Blind hiring removes personal identifiers such as name, gender, and age from applications to reduce unconscious bias and promote diversity in recruitment. Skills-based assessment focuses on evaluating candidates' actual abilities and competencies through practical tests and simulations, ensuring a meritocratic selection process. Discover how combining these methods can enhance fairness and efficiency in talent acquisition.
Why it is important
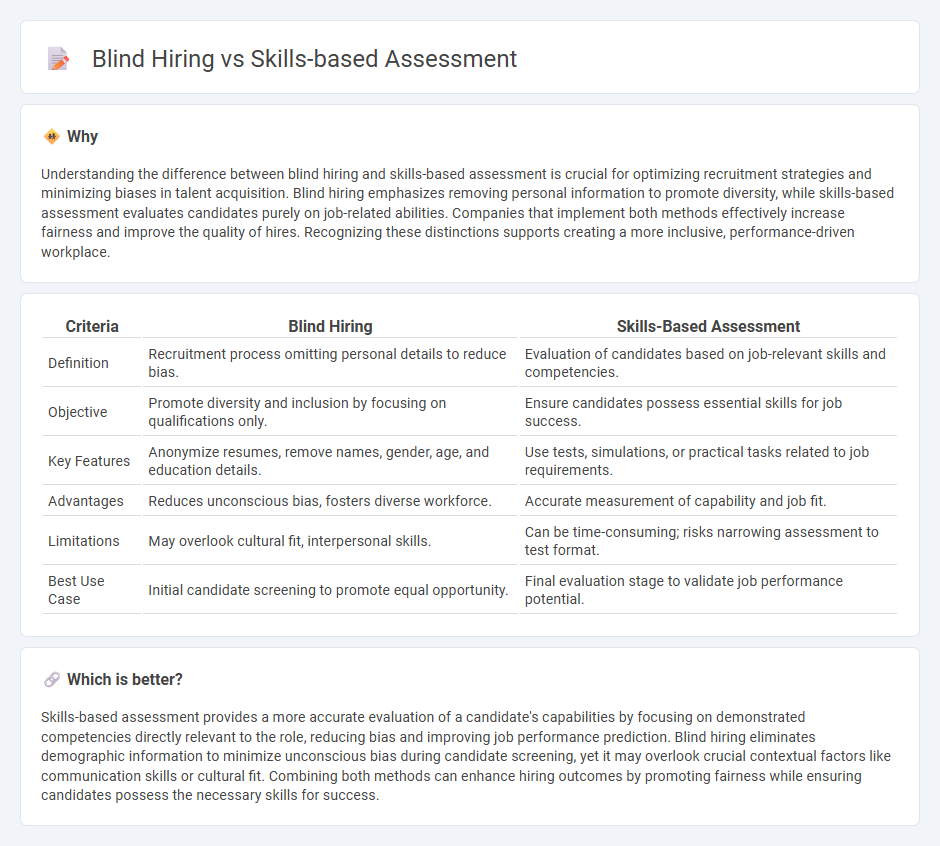
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and skills-based assessment is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies and minimizing biases in talent acquisition. Blind hiring emphasizes removing personal information to promote diversity, while skills-based assessment evaluates candidates purely on job-related abilities. Companies that implement both methods effectively increase fairness and improve the quality of hires. Recognizing these distinctions supports creating a more inclusive, performance-driven workplace.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Blind Hiring | Skills-Based Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment process omitting personal details to reduce bias. | Evaluation of candidates based on job-relevant skills and competencies. |
| Objective | Promote diversity and inclusion by focusing on qualifications only. | Ensure candidates possess essential skills for job success. |
| Key Features | Anonymize resumes, remove names, gender, age, and education details. | Use tests, simulations, or practical tasks related to job requirements. |
| Advantages | Reduces unconscious bias, fosters diverse workforce. | Accurate measurement of capability and job fit. |
| Limitations | May overlook cultural fit, interpersonal skills. | Can be time-consuming; risks narrowing assessment to test format. |
| Best Use Case | Initial candidate screening to promote equal opportunity. | Final evaluation stage to validate job performance potential. |
Which is better?
Skills-based assessment provides a more accurate evaluation of a candidate's capabilities by focusing on demonstrated competencies directly relevant to the role, reducing bias and improving job performance prediction. Blind hiring eliminates demographic information to minimize unconscious bias during candidate screening, yet it may overlook crucial contextual factors like communication skills or cultural fit. Combining both methods can enhance hiring outcomes by promoting fairness while ensuring candidates possess the necessary skills for success.
Connection
Blind hiring eliminates bias by removing demographic information during candidate evaluation, focusing solely on skills and qualifications. Skills-based assessment directly measures a candidate's expertise and capabilities, ensuring objective evaluation aligned with job requirements. Together, these methods enhance diversity and improve talent acquisition by prioritizing merit and competency over personal characteristics.
Key Terms
Competency Mapping
Skills-based assessment evaluates candidates through practical tasks directly related to job functions, ensuring precise competency mapping for roles. Blind hiring eliminates bias by anonymizing personal information but may overlook assessing specific skill sets critical for competency alignment. Explore how integrating both approaches can optimize talent acquisition strategies.
Unconscious Bias Reduction
Skills-based assessment evaluates candidates based on specific job-related abilities, which minimizes the influence of unconscious biases related to gender, ethnicity, or background. Blind hiring techniques further reduce bias by anonymizing candidate information, allowing employers to prioritize competencies over demographic factors. Explore how integrating both strategies can enhance diversity and fairness in recruitment.
Job-Relevant Criteria
Skills-based assessment targets evaluation of candidates' actual abilities through practical tests and real-world simulations, ensuring alignment with job-relevant criteria. Blind hiring removes demographic and personal information to combat unconscious bias, but skills-based assessments provide a more direct measure of job performance potential. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize hiring accuracy and inclusivity.
Source and External Links
A New Vision for Skills-Based Assessment - ETS - This report outlines a comprehensive system of skills-based assessment that evaluates not only cognitive skills like critical thinking but also affective and behavioral skills such as empathy and collaboration, guided by five authentic assessment principles.
How to use skill-based assessment tasks - Behavioural Insights Team - Skill-based assessments involve candidates performing real job-related tasks to demonstrate their abilities, improving recruitment quality and reducing biases by focusing on practical skills rather than just interviews.
Employee Skills Assessment Examples for Workforce Development - Employee skills assessments are standardized tools used to evaluate a workforce's technical, cognitive, leadership, and behavioral skills, enabling personalized talent development and better role alignment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com