Quiet firing refers to subtle workplace tactics used by employers to encourage employees to leave without formal termination, often through reduced responsibilities or limited growth opportunities. Attrition denotes a natural, voluntary reduction in staff as employees resign or retire, without direct employer intervention. Explore the key differences and strategic implications of quiet firing versus attrition in modern management approaches.
Why it is important
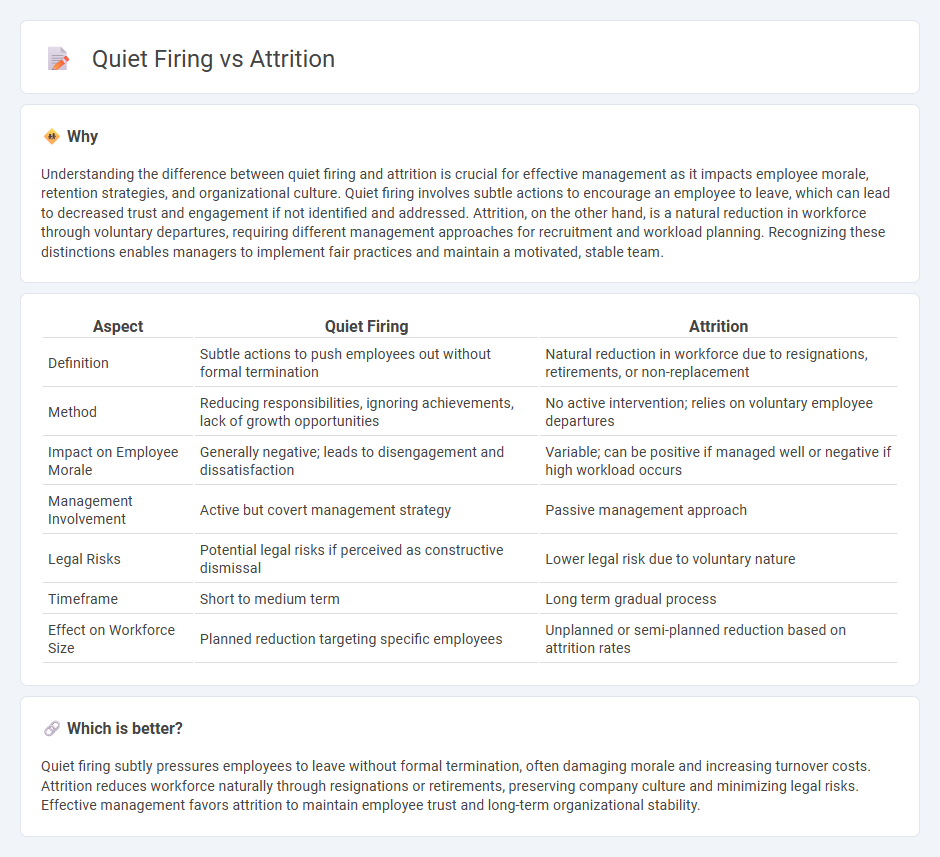
Understanding the difference between quiet firing and attrition is crucial for effective management as it impacts employee morale, retention strategies, and organizational culture. Quiet firing involves subtle actions to encourage an employee to leave, which can lead to decreased trust and engagement if not identified and addressed. Attrition, on the other hand, is a natural reduction in workforce through voluntary departures, requiring different management approaches for recruitment and workload planning. Recognizing these distinctions enables managers to implement fair practices and maintain a motivated, stable team.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Firing | Attrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subtle actions to push employees out without formal termination | Natural reduction in workforce due to resignations, retirements, or non-replacement |
| Method | Reducing responsibilities, ignoring achievements, lack of growth opportunities | No active intervention; relies on voluntary employee departures |
| Impact on Employee Morale | Generally negative; leads to disengagement and dissatisfaction | Variable; can be positive if managed well or negative if high workload occurs |
| Management Involvement | Active but covert management strategy | Passive management approach |
| Legal Risks | Potential legal risks if perceived as constructive dismissal | Lower legal risk due to voluntary nature |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term | Long term gradual process |
| Effect on Workforce Size | Planned reduction targeting specific employees | Unplanned or semi-planned reduction based on attrition rates |
Which is better?
Quiet firing subtly pressures employees to leave without formal termination, often damaging morale and increasing turnover costs. Attrition reduces workforce naturally through resignations or retirements, preserving company culture and minimizing legal risks. Effective management favors attrition to maintain employee trust and long-term organizational stability.
Connection
Quiet firing, a subtle form of pushing employees out through disengagement, directly accelerates attrition by diminishing job satisfaction and reducing motivation. This practice erodes workplace morale and increases turnover rates, leading to higher costs in recruitment and training for organizations. Understanding the link between quiet firing and attrition is crucial for improving employee retention strategies and fostering a positive work environment.
Key Terms
Employee Turnover
Attrition refers to the natural reduction of employees through resignation, retirement, or voluntary departure without replacement, typically impacting overall employee turnover rates. Quiet firing, on the other hand, involves subtly pushing employees to leave through reduced responsibilities or negative work environments, directly influencing involuntary turnover and employee morale. Explore the differences between attrition and quiet firing strategies to better manage your company's employee retention.
Performance Management
Attrition refers to the natural reduction of employees due to resignations or retirements, while quiet firing involves subtly pushing employees out by withholding opportunities or support, often without formal termination. Effective performance management systems identify genuine performance issues and provide constructive feedback, reducing the risk of misinterpreting quiet firing as attrition. Explore strategies to distinguish between these phenomena and improve your organization's talent retention.
Workplace Engagement
Attrition refers to the natural reduction of employees through resignations or retirements, often impacting workplace engagement by creating gaps in productivity and team dynamics. Quiet firing involves subtly encouraging employees to leave without direct termination, leading to decreased morale and trust within the organization. Explore strategies to boost workplace engagement and effectively manage both attrition and quiet firing.
Source and External Links
Attrition Definition, Types, Causes & Mitigation Tips - This article provides an overview of attrition, including its definition, types, causes, and strategies for mitigation in the workplace.
ATTRITION Definition & Meaning - This webpage defines attrition broadly, including its use in business and warfare contexts, and provides additional meanings related to friction and theological concepts.
Understanding Attrition: Definitions, Types, and Strategic - This resource explains attrition as a gradual reduction in workforce size due to employees leaving or being dismissed without replacement, differing from employee turnover.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com