Ghost quitting refers to employees gradually disengaging from their responsibilities and reducing productivity without formal resignation, while job abandonment occurs when employees abruptly stop showing up at work without any notice. Both phenomena pose significant challenges for human resources, impacting team morale, operational continuity, and recruitment efforts. Explore strategies to effectively address ghost quitting and job abandonment to maintain a committed and efficient workforce.
Why it is important
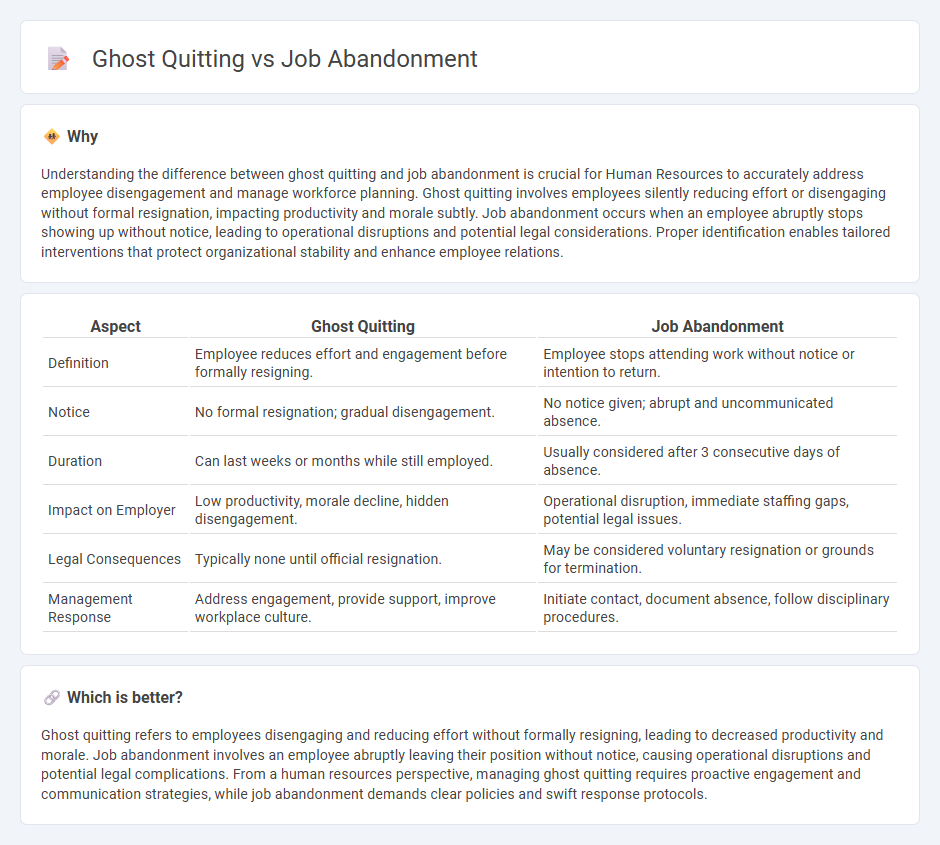
Understanding the difference between ghost quitting and job abandonment is crucial for Human Resources to accurately address employee disengagement and manage workforce planning. Ghost quitting involves employees silently reducing effort or disengaging without formal resignation, impacting productivity and morale subtly. Job abandonment occurs when an employee abruptly stops showing up without notice, leading to operational disruptions and potential legal considerations. Proper identification enables tailored interventions that protect organizational stability and enhance employee relations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Quitting | Job Abandonment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee reduces effort and engagement before formally resigning. | Employee stops attending work without notice or intention to return. |
| Notice | No formal resignation; gradual disengagement. | No notice given; abrupt and uncommunicated absence. |
| Duration | Can last weeks or months while still employed. | Usually considered after 3 consecutive days of absence. |
| Impact on Employer | Low productivity, morale decline, hidden disengagement. | Operational disruption, immediate staffing gaps, potential legal issues. |
| Legal Consequences | Typically none until official resignation. | May be considered voluntary resignation or grounds for termination. |
| Management Response | Address engagement, provide support, improve workplace culture. | Initiate contact, document absence, follow disciplinary procedures. |
Which is better?
Ghost quitting refers to employees disengaging and reducing effort without formally resigning, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Job abandonment involves an employee abruptly leaving their position without notice, causing operational disruptions and potential legal complications. From a human resources perspective, managing ghost quitting requires proactive engagement and communication strategies, while job abandonment demands clear policies and swift response protocols.
Connection
Ghost quitting and job abandonment both reflect employee disengagement manifested through unexpected or uncommunicated departure from a role. These behaviors disrupt HR processes by increasing turnover rates and complicating workforce planning due to the sudden absence of personnel. Addressing underlying causes such as workplace dissatisfaction and lack of support is critical for effective human resource management and retaining talent.
Key Terms
Notice Period
Job abandonment occurs when an employee leaves without any formal notice, violating company policies and often leading to disciplinary actions. Ghost quitting refers to employees psychologically disengaging and reducing effort before officially resigning, sometimes serving the notice period but without genuine commitment. Explore the key differences and impacts of notice periods on job abandonment and ghost quitting to better manage workforce stability.
Employee Communication
Job abandonment occurs when an employee stops showing up to work without notifying their employer, leading to potential legal and operational challenges. Ghost quitting, on the other hand, involves employees disengaging emotionally and mentally while still attending work, causing decreased productivity and hidden turnover risks. Explore effective employee communication strategies to address both issues and enhance workforce retention.
Voluntary Separation
Job abandonment occurs when an employee stops showing up to work without notifying their employer, often leading to immediate termination due to breach of contract. Ghost quitting, a form of voluntary separation, involves employees disengaging mentally and reducing their productivity before formally resigning or leaving without notice. Explore in-depth distinctions and implications of voluntary separation strategies to better understand workforce management.
Source and External Links
Job Abandonment: What is it, How it Happens & How to Handle It - Job abandonment occurs when an employee doesn't show up to their job for a predetermined number of days without notice or intention to return, often considered a voluntary resignation despite lack of formal quit notice.
Job Abandonment: Definition and How To Prevent It - Job abandonment is an employee's failure to come to work for specified consecutive days without notice, commonly due to seeking better employment, discomfort in the role, or personal crises preventing communication.
Job Abandonment: Definition, Policy and Tips for Prevention - Job abandonment is defined as an employee leaving their position without notice or intent to return, often linked to dissatisfaction or external opportunities, and can disrupt business workflows and employee eligibility for benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com