Bootstrapped SaaS startups leverage minimal external funding to develop scalable software solutions with rapid deployment and low overhead costs, contrasting sharply with physical product startups that require significant capital for manufacturing, inventory, and distribution. SaaS ventures benefit from recurring revenue models and easier iteration cycles, while physical products pose challenges in supply chain management and upfront investment risks. Explore detailed insights to determine which startup model aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Bootstrapped SaaS and Physical Product Startups is crucial for tailoring business strategies, funding approaches, and resource allocation effectively. Bootstrapped SaaS startups often prioritize rapid scalability with minimal upfront capital due to lower manufacturing costs and digital distribution. Physical product startups require significant investment in inventory, supply chain management, and production facilities, impacting cash flow and growth timelines. Entrepreneurs can optimize operational decisions and risk management by distinguishing these business models.
Comparison Table
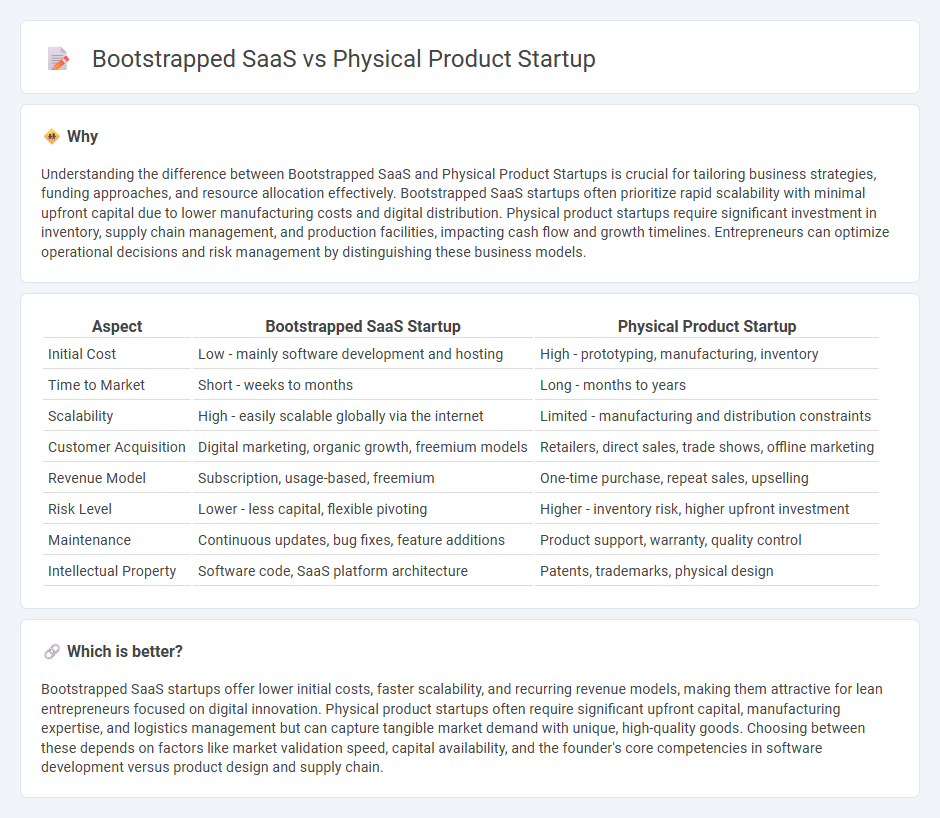
| Aspect | Bootstrapped SaaS Startup | Physical Product Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low - mainly software development and hosting | High - prototyping, manufacturing, inventory |
| Time to Market | Short - weeks to months | Long - months to years |
| Scalability | High - easily scalable globally via the internet | Limited - manufacturing and distribution constraints |
| Customer Acquisition | Digital marketing, organic growth, freemium models | Retailers, direct sales, trade shows, offline marketing |
| Revenue Model | Subscription, usage-based, freemium | One-time purchase, repeat sales, upselling |
| Risk Level | Lower - less capital, flexible pivoting | Higher - inventory risk, higher upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Continuous updates, bug fixes, feature additions | Product support, warranty, quality control |
| Intellectual Property | Software code, SaaS platform architecture | Patents, trademarks, physical design |
Which is better?
Bootstrapped SaaS startups offer lower initial costs, faster scalability, and recurring revenue models, making them attractive for lean entrepreneurs focused on digital innovation. Physical product startups often require significant upfront capital, manufacturing expertise, and logistics management but can capture tangible market demand with unique, high-quality goods. Choosing between these depends on factors like market validation speed, capital availability, and the founder's core competencies in software development versus product design and supply chain.
Connection
Bootstrapped SaaS and physical product startups share core entrepreneurial principles such as resourcefulness, lean operations, and customer-centric innovation, driving sustainable growth without external funding. Both models emphasize rapid iteration based on direct user feedback to enhance product-market fit and optimize cash flow management. Integrating SaaS solutions into physical product businesses can streamline operations, improve customer experience, and accelerate scalability through automation and data analytics.
Key Terms
**Physical Product Startup:**
Physical product startups require significant upfront investment in manufacturing, inventory, and supply chain logistics, making capital efficiency crucial for success. These startups must navigate challenges like product design, prototyping, quality control, and distribution channels to bring innovative hardware to market. Explore strategies to optimize production costs and scale your physical product startup effectively.
Supply Chain Management
Physical product startups require intricate supply chain management involving procurement, manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution logistics to ensure timely delivery and quality control. Bootstrapped SaaS companies optimize virtual infrastructure, cloud service integration, and agile software deployment pipelines while minimizing physical inventory and logistics costs. Explore deeper insights into how supply chain strategies influence operational efficiency and scalability across these business models.
Inventory
Physical product startups require meticulous inventory management to avoid overstocking and costly storage fees, often necessitating partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers for efficient supply chain control. Bootstrapped SaaS companies eliminate physical inventory concerns, allowing resources to be allocated toward product development and customer acquisition without the overhead of warehousing. Explore how inventory strategies impact startup scalability and financial planning in different business models.
Source and External Links
The start-up guide for developing a physical product - assemblean - This guide explains a 6-step product development process for physical product startups, covering ideation, planning, development, design, production, and market launch for structured implementation of product ideas.
Physical Product Development 101 | Gocious - Overview of the physical product development lifecycle including idea generation, design, prototyping, manufacturing, testing, and launch, emphasizing detailed planning and communication for success.
How to launch a physical product without investors | Enterprise Nation - Practical advice for launching a physical product without investors, focusing on building a simple, unique prototype that can be self-assembled or affordably produced to mitigate risk and costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com