Second chance hiring offers a strategic approach for Human Resources to reintegrate individuals with criminal records into the workforce, reducing recidivism and expanding talent pools. Social enterprise employment focuses on creating sustainable job opportunities within mission-driven businesses that address social issues, fostering community development and workforce diversity. Explore more about how these innovative hiring practices transform organizations and uplift communities.
Why it is important
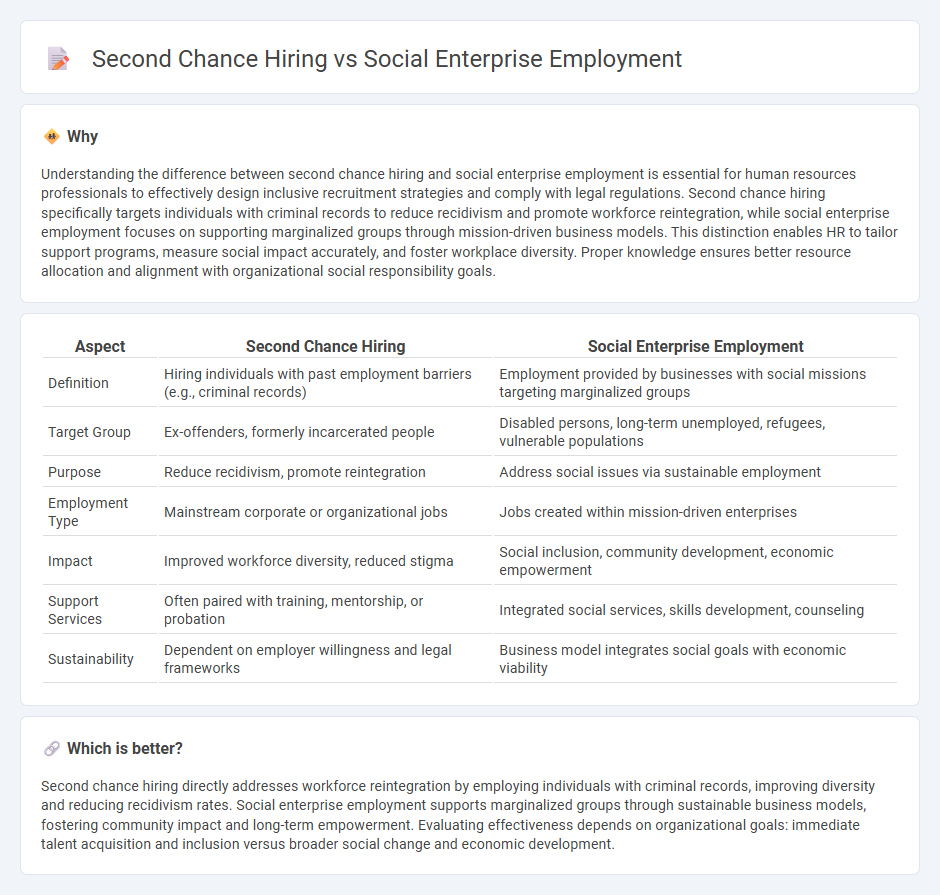
Understanding the difference between second chance hiring and social enterprise employment is essential for human resources professionals to effectively design inclusive recruitment strategies and comply with legal regulations. Second chance hiring specifically targets individuals with criminal records to reduce recidivism and promote workforce reintegration, while social enterprise employment focuses on supporting marginalized groups through mission-driven business models. This distinction enables HR to tailor support programs, measure social impact accurately, and foster workplace diversity. Proper knowledge ensures better resource allocation and alignment with organizational social responsibility goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Second Chance Hiring | Social Enterprise Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring individuals with past employment barriers (e.g., criminal records) | Employment provided by businesses with social missions targeting marginalized groups |
| Target Group | Ex-offenders, formerly incarcerated people | Disabled persons, long-term unemployed, refugees, vulnerable populations |
| Purpose | Reduce recidivism, promote reintegration | Address social issues via sustainable employment |
| Employment Type | Mainstream corporate or organizational jobs | Jobs created within mission-driven enterprises |
| Impact | Improved workforce diversity, reduced stigma | Social inclusion, community development, economic empowerment |
| Support Services | Often paired with training, mentorship, or probation | Integrated social services, skills development, counseling |
| Sustainability | Dependent on employer willingness and legal frameworks | Business model integrates social goals with economic viability |
Which is better?
Second chance hiring directly addresses workforce reintegration by employing individuals with criminal records, improving diversity and reducing recidivism rates. Social enterprise employment supports marginalized groups through sustainable business models, fostering community impact and long-term empowerment. Evaluating effectiveness depends on organizational goals: immediate talent acquisition and inclusion versus broader social change and economic development.
Connection
Second chance hiring improves workforce diversity and reduces recidivism by providing employment opportunities to individuals with criminal records, which aligns with social enterprises' missions to create inclusive jobs that address societal challenges. Both approaches leverage social impact hiring practices that enhance community reintegration and economic empowerment. This connection promotes sustainable employment solutions while advancing corporate social responsibility and social equity within Human Resources.
Key Terms
Mission-driven Recruitment
Social enterprise employment emphasizes creating job opportunities that align with a company's mission to address social issues, often providing sustainable work environments for underserved populations. Second chance hiring specifically targets individuals with criminal records or other barriers to employment, aiming to reduce recidivism and promote economic reintegration. Explore more about how mission-driven recruitment strategies transform communities and businesses alike.
Inclusive Workforce
Social enterprise employment integrates business strategies with social impact goals to create sustainable job opportunities for marginalized populations, fostering inclusive workforce development through tailored training and support services. Second chance hiring specifically targets individuals with criminal records, offering them meaningful employment and reducing recidivism rates while enhancing workplace diversity and social equity. Explore how these approaches transform hiring practices and drive inclusive workforce solutions.
Rehabilitation Employment
Social enterprise employment integrates marginalized individuals into the workforce through sustainable business models, promoting economic inclusion and skill development. Second chance hiring specifically targets formerly incarcerated individuals to reduce recidivism and support community reintegration by providing meaningful job opportunities. Explore how rehabilitation employment transforms lives and strengthens communities through innovative workforce solutions.
Source and External Links
Overview: What is an Employment Social Enterprise? - REDF - Employment social enterprises (ESEs) are businesses designed to provide jobs, training, and support to people facing barriers like incarceration or homelessness, helping them build skills, confidence, and move toward stable employment while reinvesting profits into their workforce and services such as housing and mental health support.
Employment Social Enterprise - Central City Concern - Employment Social Enterprises focus on hiring individuals facing employment barriers and demonstrate significant positive outcomes in job retention, wages, housing stability, and access to employer-sponsored insurance among their employees.
Social Enterprise and Workforce Development - Catholic Charities USA - Social enterprises linked with workforce development programs provide clients with on-the-job training in areas like food services and maintenance, leading to economic self-sufficiency, professional certification, and reduced reliance on government benefits through social enterprise employment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com