Silent quitting involves employees disengaging by doing the bare minimum without formally resigning, negatively impacting productivity and workplace morale. Quiet firing occurs when employers subtly encourage employees to leave through reduced responsibilities or exclusion rather than official termination. Explore the nuances and strategies to address these emerging workforce challenges.
Why it is important
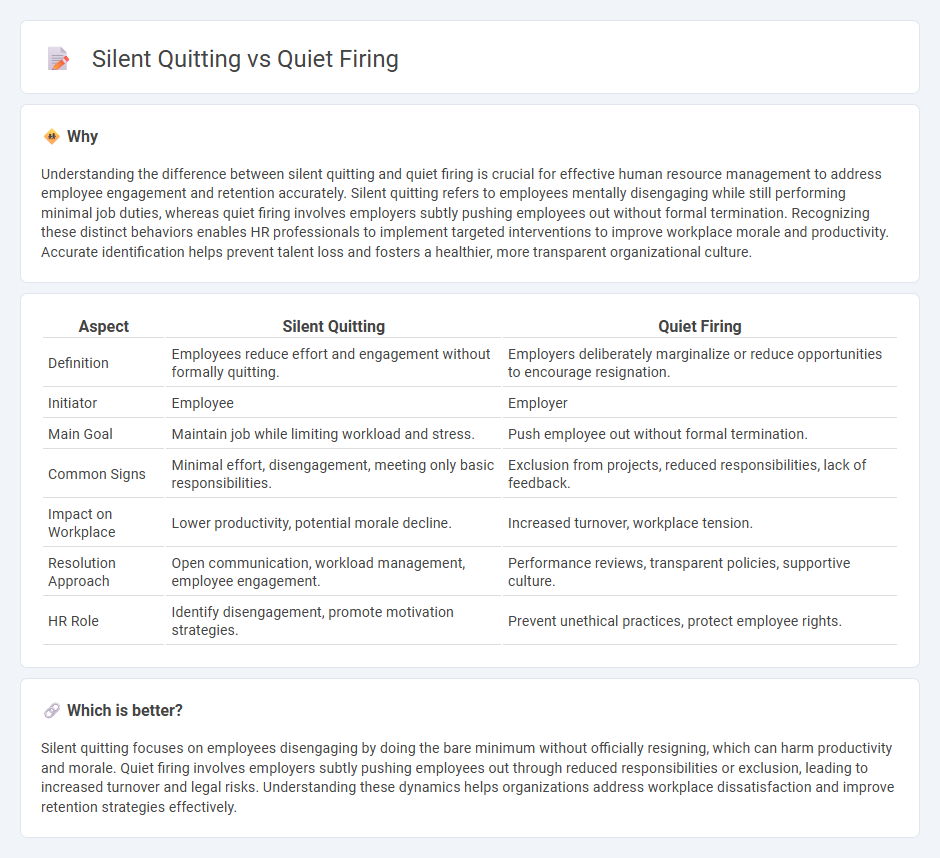
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and quiet firing is crucial for effective human resource management to address employee engagement and retention accurately. Silent quitting refers to employees mentally disengaging while still performing minimal job duties, whereas quiet firing involves employers subtly pushing employees out without formal termination. Recognizing these distinct behaviors enables HR professionals to implement targeted interventions to improve workplace morale and productivity. Accurate identification helps prevent talent loss and fosters a healthier, more transparent organizational culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Quiet Firing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees reduce effort and engagement without formally quitting. | Employers deliberately marginalize or reduce opportunities to encourage resignation. |
| Initiator | Employee | Employer |
| Main Goal | Maintain job while limiting workload and stress. | Push employee out without formal termination. |
| Common Signs | Minimal effort, disengagement, meeting only basic responsibilities. | Exclusion from projects, reduced responsibilities, lack of feedback. |
| Impact on Workplace | Lower productivity, potential morale decline. | Increased turnover, workplace tension. |
| Resolution Approach | Open communication, workload management, employee engagement. | Performance reviews, transparent policies, supportive culture. |
| HR Role | Identify disengagement, promote motivation strategies. | Prevent unethical practices, protect employee rights. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting focuses on employees disengaging by doing the bare minimum without officially resigning, which can harm productivity and morale. Quiet firing involves employers subtly pushing employees out through reduced responsibilities or exclusion, leading to increased turnover and legal risks. Understanding these dynamics helps organizations address workplace dissatisfaction and improve retention strategies effectively.
Connection
Silent quitting and quiet firing are interconnected phenomena reflecting deteriorating employee-employer relationships, where employees deliberately reduce engagement and effort while employers marginalize or overlook underperforming staff without formal termination. Both practices contribute to lowered workplace productivity and morale, highlighting the need for transparent communication and proactive human resource management strategies. Understanding these trends enables HR professionals to develop retention programs and foster a more supportive organizational culture.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Quiet firing involves subtle managerial actions aimed at pushing employees out by reducing responsibilities or growth opportunities, negatively impacting employee engagement and morale. Silent quitting refers to employees disengaging emotionally and doing the bare minimum at work without formally resigning, which lowers productivity and team spirit. Discover effective strategies to address these issues and boost employee engagement.
Performance Management
Quiet firing involves managers deliberately reducing an employee's responsibilities or growth opportunities to encourage them to leave, negatively impacting performance management metrics like productivity and engagement. Silent quitting describes employees doing the bare minimum at work, often due to disengagement or burnout, which hampers goal attainment and overall team effectiveness. Explore more to understand how these dynamics influence performance management strategies and workplace culture.
Workplace Communication
Quiet firing involves employers subtly pushing employees out by reducing responsibilities or providing limited feedback, impacting motivation and engagement. Silent quitting refers to employees disengaging by doing the bare minimum, avoiding extra tasks without official resignation. Explore how effective workplace communication strategies can address these challenges and promote a healthier work environment.
Source and External Links
What Is Quiet Firing & What Are the Signs? - Quiet firing refers to the deliberate creation of a poor work environment to encourage an employee to resign rather than being directly fired.
Quiet Firing: What It Is and How to Spot It - Quiet firing involves creating non-ideal work conditions to make underperforming employees quit, and it can be prevented through open communication and fair management practices.
Quiet Firing - Quiet firing is the practice of neglecting employees or pushing them to quit by setting unattainable goals or denying opportunities, often to avoid termination costs and legal repercussions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com