Skills adjacency mapping identifies related competencies that enable employees to transition smoothly between roles, enhancing talent mobility within organizations. Career pathing focuses on structured progression plans that align employee aspirations with company goals, fostering long-term growth and retention. Explore the differences and benefits of these approaches to optimize workforce development strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between skills adjacency mapping and career pathing is crucial for effective talent management and employee development within Human Resources. Skills adjacency mapping identifies transferable skills that enable employees to shift laterally across roles, enhancing workforce agility. Career pathing outlines a structured progression of roles aligned with long-term career goals, supporting retention and growth planning. Mastery of both concepts empowers HR professionals to design strategic training programs and succession plans that optimize organizational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Skills Adjacency Mapping | Career Pathing |
|---|---|---|
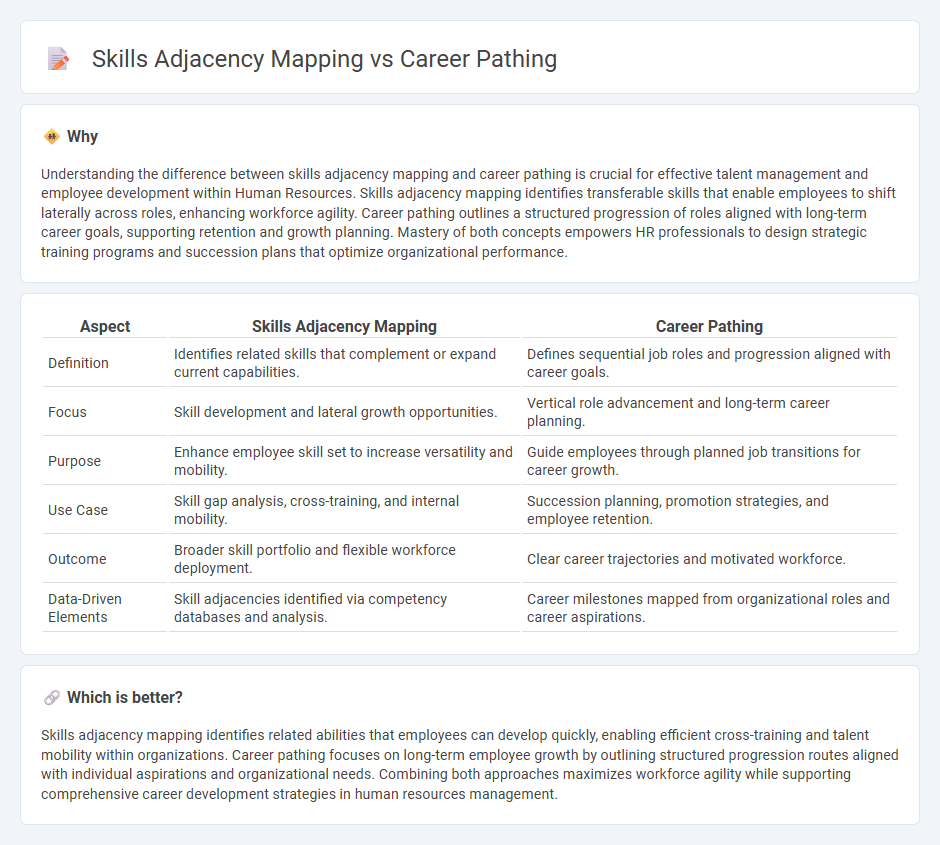
| Definition | Identifies related skills that complement or expand current capabilities. | Defines sequential job roles and progression aligned with career goals. |
| Focus | Skill development and lateral growth opportunities. | Vertical role advancement and long-term career planning. |
| Purpose | Enhance employee skill set to increase versatility and mobility. | Guide employees through planned job transitions for career growth. |
| Use Case | Skill gap analysis, cross-training, and internal mobility. | Succession planning, promotion strategies, and employee retention. |
| Outcome | Broader skill portfolio and flexible workforce deployment. | Clear career trajectories and motivated workforce. |
| Data-Driven Elements | Skill adjacencies identified via competency databases and analysis. | Career milestones mapped from organizational roles and career aspirations. |
Which is better?
Skills adjacency mapping identifies related abilities that employees can develop quickly, enabling efficient cross-training and talent mobility within organizations. Career pathing focuses on long-term employee growth by outlining structured progression routes aligned with individual aspirations and organizational needs. Combining both approaches maximizes workforce agility while supporting comprehensive career development strategies in human resources management.
Connection
Skills adjacency mapping identifies related competencies and skill clusters that employees can acquire to transition into new roles, enabling effective career pathing by outlining clear, attainable progression routes. This process leverages data on skill overlaps and gaps to personalize employee development plans, ensuring alignment between organizational needs and individual career goals. Integrating skills adjacency mapping into career pathing strategies enhances talent mobility, reduces skill shortages, and supports workforce agility in dynamic business environments.
Key Terms
Career Progression
Career pathing charts a structured trajectory within an organization or industry, highlighting potential roles employees can progress to based on experience and qualifications, whereas skills adjacency mapping identifies complementary skills that facilitate lateral or vertical moves. Career progression relies heavily on aligning employees' current capabilities with future role requirements, fostering growth and promotion opportunities. Explore deeper insights on how aligning career pathing with skills adjacency can optimize talent development strategies.
Competency Gaps
Career pathing identifies future roles by aligning individual career goals with organizational needs, emphasizing competency gaps to target development areas effectively. Skills adjacency mapping analyzes related skills to facilitate lateral moves and skill transitions, helping close competency gaps through strategic upskilling. Explore how these approaches can optimize workforce development and bridge your team's skill gaps efficiently.
Transferable Skills
Career pathing identifies potential job roles aligned with an individual's current experience and aspirations, while skills adjacency mapping highlights transferable skills that enable movement across different functions or industries. Emphasizing transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and project management facilitates seamless transitions and broadens career mobility. Explore more about optimizing career development strategies through transferable skills analysis.
Source and External Links
What Is Career Pathing & Why Is It Important? - Paychex - Career pathing is the process employers use to create a personalized plan and development track that aligns employees' unique skills, interests, and career objectives with possible roles and growth opportunities in the organization or beyond, serving as a comprehensive roadmap from current position to long-term goals.
Definition of Career Pathing - Gartner Human Resources Glossary - Career pathing aligns employee career growth opportunities with organizational talent priorities through mapping vertical, lateral, and cross-functional roles based on employees' skills, interests, and goals, encouraging participation in learning and development programs.
Career Pathing: The Complete Guide - Qualtrics - Career pathing approaches include the formalized career ladder, which focuses on linear promotions, and the career lattice, which supports lateral moves and role exploration in flatter organizational structures providing flexible growth options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com