Fractional employment offers companies flexible access to specialized skills by hiring professionals for a portion of their time, enhancing productivity without the commitment of full-time roles. Seasonal employment caters to fluctuating business demands by employing workers during peak periods, optimizing labor costs and operational efficiency. Explore the key differences and benefits of these employment types to optimize your workforce strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between fractional employment and seasonal employment is crucial for businesses to optimize workforce management, comply with labor laws, and control costs effectively. Fractional employment involves hiring employees for a fixed portion of time or tasks, ideal for ongoing specialized roles, whereas seasonal employment is temporary and tied to specific peak periods or seasons. Accurate classification ensures proper contract terms, benefits administration, and tax obligations are met, reducing legal risks. Employers can strategically plan recruitment and retention by distinguishing these employment types to meet fluctuating business demands efficiently.
Comparison Table
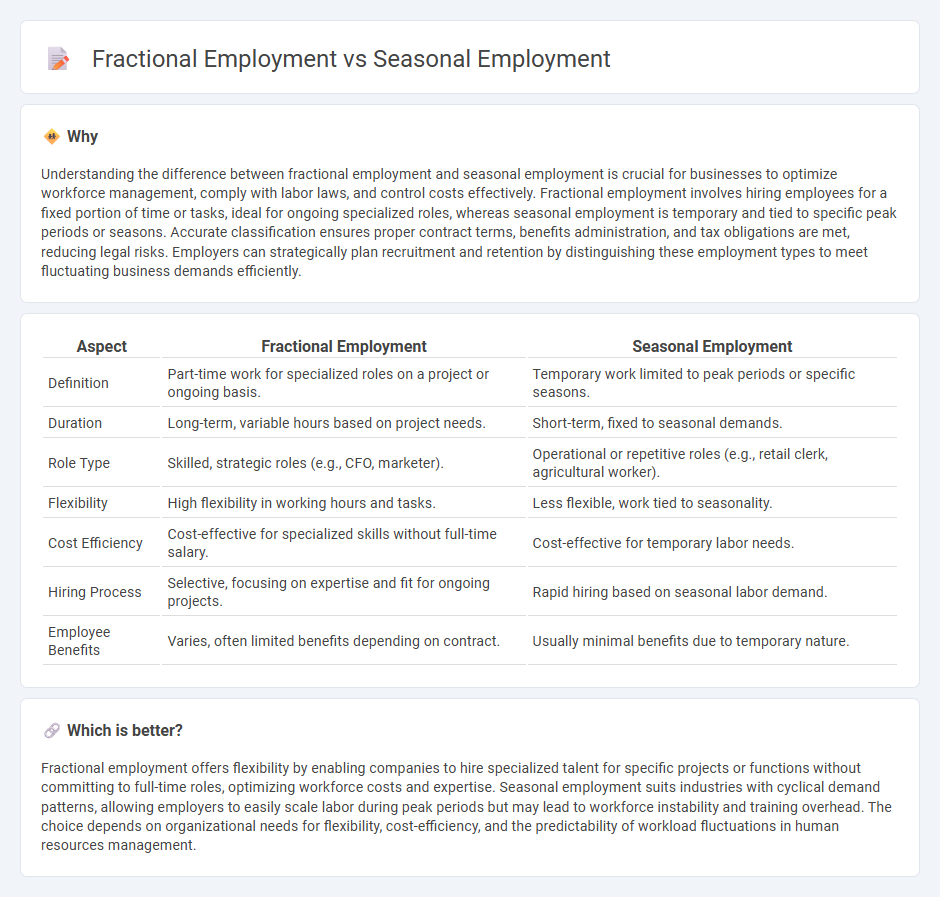
| Aspect | Fractional Employment | Seasonal Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time work for specialized roles on a project or ongoing basis. | Temporary work limited to peak periods or specific seasons. |
| Duration | Long-term, variable hours based on project needs. | Short-term, fixed to seasonal demands. |
| Role Type | Skilled, strategic roles (e.g., CFO, marketer). | Operational or repetitive roles (e.g., retail clerk, agricultural worker). |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in working hours and tasks. | Less flexible, work tied to seasonality. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for specialized skills without full-time salary. | Cost-effective for temporary labor needs. |
| Hiring Process | Selective, focusing on expertise and fit for ongoing projects. | Rapid hiring based on seasonal labor demand. |
| Employee Benefits | Varies, often limited benefits depending on contract. | Usually minimal benefits due to temporary nature. |
Which is better?
Fractional employment offers flexibility by enabling companies to hire specialized talent for specific projects or functions without committing to full-time roles, optimizing workforce costs and expertise. Seasonal employment suits industries with cyclical demand patterns, allowing employers to easily scale labor during peak periods but may lead to workforce instability and training overhead. The choice depends on organizational needs for flexibility, cost-efficiency, and the predictability of workload fluctuations in human resources management.
Connection
Fractional employment and seasonal employment are connected through their flexible workforce structures that allow businesses to adjust labor resources based on fluctuating demands. Both employment types enable companies to hire talent for specific time periods or projects, optimizing operational efficiency and cost management. This flexibility supports dynamic workforce planning and improves human resource allocation during peak seasons or business cycles.
Key Terms
Contract Duration
Seasonal employment typically involves fixed, short-term contracts aligned with specific seasons or peak periods, often lasting a few weeks to several months. Fractional employment offers flexible contract durations, allowing professionals to work part-time or on-demand for extended periods, often months to years, depending on project needs. Explore deeper insights into how contract duration impacts workforce planning and operational efficiency.
Work Schedule
Seasonal employment offers work schedules tied to specific times of the year, often fluctuating sharply based on demand during holidays or peak seasons, while fractional employment provides a flexible, part-time work arrangement spread consistently throughout the year. Seasonal workers may face periods of intense work followed by inactivity, whereas fractional employees maintain a steady workload tailored to employer needs. Explore how varying work patterns in these employment types impact productivity and work-life balance.
Benefit Eligibility
Seasonal employment typically grants workers access to benefits tied to the employment period, such as prorated vacation or sick leave, while fractional employment often includes eligibility for a proportionate share of company benefits like health insurance and retirement contributions based on hours worked. Eligibility for benefits in seasonal roles depends on the duration and timing of work, whereas fractional employment benefits depend on agreed-upon work fractions and company policies. Explore how these employment types impact your benefits eligibility to make informed career decisions.
Source and External Links
What is Seasonal Employment? | Definition and Meaning - OnPay - Seasonal employment is temporary work to help employers meet staffing needs during holidays, high seasons, or other peak business periods, usually lasting 12 months or less.
Maximizing Seasonal Workforce - BambooHR - Seasonal employment provides organizations with temporary workers during specific times of the year, helping them manage increased demand without carrying extra staff year-round.
Seasonal Jobs | Benefits, Laws & Regulations - ADP - Seasonal jobs are temporary positions that allow businesses to scale their workforce based on cyclical demand, often in industries like retail, hospitality, and tourism, without offering year-round employment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com