Silent quitting reflects employees doing the minimum required without extra effort, often driven by disengagement or burnout. Presenteeism involves workers physically present but mentally unproductive, frequently caused by stress or health issues. Explore the impacts of silent quitting and presenteeism on workforce productivity and strategies for effective human resources management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and presenteeism is crucial in Human Resources to effectively address employee engagement and productivity challenges. Silent quitting refers to employees disengaging and doing the bare minimum, while presenteeism involves employees physically present but mentally unproductive due to stress or health issues. Identifying these behaviors helps HR implement targeted strategies to improve workplace morale and reduce turnover. Accurate recognition of these issues supports better resource allocation and enhances overall organizational performance.
Comparison Table
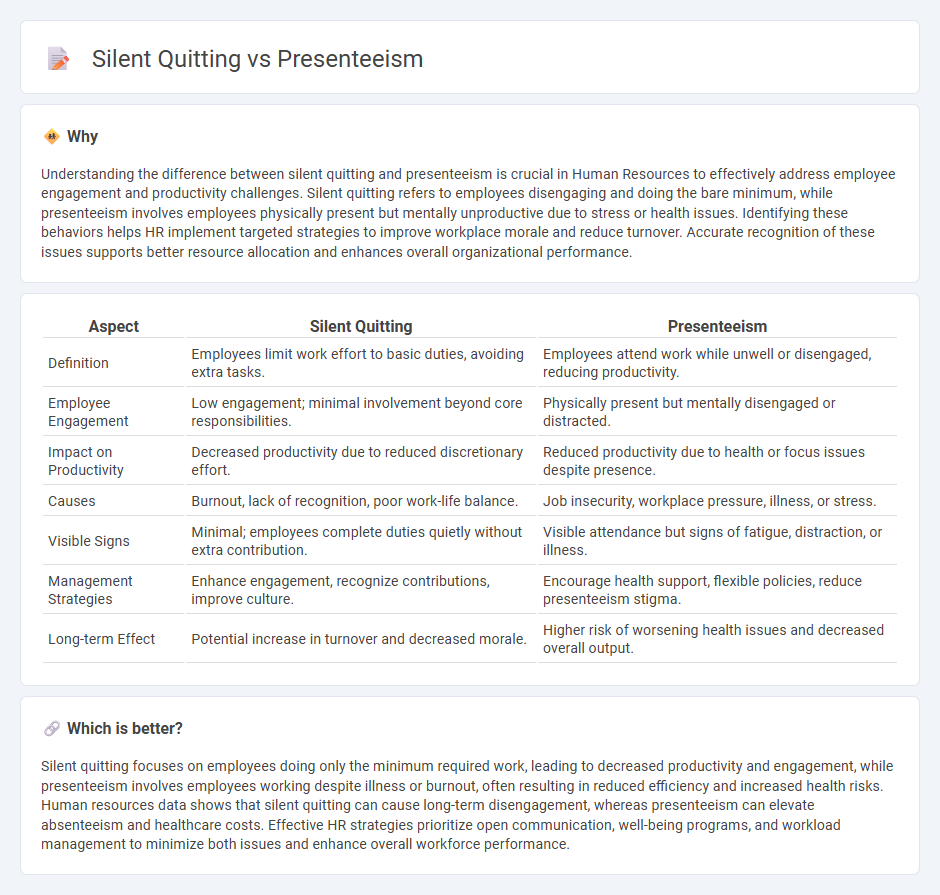
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Presenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees limit work effort to basic duties, avoiding extra tasks. | Employees attend work while unwell or disengaged, reducing productivity. |
| Employee Engagement | Low engagement; minimal involvement beyond core responsibilities. | Physically present but mentally disengaged or distracted. |
| Impact on Productivity | Decreased productivity due to reduced discretionary effort. | Reduced productivity due to health or focus issues despite presence. |
| Causes | Burnout, lack of recognition, poor work-life balance. | Job insecurity, workplace pressure, illness, or stress. |
| Visible Signs | Minimal; employees complete duties quietly without extra contribution. | Visible attendance but signs of fatigue, distraction, or illness. |
| Management Strategies | Enhance engagement, recognize contributions, improve culture. | Encourage health support, flexible policies, reduce presenteeism stigma. |
| Long-term Effect | Potential increase in turnover and decreased morale. | Higher risk of worsening health issues and decreased overall output. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting focuses on employees doing only the minimum required work, leading to decreased productivity and engagement, while presenteeism involves employees working despite illness or burnout, often resulting in reduced efficiency and increased health risks. Human resources data shows that silent quitting can cause long-term disengagement, whereas presenteeism can elevate absenteeism and healthcare costs. Effective HR strategies prioritize open communication, well-being programs, and workload management to minimize both issues and enhance overall workforce performance.
Connection
Silent quitting and presenteeism both reflect underlying employee disengagement issues that affect productivity and workplace morale. While silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum and mentally checking out without formally resigning, presenteeism occurs when employees show up physically but perform below capacity due to stress or health problems. Human Resources must address both phenomena by fostering a supportive culture and promoting work-life balance to maintain employee engagement and organizational performance.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Presenteeism occurs when employees are physically present but mentally disengaged, often reducing productivity and innovation within teams, whereas silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum, minimizing effort to avoid burnout without formally resigning. Both behaviors signal low employee engagement and can be mitigated by fostering transparent communication, recognizing achievements, and promoting work-life balance. Discover effective strategies to enhance employee engagement and overcome these challenges.
Productivity
Presenteeism, where employees are physically present but mentally disengaged, directly decreases productivity by limiting focus and creativity, whereas silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum, resulting in underperformance and stalled progress. Both behaviors significantly impact organizational efficiency, employee morale, and overall output quality, with presenteeism leading to burnout and silent quitting fostering disengagement. Discover effective strategies to address presenteeism and silent quitting to boost workplace productivity and employee satisfaction.
Workplace Well-being
Presenteeism, characterized by employees physically present but mentally disengaged, significantly hampers productivity and workplace well-being by fostering stress and burnout. Silent quitting, where employees withdraw from exceeding job expectations, subtly affects team dynamics and overall organizational morale without overtly signaling dissatisfaction. Explore the impact of these phenomena on workplace culture and strategies to enhance employee engagement and health.
Source and External Links
Presenteeism - Wikipedia - Presenteeism is the act of employees continuing to work while sick or otherwise unwell, often resulting in reduced productivity and sometimes risky workplace behaviors.
What is presenteeism? - Future Forum - Presenteeism is the pressure employees feel to meet company expectations of presence or visibility, rather than focusing on actual productivity, which can lead to burnout and lower performance.
Presenteeism - how to identify it and stop it - Cigna Global - Presenteeism occurs when tired, unmotivated, or ill employees come to work despite being unfit, which can harm both their well-being and workplace morale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com