Blind hiring eliminates bias by removing personal information such as names, gender, and education from applications, focusing solely on candidates' skills and qualifications. Behavioral interviewing assesses a candidate's past experiences and actions to predict future job performance, emphasizing real-life examples over abstract responses. Discover how integrating these approaches can enhance diversity and improve hiring accuracy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and behavioral interviewing is crucial for optimizing talent acquisition strategies; blind hiring minimizes unconscious bias by focusing solely on skills and qualifications, while behavioral interviewing assesses candidates' past experiences and cultural fit through situational questions. Companies utilizing blind hiring report a 25% increase in workforce diversity, whereas behavioral interviewing improves employee retention rates by 15% due to better role alignment. Knowing these distinctions allows HR professionals to tailor their recruitment methods effectively, enhancing both fairness and job performance prediction. Adopting the appropriate hiring technique directly impacts organizational inclusivity and long-term success.
Comparison Table
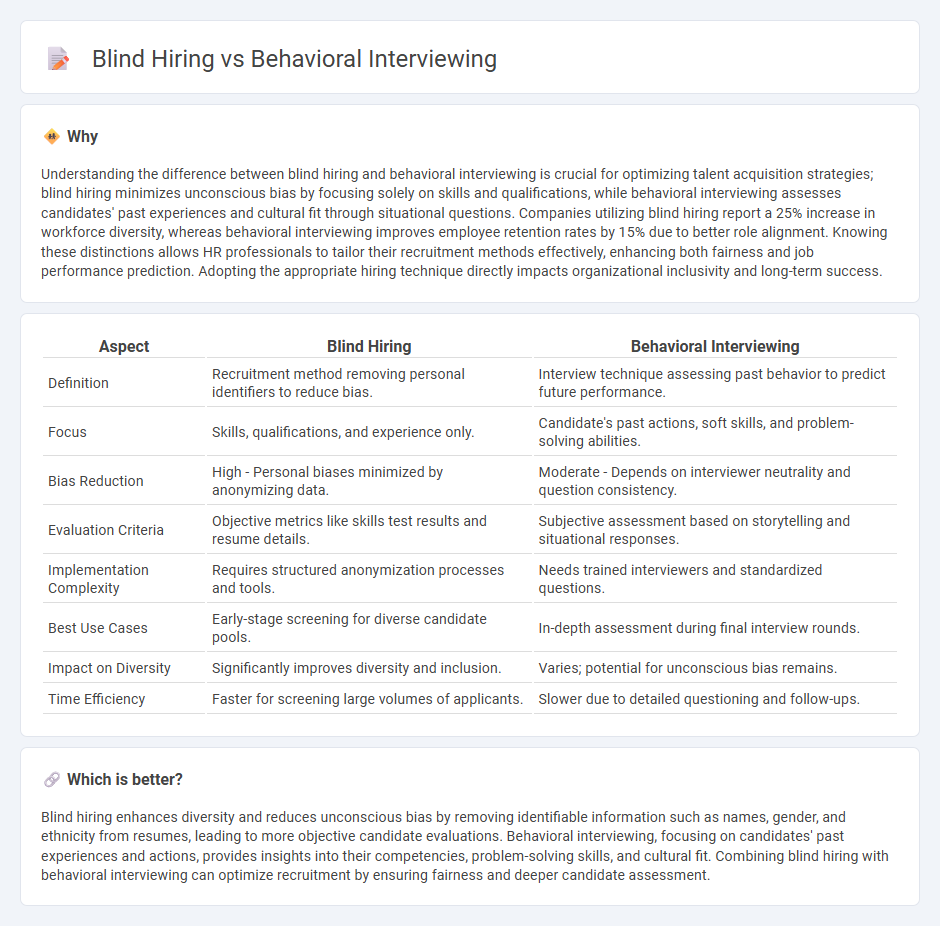
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Behavioral Interviewing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment method removing personal identifiers to reduce bias. | Interview technique assessing past behavior to predict future performance. |
| Focus | Skills, qualifications, and experience only. | Candidate's past actions, soft skills, and problem-solving abilities. |
| Bias Reduction | High - Personal biases minimized by anonymizing data. | Moderate - Depends on interviewer neutrality and question consistency. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Objective metrics like skills test results and resume details. | Subjective assessment based on storytelling and situational responses. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires structured anonymization processes and tools. | Needs trained interviewers and standardized questions. |
| Best Use Cases | Early-stage screening for diverse candidate pools. | In-depth assessment during final interview rounds. |
| Impact on Diversity | Significantly improves diversity and inclusion. | Varies; potential for unconscious bias remains. |
| Time Efficiency | Faster for screening large volumes of applicants. | Slower due to detailed questioning and follow-ups. |
Which is better?
Blind hiring enhances diversity and reduces unconscious bias by removing identifiable information such as names, gender, and ethnicity from resumes, leading to more objective candidate evaluations. Behavioral interviewing, focusing on candidates' past experiences and actions, provides insights into their competencies, problem-solving skills, and cultural fit. Combining blind hiring with behavioral interviewing can optimize recruitment by ensuring fairness and deeper candidate assessment.
Connection
Blind hiring enhances diversity by removing identifiable information such as names and demographics, focusing solely on candidates' skills and experiences. Behavioral interviewing complements this approach by assessing candidates' past actions and problem-solving abilities, providing objective insights into their potential job performance. Together, these methods reduce bias and improve the accuracy of talent selection in human resources.
Key Terms
**Behavioral Interviewing:**
Behavioral interviewing assesses candidates by analyzing past experiences and actions to predict future job performance, emphasizing specific examples and situational responses. This technique uncovers skill proficiency, problem-solving abilities, and cultural fit through targeted questions based on competencies. Discover more about how behavioral interviewing drives effective hiring decisions.
STAR Method
Behavioral interviewing leverages the STAR Method--Situation, Task, Action, Result--to evaluate candidates' past experiences and predict future job performance through structured storytelling. Blind hiring minimizes bias by omitting personal information and emphasizes objective assessment criteria, yet the STAR Method remains integral for articulating competencies clearly during interviews. Explore how combining these approaches enhances fair and effective talent acquisition strategies.
Competency-Based Questions
Behavioral interviewing uses competency-based questions to assess candidates' past experiences and skills relevant to job performance, focusing on specific examples that demonstrate abilities such as problem-solving, teamwork, and communication. Blind hiring removes demographic information to reduce unconscious bias, but competency-based questions remain central to evaluating a candidate's qualifications objectively. Explore how integrating competency-based questions with blind hiring can enhance fair and effective talent acquisition.
Source and External Links
Using the STAR method for your next behavioral interview - This webpage provides guidance on using the STAR method for behavioral interviews, which helps predict future performance by assessing past behaviors.
Behavioral Interviewing: What It Is, Benefits & More - This article explores the benefits and practices of behavioral interviewing, which goes beyond surface-level assessments to predict future performance.
Behavioral Interviewing - This webpage explains behavioral interviewing as a structured approach that uses past behavior to predict future performance, aiming to minimize bias in hiring decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com