Entrepreneurship in the alternative protein sector drives innovation to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable and health-conscious food options, contrasting with clean label foods that emphasize transparency and natural ingredients in product formulations. Startups in alt protein focus on plant-based, cultured, and fermentation-derived options, while clean label businesses prioritize minimal processing and avoidance of artificial additives. Explore the latest trends and entrepreneurial opportunities shaping these dynamic food markets.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between alternative proteins and clean label foods is crucial for entrepreneurs to target the right consumer demographics and meet specific market demands. Alternative proteins focus on sustainable, plant-based or lab-grown sources to reduce environmental impact and support food security. Clean label foods emphasize transparency, natural ingredients, and minimal processing to cater to health-conscious consumers. This knowledge enables strategic product development and marketing, enhancing competitive advantage in the evolving food industry.
Comparison Table
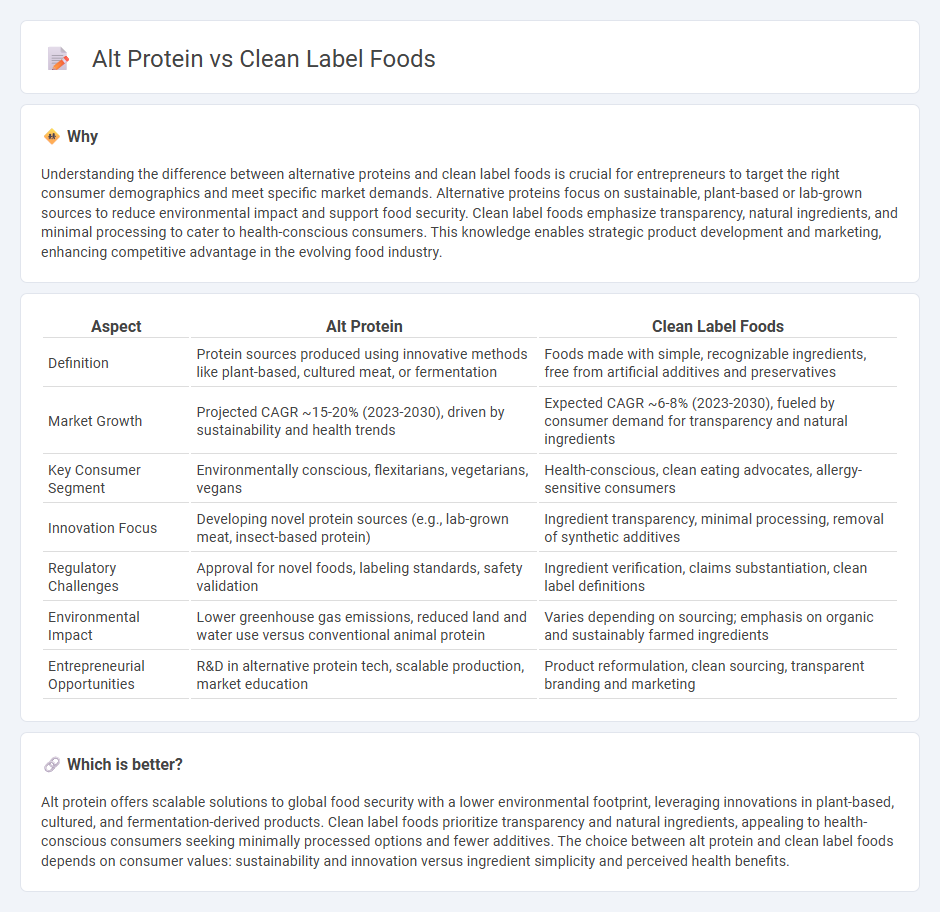
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Clean Label Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protein sources produced using innovative methods like plant-based, cultured meat, or fermentation | Foods made with simple, recognizable ingredients, free from artificial additives and preservatives |
| Market Growth | Projected CAGR ~15-20% (2023-2030), driven by sustainability and health trends | Expected CAGR ~6-8% (2023-2030), fueled by consumer demand for transparency and natural ingredients |
| Key Consumer Segment | Environmentally conscious, flexitarians, vegetarians, vegans | Health-conscious, clean eating advocates, allergy-sensitive consumers |
| Innovation Focus | Developing novel protein sources (e.g., lab-grown meat, insect-based protein) | Ingredient transparency, minimal processing, removal of synthetic additives |
| Regulatory Challenges | Approval for novel foods, labeling standards, safety validation | Ingredient verification, claims substantiation, clean label definitions |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced land and water use versus conventional animal protein | Varies depending on sourcing; emphasis on organic and sustainably farmed ingredients |
| Entrepreneurial Opportunities | R&D in alternative protein tech, scalable production, market education | Product reformulation, clean sourcing, transparent branding and marketing |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers scalable solutions to global food security with a lower environmental footprint, leveraging innovations in plant-based, cultured, and fermentation-derived products. Clean label foods prioritize transparency and natural ingredients, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking minimally processed options and fewer additives. The choice between alt protein and clean label foods depends on consumer values: sustainability and innovation versus ingredient simplicity and perceived health benefits.
Connection
Alt protein and clean label foods intersect through consumer demand for transparent, sustainable, and health-focused products. Entrepreneurs in the alt protein sector innovate by using natural, minimally processed ingredients to create clean label alternatives that appeal to health-conscious and environmentally aware markets. This synergy drives growth in both industries by aligning product development with evolving consumer values on nutrition and sustainability.
Key Terms
Ingredient Transparency
Clean label foods emphasize ingredient transparency by listing simple, recognizable components to build consumer trust and meet demand for natural products. Alternative protein companies face challenges balancing transparent ingredient disclosure with proprietary blends and novel ingredients. Explore how ingredient transparency shapes consumer preferences in clean label and alternative protein markets.
Plant-Based Innovation
Clean label foods emphasize minimally processed ingredients with no artificial additives, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking transparency in plant-based innovation. Alternative proteins, sourced from plants, microbes, or fermentation, drive sustainable advancements by replicating animal protein textures and flavors with clean, natural inputs. Explore the future of food by diving deeper into the synergy between clean label trends and alternative protein developments.
Consumer Trust
Clean label foods emphasize transparency and minimal processing, fostering higher consumer trust through recognizable ingredients and clear labeling. Alternative proteins face skepticism due to novel production methods and ingredient unfamiliarity, challenging consumer acceptance despite sustainability advantages. Explore deeper insights on how trust shapes the future of clean label and alternative protein markets.
Source and External Links
Clean label - Wikipedia - A clean label is a food label that avoids listing ingredients perceived as undesirable, such as artificial additives, preservatives, and food colorings, aiming to present a natural and healthy image though it does not guarantee the product is free of additives as some may be hidden in natural ingredients.
Clean labels | Center for Science in the Public Interest - CSPI - Clean label foods should be free of unsafe additives and avoid vague or misleading labeling, emphasizing transparency and safety based on scientific evidence to prevent health risks from hidden or substituted harmful ingredients.
Clean Labeling and the Real Food Movement - Clean labeling is a consumer-driven food industry movement promoting simple, natural, minimally processed products with easy-to-understand labels listing natural ingredients and minimal artificial additives, without a formal regulatory definition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com