Workforce ecosystems encompass the interconnected networks of employees, contractors, technology, and external partners that drive organizational performance, emphasizing flexibility and collaboration. Organizational culture defines the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that influence employee engagement and decision-making within a company. Explore how aligning workforce ecosystems with organizational culture can enhance productivity and innovation.
Why it is important
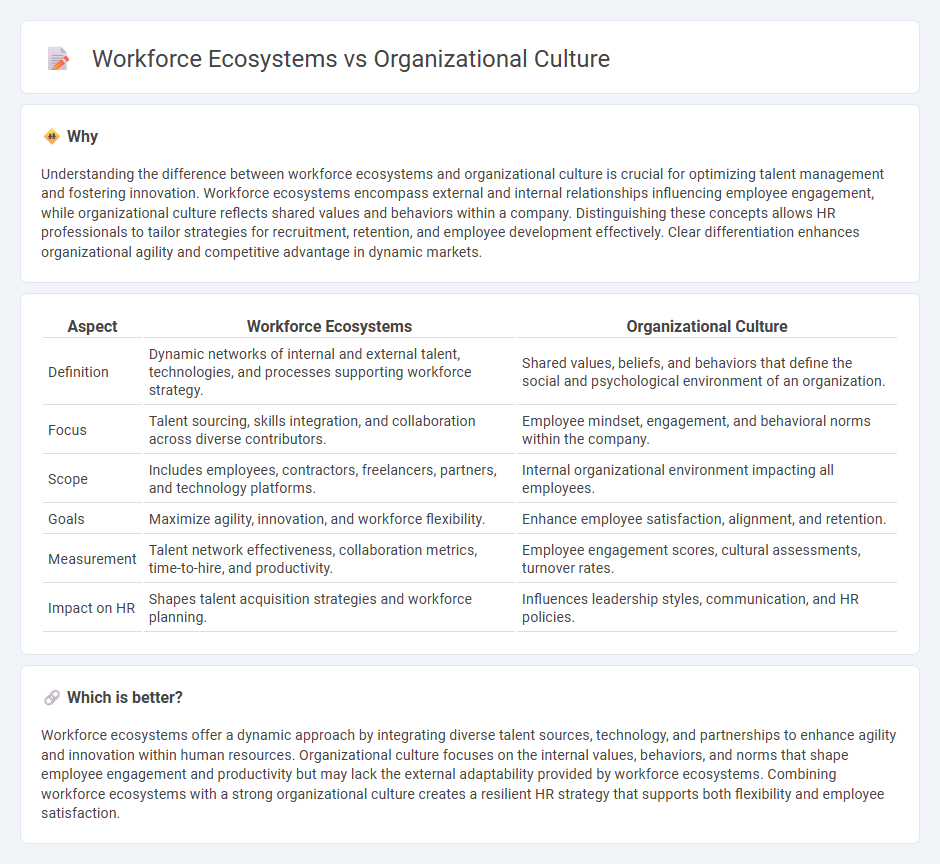
Understanding the difference between workforce ecosystems and organizational culture is crucial for optimizing talent management and fostering innovation. Workforce ecosystems encompass external and internal relationships influencing employee engagement, while organizational culture reflects shared values and behaviors within a company. Distinguishing these concepts allows HR professionals to tailor strategies for recruitment, retention, and employee development effectively. Clear differentiation enhances organizational agility and competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Workforce Ecosystems | Organizational Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic networks of internal and external talent, technologies, and processes supporting workforce strategy. | Shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that define the social and psychological environment of an organization. |
| Focus | Talent sourcing, skills integration, and collaboration across diverse contributors. | Employee mindset, engagement, and behavioral norms within the company. |
| Scope | Includes employees, contractors, freelancers, partners, and technology platforms. | Internal organizational environment impacting all employees. |
| Goals | Maximize agility, innovation, and workforce flexibility. | Enhance employee satisfaction, alignment, and retention. |
| Measurement | Talent network effectiveness, collaboration metrics, time-to-hire, and productivity. | Employee engagement scores, cultural assessments, turnover rates. |
| Impact on HR | Shapes talent acquisition strategies and workforce planning. | Influences leadership styles, communication, and HR policies. |
Which is better?
Workforce ecosystems offer a dynamic approach by integrating diverse talent sources, technology, and partnerships to enhance agility and innovation within human resources. Organizational culture focuses on the internal values, behaviors, and norms that shape employee engagement and productivity but may lack the external adaptability provided by workforce ecosystems. Combining workforce ecosystems with a strong organizational culture creates a resilient HR strategy that supports both flexibility and employee satisfaction.
Connection
Workforce ecosystems directly influence organizational culture by shaping employee interactions, collaboration patterns, and value alignment. A dynamic workforce ecosystem that includes diverse talent sources, flexible work arrangements, and integrated technology fosters a culture of innovation and adaptability. Organizations with well-developed workforce ecosystems demonstrate higher employee engagement, retention, and overall performance.
Key Terms
Values Alignment
Organizational culture centers on shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape the company's internal environment, fostering cohesion and guiding decision-making. Workforce ecosystems encompass a broader network of internal employees, external partners, suppliers, and technology platforms, emphasizing collaboration and adaptability to dynamic market demands. Explore how aligning values across both organizational culture and workforce ecosystems drives innovation and competitive advantage.
Collaboration Networks
Collaboration networks within organizational culture emphasize shared values, trust, and open communication that foster teamwork and innovation among employees. Workforce ecosystems focus on dynamic interactions across internal teams and external partners, leveraging technology to enhance connectivity, knowledge sharing, and agile collaboration. Explore how integrating collaboration networks into workforce ecosystems can drive productivity and competitive advantage.
Talent Fluidity
Organizational culture shapes employee behaviors, values, and collaboration patterns, directly influencing talent fluidity by creating an environment where skills can be dynamically leveraged and roles evolve seamlessly. Workforce ecosystems extend beyond internal culture, encompassing external partnerships, technologies, and gig talent that enhance flexibility and agility in talent deployment. Explore how aligning organizational culture with expansive workforce ecosystems maximizes talent fluidity for competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
The 4 Types of Organizational Culture & How to Design Change - This article discusses the four main types of organizational culture--Adhocracy, Clan, Hierarchy, and Market--and how they influence a company's operations.
Organizational Culture: Definition, Importance, and Development - This blog post defines organizational culture, explains its importance, and outlines the four main types: Clan, Adhocracy, Market, and Hierarchy.
Organizational Culture: Definition and Types - This article explores the definition of organizational culture and its four main types--Clan, Adhocracy, Market, and Hierarchy--based on the Competing Values Framework.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com