Blind hiring focuses on removing personal information such as name, gender, and ethnicity from resumes to minimize unconscious bias during recruitment, enhancing diversity and inclusion. Cognitive ability testing evaluates problem-solving skills, learning aptitude, and critical thinking, providing objective data to predict job performance. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of blind hiring and cognitive ability testing in modern HR practices.
Why it is important
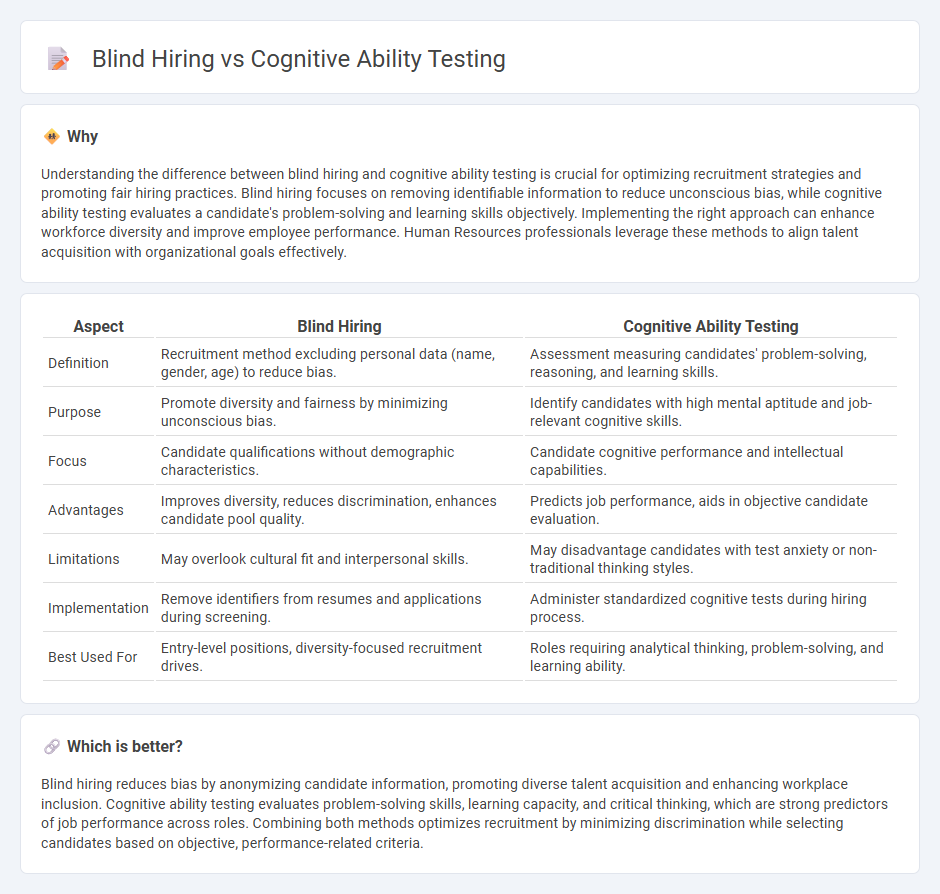
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and cognitive ability testing is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies and promoting fair hiring practices. Blind hiring focuses on removing identifiable information to reduce unconscious bias, while cognitive ability testing evaluates a candidate's problem-solving and learning skills objectively. Implementing the right approach can enhance workforce diversity and improve employee performance. Human Resources professionals leverage these methods to align talent acquisition with organizational goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Cognitive Ability Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment method excluding personal data (name, gender, age) to reduce bias. | Assessment measuring candidates' problem-solving, reasoning, and learning skills. |
| Purpose | Promote diversity and fairness by minimizing unconscious bias. | Identify candidates with high mental aptitude and job-relevant cognitive skills. |
| Focus | Candidate qualifications without demographic characteristics. | Candidate cognitive performance and intellectual capabilities. |
| Advantages | Improves diversity, reduces discrimination, enhances candidate pool quality. | Predicts job performance, aids in objective candidate evaluation. |
| Limitations | May overlook cultural fit and interpersonal skills. | May disadvantage candidates with test anxiety or non-traditional thinking styles. |
| Implementation | Remove identifiers from resumes and applications during screening. | Administer standardized cognitive tests during hiring process. |
| Best Used For | Entry-level positions, diversity-focused recruitment drives. | Roles requiring analytical thinking, problem-solving, and learning ability. |
Which is better?
Blind hiring reduces bias by anonymizing candidate information, promoting diverse talent acquisition and enhancing workplace inclusion. Cognitive ability testing evaluates problem-solving skills, learning capacity, and critical thinking, which are strong predictors of job performance across roles. Combining both methods optimizes recruitment by minimizing discrimination while selecting candidates based on objective, performance-related criteria.
Connection
Blind hiring eliminates bias by removing demographic information from applications, allowing cognitive ability testing to more accurately assess a candidate's problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Cognitive ability tests measure key competencies that predict job performance, ensuring hiring decisions focus on merit rather than unconscious prejudice. Integrating blind hiring with cognitive assessments enhances diversity and improves overall talent quality in Human Resources.
Key Terms
Cognitive Ability Testing:
Cognitive ability testing evaluates candidates' problem-solving, memory, and reasoning skills to predict job performance effectively across various roles. Unlike blind hiring, which removes identifiable information to reduce bias, cognitive testing provides quantifiable data on mental capabilities essential for decision-making and learning. Discover how integrating cognitive ability assessments can enhance recruitment accuracy and diversity.
Intelligence assessment
Cognitive ability testing measures mental capabilities such as problem-solving, memory, and reasoning, providing a quantifiable assessment of intelligence crucial for predicting job performance. Blind hiring removes personal identifiers to reduce bias, but may overlook cognitive potential unless paired with intelligence-specific assessments. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how combining both methods enhances hiring accuracy and fairness.
Aptitude measurement
Cognitive ability testing evaluates aptitudes such as problem-solving, memory, and reasoning skills, providing quantifiable data to predict job performance. Blind hiring, by removing demographic information, reduces bias and emphasizes candidates' actual competencies rather than background. Explore how combining these approaches can enhance fair and effective talent acquisition strategies.
Source and External Links
Cognitive ability tests for employment: The ultimate guide - TestGorilla - Cognitive ability tests measure skills like problem solving, spatial and verbal reasoning, reading comprehension, attention to detail, and numerical reasoning to evaluate a candidate's potential to perform job-related tasks.
Cognitive Abilities Tests by Cambridge Insight - These standardized, adaptive assessments evaluate cognitive strengths and weaknesses across different educational stages, helping educators tailor support to individual student needs.
Cognitive Ability Tests - College Board Accommodations - Commonly accepted cognitive ability tests include the Wechsler scales, Woodcock-Johnson, Stanford-Binet, and Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, often used to document eligibility for academic accommodations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com