Agile retrospectives focus on continuous improvement within iterative development cycles by reflecting on the team's processes and outcomes to enhance future sprints. After-action reviews analyze completed projects or events to identify successes, challenges, and lessons learned for broader organizational improvement. Explore deeper insights into how Agile retrospectives and after-action reviews drive effective management strategies.
Why it is important
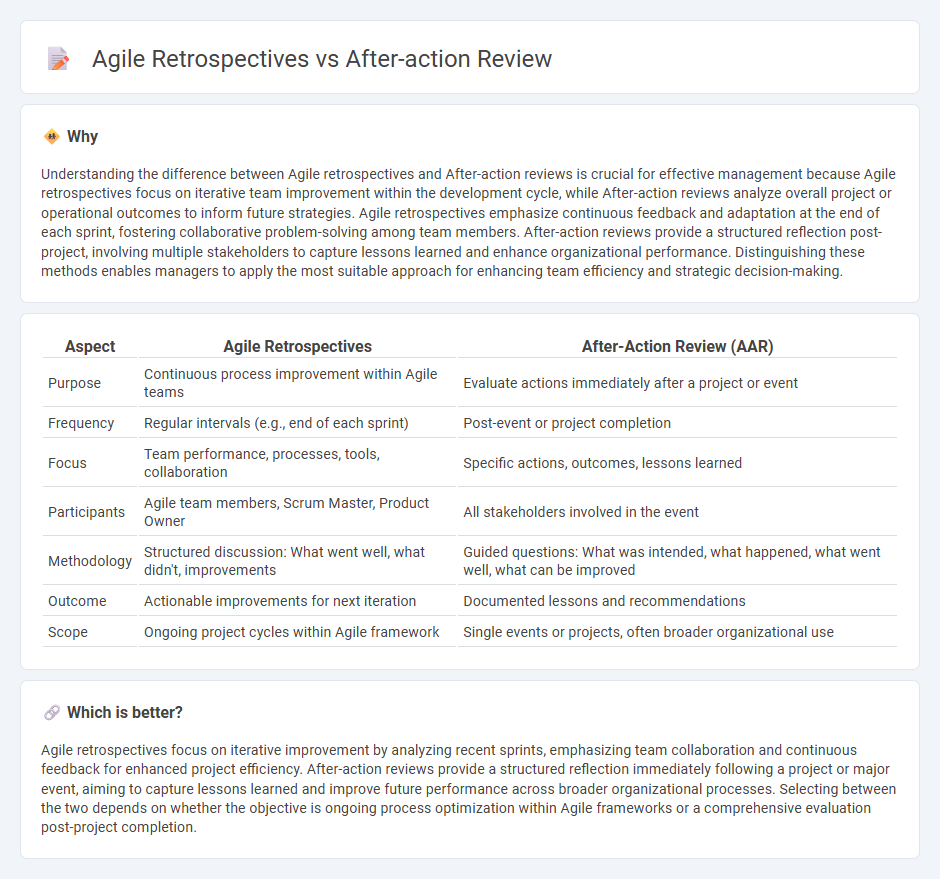
Understanding the difference between Agile retrospectives and After-action reviews is crucial for effective management because Agile retrospectives focus on iterative team improvement within the development cycle, while After-action reviews analyze overall project or operational outcomes to inform future strategies. Agile retrospectives emphasize continuous feedback and adaptation at the end of each sprint, fostering collaborative problem-solving among team members. After-action reviews provide a structured reflection post-project, involving multiple stakeholders to capture lessons learned and enhance organizational performance. Distinguishing these methods enables managers to apply the most suitable approach for enhancing team efficiency and strategic decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Agile Retrospectives | After-Action Review (AAR) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Continuous process improvement within Agile teams | Evaluate actions immediately after a project or event |
| Frequency | Regular intervals (e.g., end of each sprint) | Post-event or project completion |
| Focus | Team performance, processes, tools, collaboration | Specific actions, outcomes, lessons learned |
| Participants | Agile team members, Scrum Master, Product Owner | All stakeholders involved in the event |
| Methodology | Structured discussion: What went well, what didn't, improvements | Guided questions: What was intended, what happened, what went well, what can be improved |
| Outcome | Actionable improvements for next iteration | Documented lessons and recommendations |
| Scope | Ongoing project cycles within Agile framework | Single events or projects, often broader organizational use |
Which is better?
Agile retrospectives focus on iterative improvement by analyzing recent sprints, emphasizing team collaboration and continuous feedback for enhanced project efficiency. After-action reviews provide a structured reflection immediately following a project or major event, aiming to capture lessons learned and improve future performance across broader organizational processes. Selecting between the two depends on whether the objective is ongoing process optimization within Agile frameworks or a comprehensive evaluation post-project completion.
Connection
Agile retrospectives and After-action reviews both focus on continuous improvement by systematically reflecting on completed projects or iterations to identify successes and areas for growth. These processes emphasize team collaboration, open communication, and actionable feedback to enhance future performance. By fostering a culture of learning and adaptability, they drive effective management practices that improve project outcomes and organizational agility.
Key Terms
Reflection
After-action reviews emphasize structured reflection immediately following project completion to identify lessons learned and improve future performance. Agile retrospectives occur at regular intervals within sprints, fostering continuous team collaboration and iterative improvements. Explore detailed strategies to enhance reflection processes in Agile and project management for optimized outcomes.
Continuous improvement
After-action reviews (AARs) and Agile retrospectives both emphasize continuous improvement by analyzing past actions to enhance future performance. AARs typically occur immediately after a project or event, focusing on what happened, why it happened, and how to improve; Agile retrospectives are iterative, held at the end of each sprint to refine team processes and collaboration. Explore further to understand how integrating both methods can optimize your team's growth and productivity.
Feedback
After-action reviews emphasize structured evaluation of completed projects to capture lessons learned and improve future performance, focusing on specific feedback from events. Agile retrospectives prioritize continuous improvement within iterative cycles, encouraging team reflection on processes, collaboration, and outcomes to enhance agility. Explore how integrating both methods can optimize feedback for sustained team growth.
Source and External Links
What are After Action Reviews (AARs)? - This free template explains the process of conducting an after-action review, helping teams debrief projects and improve future outcomes by answering key questions and creating actionable recommendations.
After Action Review in Project Management - This guide outlines the AAR as a tool for teams to learn from experiences, identify improvements, and enhance future performance by reflecting on successes and challenges without assigning blame.
After-action review - The AAR is a technique originally developed by the U.S. Army to analyze the intended versus actual outcomes of actions, identifying practices to sustain or improve for future iterations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com