Workforce ecosystems integrate diverse talent pools, including full-time employees, freelancers, and contractors, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing market demands. The gig economy emphasizes flexible, short-term engagements, empowering workers with autonomy but often lacking traditional employment benefits. Explore how these models impact talent management strategies and business performance.
Why it is important
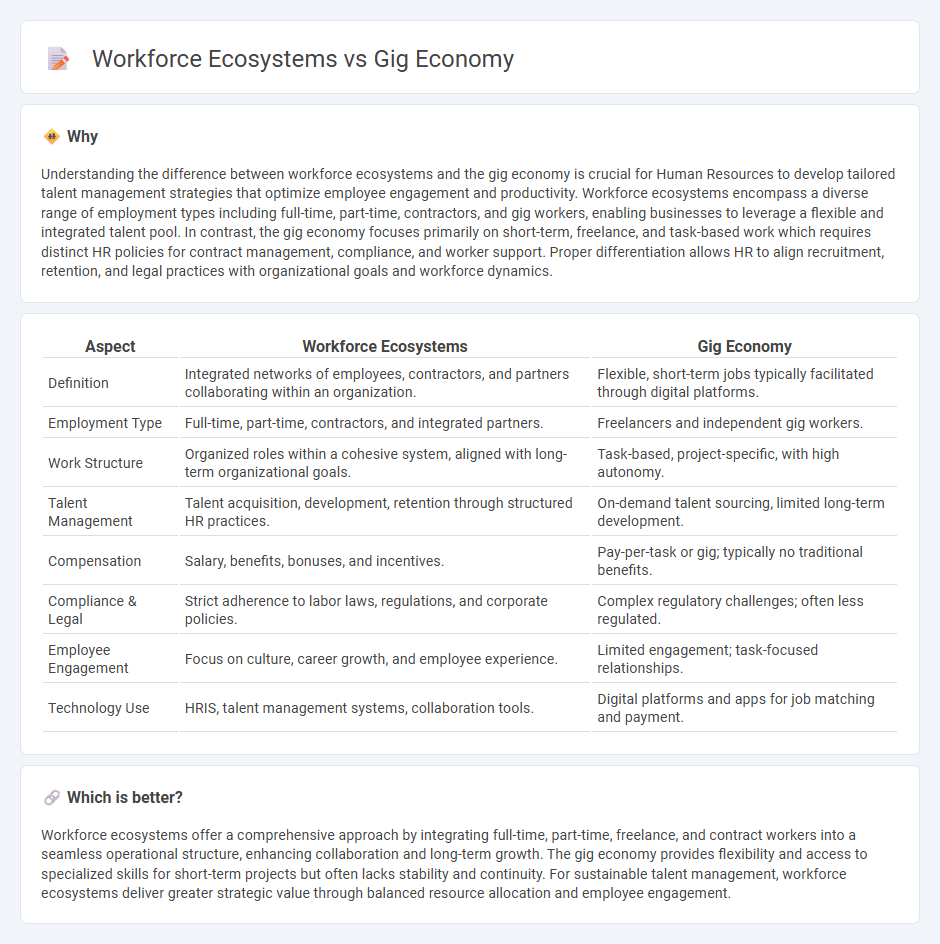
Understanding the difference between workforce ecosystems and the gig economy is crucial for Human Resources to develop tailored talent management strategies that optimize employee engagement and productivity. Workforce ecosystems encompass a diverse range of employment types including full-time, part-time, contractors, and gig workers, enabling businesses to leverage a flexible and integrated talent pool. In contrast, the gig economy focuses primarily on short-term, freelance, and task-based work which requires distinct HR policies for contract management, compliance, and worker support. Proper differentiation allows HR to align recruitment, retention, and legal practices with organizational goals and workforce dynamics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Workforce Ecosystems | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated networks of employees, contractors, and partners collaborating within an organization. | Flexible, short-term jobs typically facilitated through digital platforms. |
| Employment Type | Full-time, part-time, contractors, and integrated partners. | Freelancers and independent gig workers. |
| Work Structure | Organized roles within a cohesive system, aligned with long-term organizational goals. | Task-based, project-specific, with high autonomy. |
| Talent Management | Talent acquisition, development, retention through structured HR practices. | On-demand talent sourcing, limited long-term development. |
| Compensation | Salary, benefits, bonuses, and incentives. | Pay-per-task or gig; typically no traditional benefits. |
| Compliance & Legal | Strict adherence to labor laws, regulations, and corporate policies. | Complex regulatory challenges; often less regulated. |
| Employee Engagement | Focus on culture, career growth, and employee experience. | Limited engagement; task-focused relationships. |
| Technology Use | HRIS, talent management systems, collaboration tools. | Digital platforms and apps for job matching and payment. |
Which is better?
Workforce ecosystems offer a comprehensive approach by integrating full-time, part-time, freelance, and contract workers into a seamless operational structure, enhancing collaboration and long-term growth. The gig economy provides flexibility and access to specialized skills for short-term projects but often lacks stability and continuity. For sustainable talent management, workforce ecosystems deliver greater strategic value through balanced resource allocation and employee engagement.
Connection
Workforce ecosystems integrate diverse employment models, including the gig economy, to create flexible and dynamic labor markets. The gig economy contributes to workforce ecosystems by offering on-demand, project-based talent that enhances organizational agility and supports rapid scaling. This interconnection drives innovation in talent management, enabling companies to optimize workforce composition and respond swiftly to market fluctuations.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility by enabling workers to choose projects, set schedules, and balance multiple roles without long-term commitments. Workforce ecosystems integrate gig workers with traditional employees, promoting a dynamic labor model that enhances adaptability and resource allocation in real time. Explore how these flexible labor models reshape modern employment structures and drive organizational agility.
Collaboration
Collaboration within the gig economy is characterized by flexible, task-specific partnerships often mediated through digital platforms, enabling rapid and efficient resource sharing. Workforce ecosystems emphasize interconnected networks of diverse stakeholders, including employers, employees, freelancers, and technology providers, fostering long-term collaboration and co-innovation. Explore how these models reshape business strategies and talent management by deepening your understanding of their collaborative dynamics.
Talent Marketplace
Talent marketplaces in gig economy models emphasize flexibility and project-based engagements, enabling businesses to quickly access specialized skills without long-term commitments. Workforce ecosystems extend this approach by integrating diverse talent pools, including full-time employees, freelancers, and gig workers, fostering collaboration and skill development across platforms. Explore how leveraging talent marketplaces within workforce ecosystems can optimize agility and innovation in modern organizations.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible system involving digital platforms to connect buyers and sellers, often seen in companies like Uber and DoorDash.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy offers individuals flexible work through short-term projects, affecting both the workforce and businesses, with significant growth projected.
What is the Gig Economy? - The gig economy is a free market system featuring temporary positions, driven by digital platforms connecting customers with independent workers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com