Fractional employment offers companies flexible access to skilled professionals who work part-time or on project-specific tasks, optimizing talent costs without long-term commitments. Apprenticeships provide structured training programs where individuals develop hands-on experience and industry-specific skills while contributing to the organization, fostering workforce development. Explore how fractional employment and apprenticeships can strategically enhance your human resources approach.
Why it is important
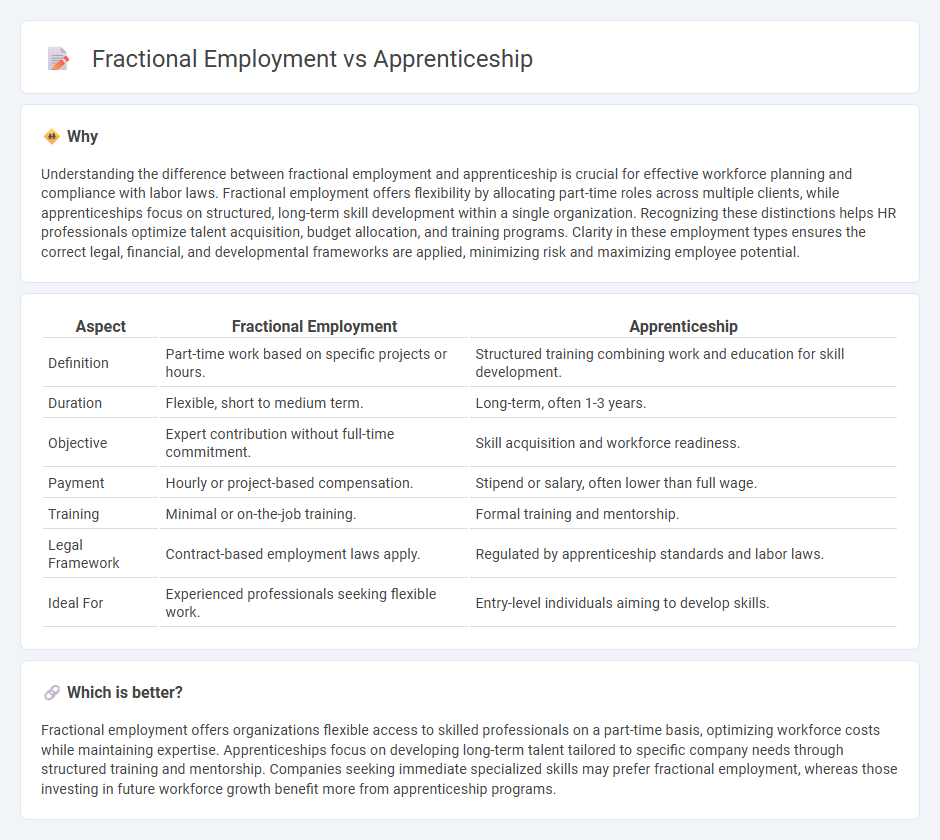
Understanding the difference between fractional employment and apprenticeship is crucial for effective workforce planning and compliance with labor laws. Fractional employment offers flexibility by allocating part-time roles across multiple clients, while apprenticeships focus on structured, long-term skill development within a single organization. Recognizing these distinctions helps HR professionals optimize talent acquisition, budget allocation, and training programs. Clarity in these employment types ensures the correct legal, financial, and developmental frameworks are applied, minimizing risk and maximizing employee potential.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Employment | Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time work based on specific projects or hours. | Structured training combining work and education for skill development. |
| Duration | Flexible, short to medium term. | Long-term, often 1-3 years. |
| Objective | Expert contribution without full-time commitment. | Skill acquisition and workforce readiness. |
| Payment | Hourly or project-based compensation. | Stipend or salary, often lower than full wage. |
| Training | Minimal or on-the-job training. | Formal training and mentorship. |
| Legal Framework | Contract-based employment laws apply. | Regulated by apprenticeship standards and labor laws. |
| Ideal For | Experienced professionals seeking flexible work. | Entry-level individuals aiming to develop skills. |
Which is better?
Fractional employment offers organizations flexible access to skilled professionals on a part-time basis, optimizing workforce costs while maintaining expertise. Apprenticeships focus on developing long-term talent tailored to specific company needs through structured training and mentorship. Companies seeking immediate specialized skills may prefer fractional employment, whereas those investing in future workforce growth benefit more from apprenticeship programs.
Connection
Fractional employment and apprenticeship intersect by allowing organizations to secure skilled talent on a part-time basis while facilitating hands-on learning experiences. Apprenticeships provide structured training and skill development, which fractional employees can leverage to enhance their expertise within specific roles. This synergy supports workforce flexibility and continuous professional growth, enabling businesses to adapt efficiently to changing labor demands.
Key Terms
Training
Apprenticeship programs offer structured, hands-on training designed to develop specific skills over an extended period, providing apprentices with comprehensive industry knowledge and certifications. Fractional employment focuses on hiring part-time experts to perform specialized tasks without the intensive, skill-building training component, emphasizing immediate contribution over long-term development. Explore more to understand which approach best suits your business training needs.
Time commitment
Apprenticeship typically requires a full-time commitment over an extended period, often ranging from six months to several years, providing in-depth training and skill development. Fractional employment offers flexible, part-time work arrangements tailored to specific projects or tasks, allowing professionals to allocate limited hours per week or month. Explore the nuances of time commitment in both models to determine the best fit for your career goals or business needs.
Employment status
Apprenticeship typically designates a formal employment status where individuals gain hands-on skills under a structured training agreement, often including legal protections and benefits akin to full-time employees. Fractional employment involves part-time, contract-based roles with flexible hours and fewer entitlements, focusing on delivering specific expertise without full employee status. Explore in-depth comparisons of employment status implications in apprenticeship versus fractional employment models for clearer workforce planning.
Source and External Links
Apprenticeship - SEMCA Michigan Works! - Apprenticeship is an industry-driven, high-quality career pathway combining paid work experience, classroom instruction, and a nationally recognized credential, allowing employers to prepare their future workforce and individuals to gain skills and credentials through Registered Apprenticeships recognized by the U.S. Department of Labor.
Apprenticeship Services - GST Michigan Works! - Registered Apprenticeships offer paid on-the-job training with related technical classroom instruction across over 1,400 occupations, enabling apprentices to earn a salary, develop skills, gain nationally recognized credentials, and improve job security.
Earn and Learn Apprenticeships | Livonia, MI - Apprenticeships combine paid on-the-job training and formal education resulting in national credentials, providing alternative career pathways, a high retention employment rate post-completion, and opportunities in high-demand industries such as IT, manufacturing, healthcare, and engineering.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com