No code startups leverage user-friendly platforms to rapidly develop products with minimal technical expertise, reducing initial costs and increasing agility compared to traditional venture-backed startups that often require substantial funding and technical infrastructure. Venture-backed startups prioritize scalable growth and market dominance, supported by strategic investments and thorough validation processes. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of no code versus venture-backed startups to determine the best path for your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
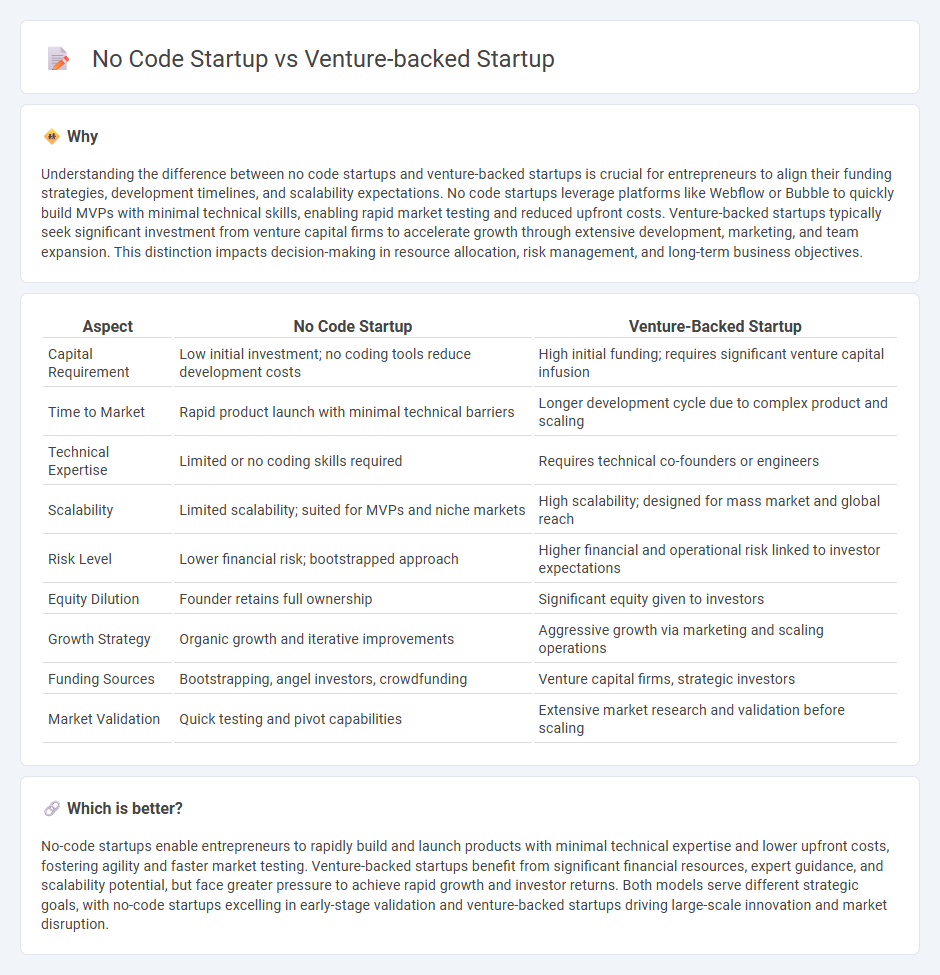
Understanding the difference between no code startups and venture-backed startups is crucial for entrepreneurs to align their funding strategies, development timelines, and scalability expectations. No code startups leverage platforms like Webflow or Bubble to quickly build MVPs with minimal technical skills, enabling rapid market testing and reduced upfront costs. Venture-backed startups typically seek significant investment from venture capital firms to accelerate growth through extensive development, marketing, and team expansion. This distinction impacts decision-making in resource allocation, risk management, and long-term business objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No Code Startup | Venture-Backed Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirement | Low initial investment; no coding tools reduce development costs | High initial funding; requires significant venture capital infusion |
| Time to Market | Rapid product launch with minimal technical barriers | Longer development cycle due to complex product and scaling |
| Technical Expertise | Limited or no coding skills required | Requires technical co-founders or engineers |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; suited for MVPs and niche markets | High scalability; designed for mass market and global reach |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk; bootstrapped approach | Higher financial and operational risk linked to investor expectations |
| Equity Dilution | Founder retains full ownership | Significant equity given to investors |
| Growth Strategy | Organic growth and iterative improvements | Aggressive growth via marketing and scaling operations |
| Funding Sources | Bootstrapping, angel investors, crowdfunding | Venture capital firms, strategic investors |
| Market Validation | Quick testing and pivot capabilities | Extensive market research and validation before scaling |
Which is better?
No-code startups enable entrepreneurs to rapidly build and launch products with minimal technical expertise and lower upfront costs, fostering agility and faster market testing. Venture-backed startups benefit from significant financial resources, expert guidance, and scalability potential, but face greater pressure to achieve rapid growth and investor returns. Both models serve different strategic goals, with no-code startups excelling in early-stage validation and venture-backed startups driving large-scale innovation and market disruption.
Connection
No code startups leverage user-friendly platforms to rapidly develop and test business ideas, attracting venture-backed funding by demonstrating scalable solutions with minimal initial capital. Venture-backed startups often invest in no code technologies to accelerate product development cycles and reduce operational risks, maximizing market entry speed. This synergy enables entrepreneurs to transform innovative concepts into viable, scalable businesses efficiently, drawing significant venture capital interest.
Key Terms
Venture Capital
Venture-backed startups leverage significant capital from venture capital firms to accelerate growth, scale operations rapidly, and compete in dynamic markets, often investing heavily in technology and talent acquisition. No code startups typically bootstrap their development, using no-code platforms to build and iterate products quickly with reduced upfront costs, attracting a different investor profile more focused on innovation and user experience. Explore how venture capital strategies vary between these startup models to optimize funding and growth outcomes.
Equity
Venture-backed startups often allocate significant equity to external investors during funding rounds, diluting founder ownership but providing crucial capital for rapid growth. No code startups typically maintain higher founder equity as they leverage low-cost development tools, reducing the need for extensive investment. Explore the strategic equity decisions that shape startup success and founder control.
Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping a venture-backed startup demands strategic resource management to maximize limited funds while pursuing rapid growth and investor milestones. In contrast, no-code startups leverage low-cost platforms and minimal technical debt to accelerate product development and reduce initial capital requirements. Explore effective bootstrapping techniques tailored for both startup types to optimize growth and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What Does It Mean to Be a VC-Backed Startup? - Montague Law - A venture-backed startup is a private company that has received venture capital funding which provides both capital and strategic mentorship, enabling the startup to grow, build a team, attract further financing, and potentially reach an IPO.
Venture Backed Startup: Definition and Examples (2022) - A venture backed startup is a startup company that uses venture capital funding to financially support its operations, helping it to grow and expand during its early stages when it often lacks sufficient liquid assets.
What Does VC-Backed Company Mean? - Forge Global - A VC-backed company is at least partly funded by venture capital firms, typically raising money in exchange for equity during growth stages to fuel hiring, marketing, and product development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com