Blind hiring minimizes bias by removing identifying information such as names, gender, and age from applications, promoting diversity and inclusion in recruitment. Employee referrals leverage existing staff networks to identify candidates who align with company culture, often speeding up the hiring process and improving retention rates. Discover how integrating blind hiring with employee referrals can enhance your workforce quality and diversity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and employee referrals is crucial because blind hiring minimizes bias by focusing on skills and qualifications, while employee referrals can enhance cultural fit and reduce onboarding time. Blind hiring promotes diversity and inclusion by anonymizing candidate information such as names and backgrounds. Employee referrals often generate higher-quality candidates and lower turnover rates due to trusted recommendations. Knowing these differences helps HR professionals design effective recruitment strategies tailored to their organization's goals.
Comparison Table
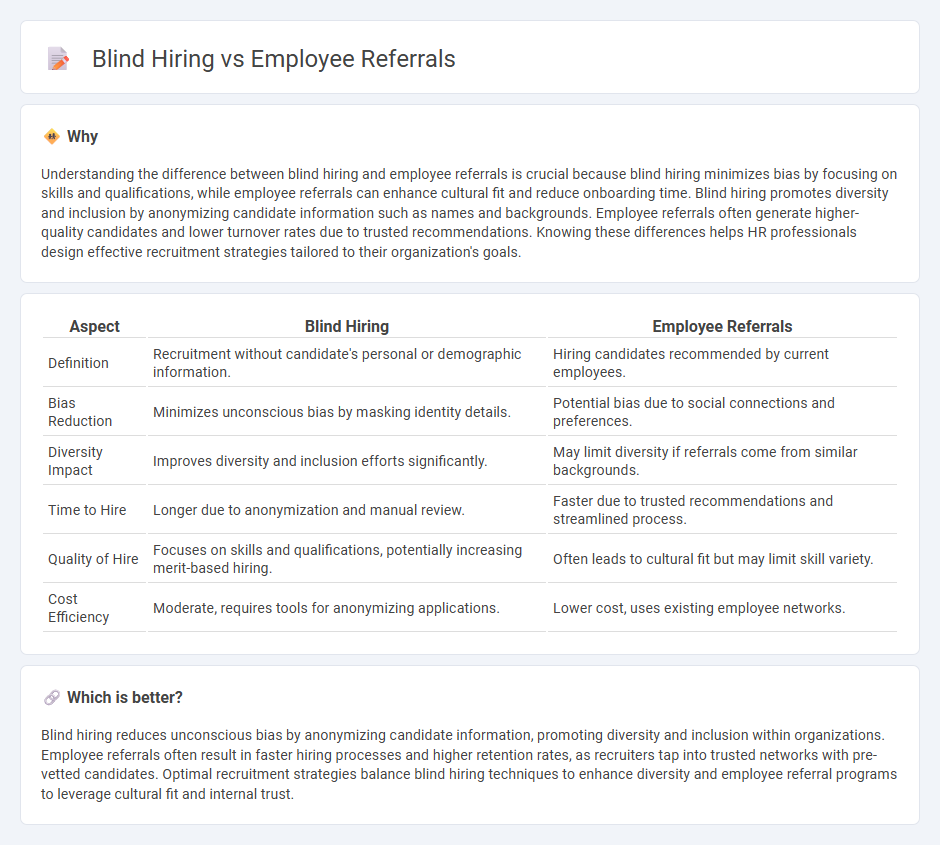
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Employee Referrals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment without candidate's personal or demographic information. | Hiring candidates recommended by current employees. |
| Bias Reduction | Minimizes unconscious bias by masking identity details. | Potential bias due to social connections and preferences. |
| Diversity Impact | Improves diversity and inclusion efforts significantly. | May limit diversity if referrals come from similar backgrounds. |
| Time to Hire | Longer due to anonymization and manual review. | Faster due to trusted recommendations and streamlined process. |
| Quality of Hire | Focuses on skills and qualifications, potentially increasing merit-based hiring. | Often leads to cultural fit but may limit skill variety. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate, requires tools for anonymizing applications. | Lower cost, uses existing employee networks. |
Which is better?
Blind hiring reduces unconscious bias by anonymizing candidate information, promoting diversity and inclusion within organizations. Employee referrals often result in faster hiring processes and higher retention rates, as recruiters tap into trusted networks with pre-vetted candidates. Optimal recruitment strategies balance blind hiring techniques to enhance diversity and employee referral programs to leverage cultural fit and internal trust.
Connection
Blind hiring minimizes unconscious bias by anonymizing candidate information, allowing hiring decisions to focus purely on skills and qualifications. Employee referrals, when integrated into blind hiring practices, can diversify the talent pool by reducing favoritism linked to personal connections. Combining these methods improves hiring fairness and promotes a more inclusive workplace culture.
Key Terms
Networking
Employee referrals leverage existing networks to identify candidates who align with company culture and values, often resulting in faster hiring and improved retention rates. Blind hiring focuses on eliminating biases by anonymizing candidate information, promoting diversity and merit-based selection. Explore how combining strategic networking with unbiased hiring can transform your talent acquisition process.
Unconscious Bias
Employee referrals often reinforce unconscious bias by favoring candidates similar to current employees, leading to reduced diversity in hiring. Blind hiring mitigates this bias by anonymizing candidate information such as names, gender, and educational background, allowing recruiters to evaluate qualifications objectively. Explore how implementing blind hiring practices can enhance diversity and inclusion in your recruitment process.
Diversity
Employee referrals often lead to homogenous hiring pools due to social network similarities, limiting diversity and inclusion efforts. Blind hiring removes identifiable candidate information to minimize unconscious bias, promoting equitable opportunities and diverse workforces. Explore how these recruitment methods impact organizational diversity strategies and outcomes.
Source and External Links
Employee Referrals: Definition, Common Benefits and Tips - Employee referrals involve internal employees recommending people from their network for job openings, with companies encouraging referrals by communicating openings, promoting participation with incentives, and providing feedback to referring employees.
Employee referral program: Benefits & strategies - Employee referral programs are effective hiring tools that improve candidate quality and speed up recruitment, with recognition and rewards playing a key role in sustaining employee participation and engagement.
Why Employee Referral Programs Are a Game-Changer ... - Employee referrals typically deliver higher-quality candidates aligned with company culture, and also accelerate the hiring process by providing pre-vetted candidates and faster onboarding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com