Rage applying occurs when job seekers impulsively submit multiple applications out of frustration, often lacking tailored resumes or focused career goals, which can diminish their chances of securing interviews. Counteroffers arise when current employers respond to resignations with improved compensation or benefits to retain valuable employees, affecting turnover rates and employee satisfaction. Explore key strategies to balance rage applying and effectively negotiate counteroffers in your employment journey.
Why it is important
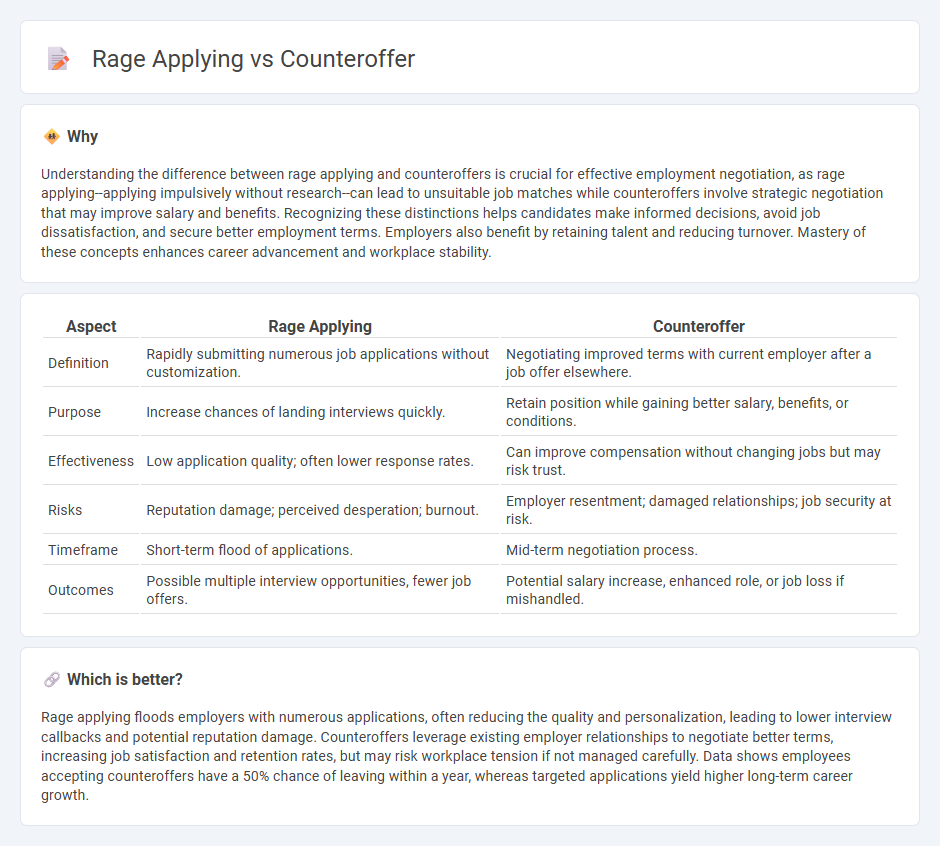
Understanding the difference between rage applying and counteroffers is crucial for effective employment negotiation, as rage applying--applying impulsively without research--can lead to unsuitable job matches while counteroffers involve strategic negotiation that may improve salary and benefits. Recognizing these distinctions helps candidates make informed decisions, avoid job dissatisfaction, and secure better employment terms. Employers also benefit by retaining talent and reducing turnover. Mastery of these concepts enhances career advancement and workplace stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Rage Applying | Counteroffer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapidly submitting numerous job applications without customization. | Negotiating improved terms with current employer after a job offer elsewhere. |
| Purpose | Increase chances of landing interviews quickly. | Retain position while gaining better salary, benefits, or conditions. |
| Effectiveness | Low application quality; often lower response rates. | Can improve compensation without changing jobs but may risk trust. |
| Risks | Reputation damage; perceived desperation; burnout. | Employer resentment; damaged relationships; job security at risk. |
| Timeframe | Short-term flood of applications. | Mid-term negotiation process. |
| Outcomes | Possible multiple interview opportunities, fewer job offers. | Potential salary increase, enhanced role, or job loss if mishandled. |
Which is better?
Rage applying floods employers with numerous applications, often reducing the quality and personalization, leading to lower interview callbacks and potential reputation damage. Counteroffers leverage existing employer relationships to negotiate better terms, increasing job satisfaction and retention rates, but may risk workplace tension if not managed carefully. Data shows employees accepting counteroffers have a 50% chance of leaving within a year, whereas targeted applications yield higher long-term career growth.
Connection
Rage applying often occurs when employees actively seek new job opportunities due to dissatisfaction at their current workplace, prompting employers to respond with counteroffers to retain valuable talent. Counteroffers serve as strategic retention tools, aiming to address employee grievances related to salary, benefits, or work environment revealed during the rage applying phase. Understanding this dynamic enhances recruitment strategies and retention policies within human resource management.
Key Terms
Offer Negotiation
Counteroffer involves actively negotiating terms after receiving an initial job offer, aiming to improve salary, benefits, or other employment conditions. Rage applying, in contrast, refers to impulsively submitting multiple job applications without strategic focus or negotiation intent, often driven by frustration or urgency. Discover how mastering offer negotiation through effective counteroffers can enhance your career opportunities and compensation packages.
Employee Satisfaction
Counteroffers often boost employee satisfaction by addressing compensation concerns and reaffirming an employer's commitment, leading to increased retention and motivation. Rage applying, driven by dissatisfaction or frustration, signals deeper workplace issues that can negatively impact morale and productivity if unaddressed. Explore strategies to enhance employee satisfaction and reduce turnover by understanding these dynamics.
Retention
Counteroffers play a crucial role in employee retention by directly addressing salary dissatisfaction and reinforcing commitment to valued talent. Rage applying, where employees aggressively pursue new jobs out of frustration, often signals low morale and potential turnover risks for employers. Discover effective retention strategies to minimize rage applying and leverage counteroffers for maintaining a stable workforce.
Source and External Links
counteroffer | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A counteroffer is a rejection of the original offer combined with a new offer that materially changes the terms, voiding the original offer and starting new contract terms.
How To Counteroffer Your Salary After Receiving a Job Offer - Indeed - A counteroffer in employment means negotiating for better salary or terms after receiving a job offer by proposing changes supported by reasoning.
COUNTEROFFER definition in American English - Collins Dictionary - A counteroffer is an offer made in response to an unsatisfactory offer, commonly used in business or real estate negotiations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com