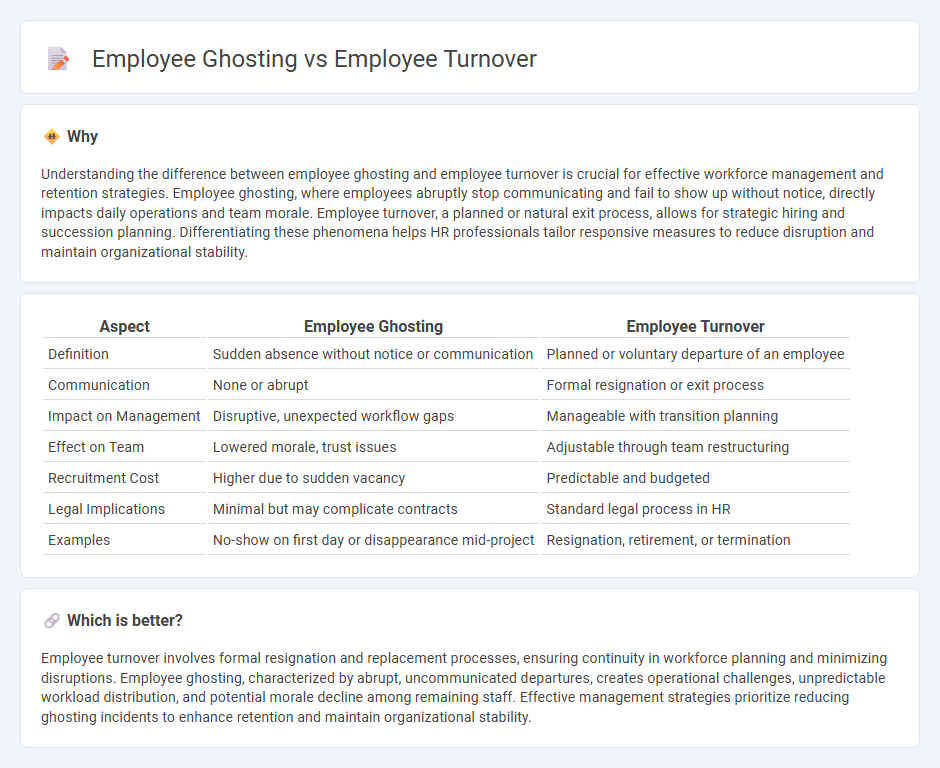
Understanding the difference between employee ghosting and employee turnover is crucial for effective workforce management and retention strategies. Employee ghosting, where employees abruptly stop communicating and fail to show up without notice, directly impacts daily operations and team morale. Employee turnover, a planned or natural exit process, allows for strategic hiring and succession planning. Differentiating these phenomena helps HR professionals tailor responsive measures to reduce disruption and maintain organizational stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Employee Ghosting | Employee Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden absence without notice or communication | Planned or voluntary departure of an employee |
| Communication | None or abrupt | Formal resignation or exit process |
| Impact on Management | Disruptive, unexpected workflow gaps | Manageable with transition planning |
| Effect on Team | Lowered morale, trust issues | Adjustable through team restructuring |
| Recruitment Cost | Higher due to sudden vacancy | Predictable and budgeted |
| Legal Implications | Minimal but may complicate contracts | Standard legal process in HR |
| Examples | No-show on first day or disappearance mid-project | Resignation, retirement, or termination |
Which is better?
Employee turnover involves formal resignation and replacement processes, ensuring continuity in workforce planning and minimizing disruptions. Employee ghosting, characterized by abrupt, uncommunicated departures, creates operational challenges, unpredictable workload distribution, and potential morale decline among remaining staff. Effective management strategies prioritize reducing ghosting incidents to enhance retention and maintain organizational stability.
Connection
Employee ghosting, where employees abruptly stop communicating or showing up for work, significantly contributes to higher employee turnover rates by creating unexpected vacancies and disrupting team dynamics. This phenomenon increases recruitment and training costs while undermining organizational productivity and morale. Understanding the link between ghosting and turnover helps management implement proactive engagement and retention strategies to reduce workforce instability.
Key Terms
Retention
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which employees leave a company and are replaced by new hires, impacting organizational stability and costs. Employee ghosting occurs when an employee abruptly stops communication and fails to show up without notice, creating challenges in workforce planning and morale. Explore effective retention strategies to reduce both turnover and ghosting for a more engaged and committed team.
Engagement
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which employees leave a company and are replaced, often driven by factors like job dissatisfaction and lack of engagement. Employee ghosting, a more recent phenomenon, occurs when employees abruptly stop communicating and fail to show up for work without notice, signaling deeper disengagement and trust issues. Explore effective employee engagement strategies to reduce both turnover and ghosting in your organization.
Exit Interviews
Employee turnover encompasses all forms of employee departures, while employee ghosting specifically refers to sudden, unexplained absences without formal resignation. Exit interviews play a crucial role in identifying underlying causes of turnover, including factors contributing to ghosting behaviors. Discover how effective exit interviews can mitigate turnover and improve employee retention strategies.
Source and External Links
Reduce Employee Turnover with BambooHR Insights - Employee turnover measures the number of employees who leave an organization during a specified time period, usually calculated by dividing the number of employees who left by the average number of employees and multiplying by 100 to get the turnover rate.
Employee turnover - Wikipedia - Employee turnover refers to the percentage of the workforce that leaves an organization over a given period, including both voluntary and involuntary departures, and tracked to understand retention and productivity impacts.
Employee retention: The real cost of losing an employee - High employee turnover decreases productivity, lowers morale, and results in financial costs due to lost productivity and recruiting delays, with replacements often taking one to four months depending on role complexity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com