Alternative protein sources, including plant-based and cultured meats, are transforming the entrepreneurship landscape by addressing sustainability and food security challenges. Startups in this sector leverage innovations in biotechnology and food science to create scalable, nutritious, and eco-friendly products that appeal to health-conscious consumers. Explore more about how entrepreneurs are reshaping the future of protein consumption through cutting-edge alternatives.
Why it is important
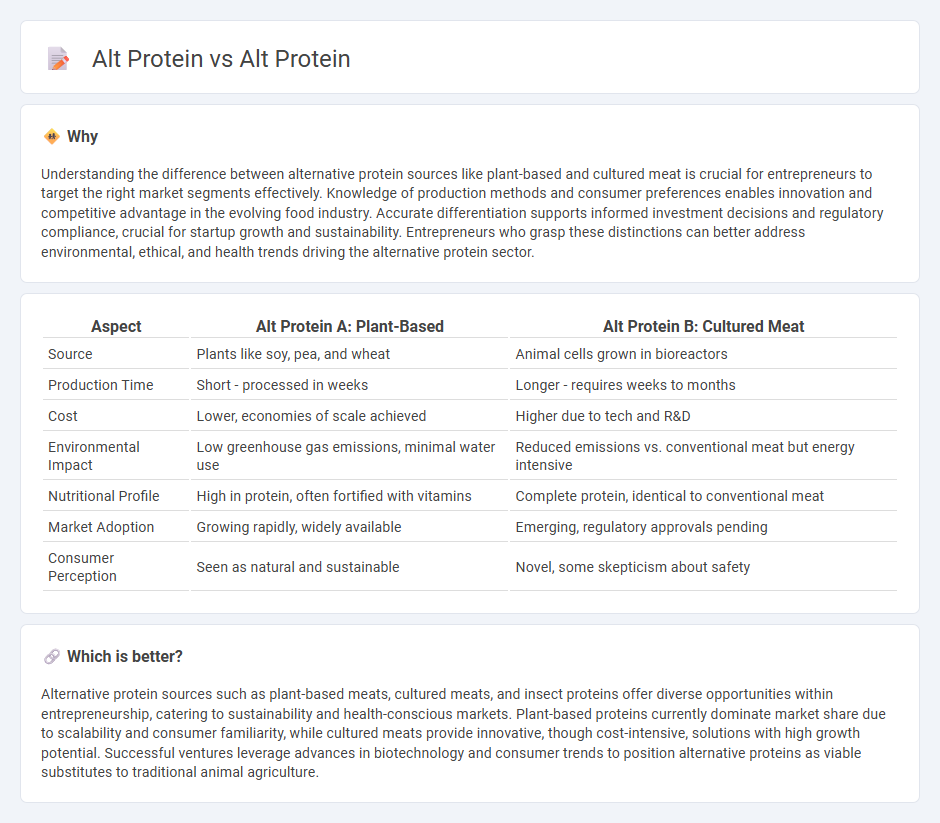
Understanding the difference between alternative protein sources like plant-based and cultured meat is crucial for entrepreneurs to target the right market segments effectively. Knowledge of production methods and consumer preferences enables innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving food industry. Accurate differentiation supports informed investment decisions and regulatory compliance, crucial for startup growth and sustainability. Entrepreneurs who grasp these distinctions can better address environmental, ethical, and health trends driving the alternative protein sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alt Protein A: Plant-Based | Alt Protein B: Cultured Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plants like soy, pea, and wheat | Animal cells grown in bioreactors |
| Production Time | Short - processed in weeks | Longer - requires weeks to months |
| Cost | Lower, economies of scale achieved | Higher due to tech and R&D |
| Environmental Impact | Low greenhouse gas emissions, minimal water use | Reduced emissions vs. conventional meat but energy intensive |
| Nutritional Profile | High in protein, often fortified with vitamins | Complete protein, identical to conventional meat |
| Market Adoption | Growing rapidly, widely available | Emerging, regulatory approvals pending |
| Consumer Perception | Seen as natural and sustainable | Novel, some skepticism about safety |
Which is better?
Alternative protein sources such as plant-based meats, cultured meats, and insect proteins offer diverse opportunities within entrepreneurship, catering to sustainability and health-conscious markets. Plant-based proteins currently dominate market share due to scalability and consumer familiarity, while cultured meats provide innovative, though cost-intensive, solutions with high growth potential. Successful ventures leverage advances in biotechnology and consumer trends to position alternative proteins as viable substitutes to traditional animal agriculture.
Connection
Alternative protein sources, including plant-based and cultured proteins, revolutionize entrepreneurship by creating innovative markets that address sustainability and food security challenges. Startups in the alt protein sector attract significant venture capital investment, driving rapid technological advancements and scalability. Entrepreneurs leverage cutting-edge biotechnology and consumer trends toward health and environmental consciousness to disrupt traditional meat industries.
Key Terms
Value Proposition
Alternative proteins offer sustainable nutrition by utilizing plant-based, cultured, or fermentation-derived sources that reduce environmental impact compared to traditional animal agriculture. These products prioritize health benefits, ethical considerations, and cost-effectiveness, appealing to eco-conscious and health-savvy consumers. Explore more about how alternative proteins redefine food value propositions and drive market innovation.
Market Differentiation
Alternative protein encompasses a broad spectrum of products including plant-based, cultured, and fermentation-derived proteins, whereas alt protein as a market category highlights innovation in sustainable production and consumer health benefits. Market differentiation hinges on product texture, nutritional profile, price competitiveness, and environmental impact, with companies leveraging unique sourcing methods and proprietary technologies to stand out. Explore the evolving landscape of alternative proteins to understand how brands are capturing diverse consumer demands and shaping the future of food.
Intellectual Property
Alternative protein companies increasingly prioritize intellectual property (IP) to safeguard innovations in plant-based, cell-cultured, and fermentation-derived products. Patents related to novel protein extraction methods, genetic modification techniques, and proprietary fermentation strains are key assets driving competitive advantage and investment attraction. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how IP strategies shape the future of alternative protein markets.
Source and External Links
The Alt Protein Project | GFI - The Alt Protein Project is a global student movement that focuses on advancing alternative protein education, research, and innovation at universities to support sustainable and just food systems with plant-based, cultivated, and fermentation-derived proteins.
Defining alternative proteins | GFI - Alternative proteins are meat, eggs, or dairy products made from plants, animal cells, or fermentation designed to taste the same or better than conventionally produced animal products but with lower environmental impact and resource use.
The Alt Protein Project | Duke University - This student-led program engages students with the alternative protein industry through multidisciplinary coursework, industry collaborations, experiential learning projects, and networking to prepare them for careers in modernizing meat and animal product alternatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com