Internal gig economy empowers employees to undertake short-term, project-based roles within their organization, boosting flexibility and skill diversification. Job rotation systematically shifts employees through different positions, enhancing cross-functional expertise and reducing monotony. Explore how these talent strategies can transform workforce agility and engagement.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the internal gig economy and job rotation is crucial for Human Resources to design effective talent management strategies that enhance employee engagement and organizational agility. The internal gig economy allows employees to take on short-term, project-based roles within the company, promoting flexibility and skill diversification. Job rotation systematically moves employees through different roles to develop broad expertise and reduce job monotony. Recognizing these distinctions helps HR optimize workforce planning and employee development initiatives tailored to business needs.
Comparison Table
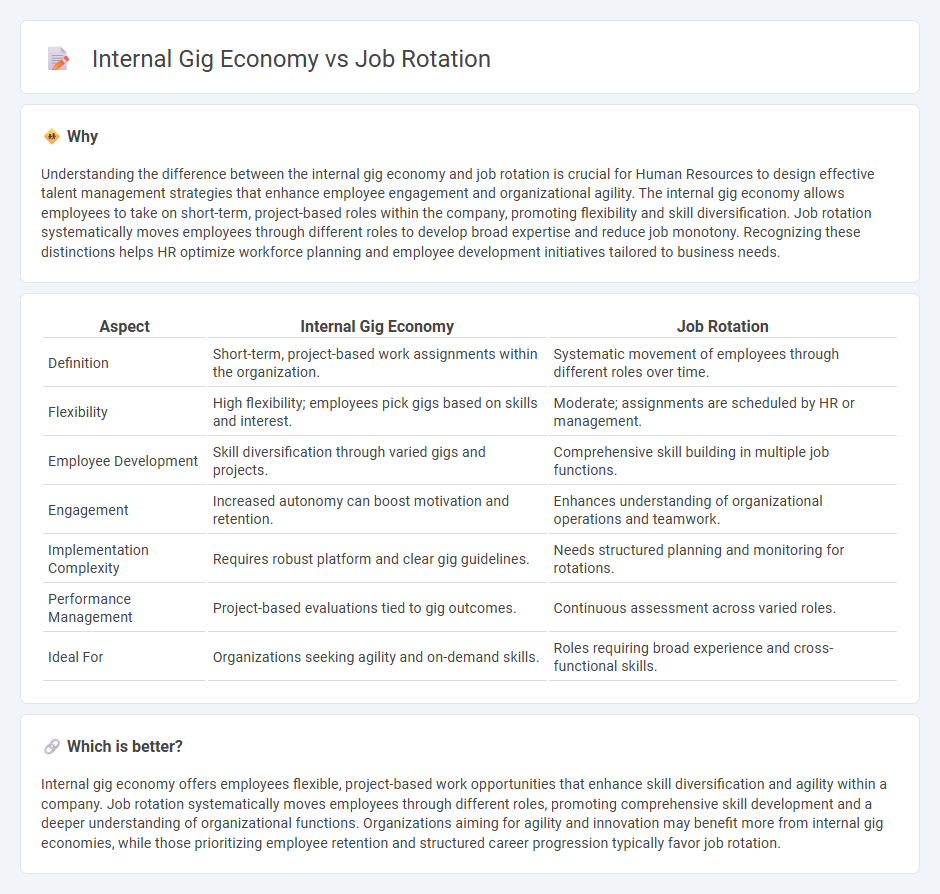
| Aspect | Internal Gig Economy | Job Rotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, project-based work assignments within the organization. | Systematic movement of employees through different roles over time. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; employees pick gigs based on skills and interest. | Moderate; assignments are scheduled by HR or management. |
| Employee Development | Skill diversification through varied gigs and projects. | Comprehensive skill building in multiple job functions. |
| Engagement | Increased autonomy can boost motivation and retention. | Enhances understanding of organizational operations and teamwork. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires robust platform and clear gig guidelines. | Needs structured planning and monitoring for rotations. |
| Performance Management | Project-based evaluations tied to gig outcomes. | Continuous assessment across varied roles. |
| Ideal For | Organizations seeking agility and on-demand skills. | Roles requiring broad experience and cross-functional skills. |
Which is better?
Internal gig economy offers employees flexible, project-based work opportunities that enhance skill diversification and agility within a company. Job rotation systematically moves employees through different roles, promoting comprehensive skill development and a deeper understanding of organizational functions. Organizations aiming for agility and innovation may benefit more from internal gig economies, while those prioritizing employee retention and structured career progression typically favor job rotation.
Connection
Internal gig economy leverages job rotation by enabling employees to take on short-term projects or roles across departments, enhancing skill diversification and organizational agility. Job rotation fosters a flexible workforce that supports internal gig opportunities, reducing talent shortages and boosting employee engagement. Integrating both strategies promotes continuous learning and optimizes human capital utilization within the company.
Key Terms
Skill diversification
Job rotation enhances skill diversification by systematically moving employees through various roles, allowing them to develop a broad range of competencies within different functions. Internal gig economy models promote skill diversification by enabling workers to take on short-term, specialized assignments across projects, fostering agility and niche expertise. Explore more to understand which approach best suits your organization's talent development strategy.
Flexibility
Job rotation enhances flexibility by systematically shifting employees across various roles, fostering diverse skill sets and adaptability within the organization. The internal gig economy offers greater flexibility through on-demand, project-based assignments that allow employees to select tasks aligning with their expertise and interests. Explore how integrating both approaches can maximize workforce agility and engagement.
Talent mobility
Job rotation enhances talent mobility by systematically moving employees through different roles to develop diverse skills and increase organizational agility. The internal gig economy facilitates flexible talent deployment by allowing employees to take on short-term, project-based assignments, promoting innovation and rapid skill acquisition. Explore how these approaches can strategically boost your workforce's adaptability and performance.
Source and External Links
Job rotation - Wikipedia - Job rotation is the lateral transfer of employees between jobs in an organization without a change in rank or salary, aimed at developing skills, managing fatigue, and supporting career development, while differing from promotion and specialization.
Job rotation | EBSCO Research Starters - Job rotation is a human resources strategy that moves employees between various jobs to cultivate a broad range of skills, combat monotony, and increase flexibility and motivation, benefiting both employees and employers.
Job Rotation: A Full Guide with 5 Examples - AIHR - Job rotation involves temporary, often lateral moves between roles, as seen in companies like The Slumber Yard and Heineken, where programs are designed to reduce turnover, develop versatile employees, and prepare trainees for multiple departments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com