Ghost hiring involves filling positions with candidates who are not formally documented or acknowledged in the organizational structure, often to maintain confidentiality or competitive advantage. Internal hiring leverages existing employees for new roles, promoting employee growth and reducing recruitment costs while enhancing organizational culture. Explore the advantages and challenges of ghost hiring versus internal hiring to optimize your talent acquisition strategy.
Why it is important
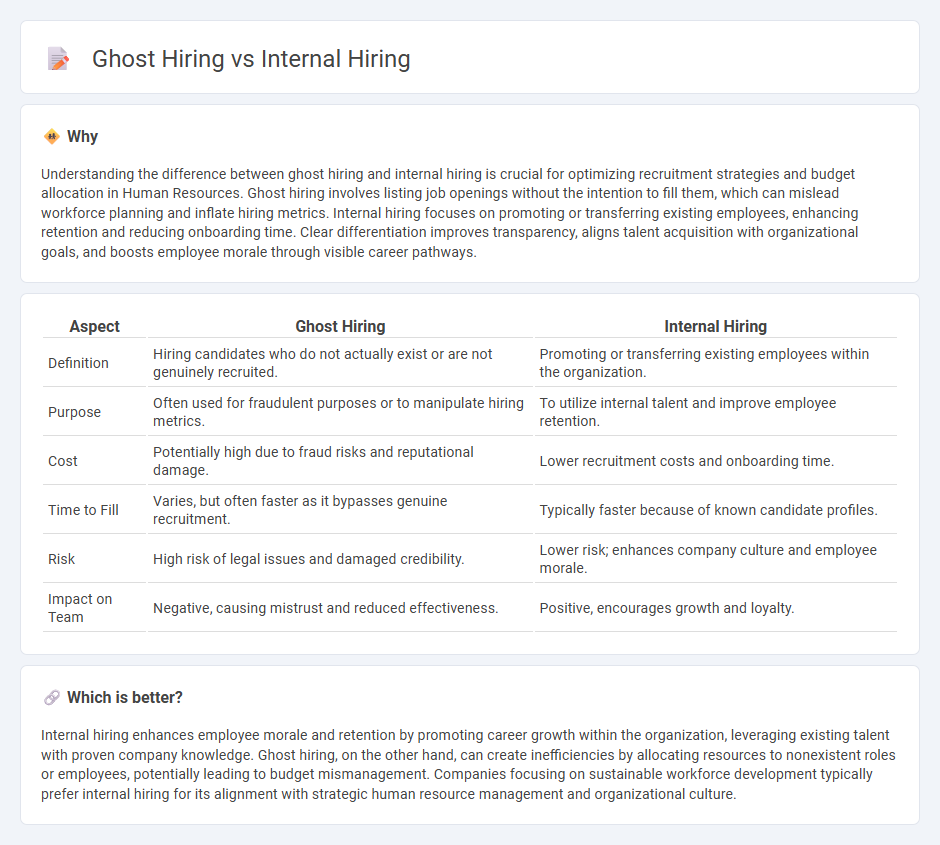
Understanding the difference between ghost hiring and internal hiring is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies and budget allocation in Human Resources. Ghost hiring involves listing job openings without the intention to fill them, which can mislead workforce planning and inflate hiring metrics. Internal hiring focuses on promoting or transferring existing employees, enhancing retention and reducing onboarding time. Clear differentiation improves transparency, aligns talent acquisition with organizational goals, and boosts employee morale through visible career pathways.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Hiring | Internal Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring candidates who do not actually exist or are not genuinely recruited. | Promoting or transferring existing employees within the organization. |
| Purpose | Often used for fraudulent purposes or to manipulate hiring metrics. | To utilize internal talent and improve employee retention. |
| Cost | Potentially high due to fraud risks and reputational damage. | Lower recruitment costs and onboarding time. |
| Time to Fill | Varies, but often faster as it bypasses genuine recruitment. | Typically faster because of known candidate profiles. |
| Risk | High risk of legal issues and damaged credibility. | Lower risk; enhances company culture and employee morale. |
| Impact on Team | Negative, causing mistrust and reduced effectiveness. | Positive, encourages growth and loyalty. |
Which is better?
Internal hiring enhances employee morale and retention by promoting career growth within the organization, leveraging existing talent with proven company knowledge. Ghost hiring, on the other hand, can create inefficiencies by allocating resources to nonexistent roles or employees, potentially leading to budget mismanagement. Companies focusing on sustainable workforce development typically prefer internal hiring for its alignment with strategic human resource management and organizational culture.
Connection
Ghost hiring, which involves unadvertised or covert recruitment, often supports internal hiring by identifying potential candidates within an organization before opening positions to external applicants. This approach enables HR departments to streamline talent acquisition, reduce recruitment costs, and fill vacancies quickly with known employees who already align with company culture and performance standards. Leveraging internal talent pools through ghost hiring enhances employee retention and accelerates career development pathways.
Key Terms
Talent Pipeline
Internal hiring leverages existing employee skills and optimizes workforce retention by filling open positions from within the organization's talent pipeline. Ghost hiring refers to maintaining unadvertised or unfilled roles to anticipate future talent needs, often keeping positions reserved to avoid recruitment delays. Understanding the strategic impact of internal versus ghost hiring can transform your talent pipeline management; explore more insights to refine your hiring strategy.
Job Vacancy Transparency
Internal hiring enhances job vacancy transparency by openly promoting positions within the organization, fostering trust and employee engagement. Ghost hiring involves listing fictitious job openings to gauge market interest or for strategic reasons, often leading to confusion and diminished transparency. Explore deeper insights into how these practices impact organizational culture and recruitment strategies.
Workforce Planning
Internal hiring leverages existing employee talent pools to fill vacancies efficiently, reducing onboarding time and fostering employee retention, which is critical for effective workforce planning. Ghost hiring, where positions remain open without active recruitment, can distort workforce analytics, leading to inaccurate demand forecasts and inefficient resource allocation. Explore deeper insights into optimizing workforce planning strategies through balanced internal hiring and realistic vacancy management.
Source and External Links
8 internal recruitment methods you need to know - Augeo - Internal hiring involves filling positions using current employees through methods such as promotions, transfers, referrals, and reorganizations, fostering motivation and career progression within a company.
HR Glossary | What is internal hiring? - Visier - Internal hiring fills open jobs from existing employees through promotions, transfers, or moving temps to permanent roles, benefiting companies by leveraging known talent and improving engagement.
Internal Hiring Factbook - JOSH BERSIN - Internal hiring and mobility reduce recruiting costs and ramp-up time, improve retention and performance, and create a culture where managers promote employee movement as a strategic advantage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com