Employment models have evolved to include digital nomadism, allowing workers to perform jobs remotely while traveling globally, and telecommuting, which involves working from a fixed remote location such as home. Digital nomads prioritize flexibility and location independence, leveraging cloud technology and coworking spaces, whereas telecommuters focus on stability and routine, often relying on consistent internet access and communication platforms. Explore the key differences and benefits of these employment trends to optimize your remote work strategy.
Why it is important
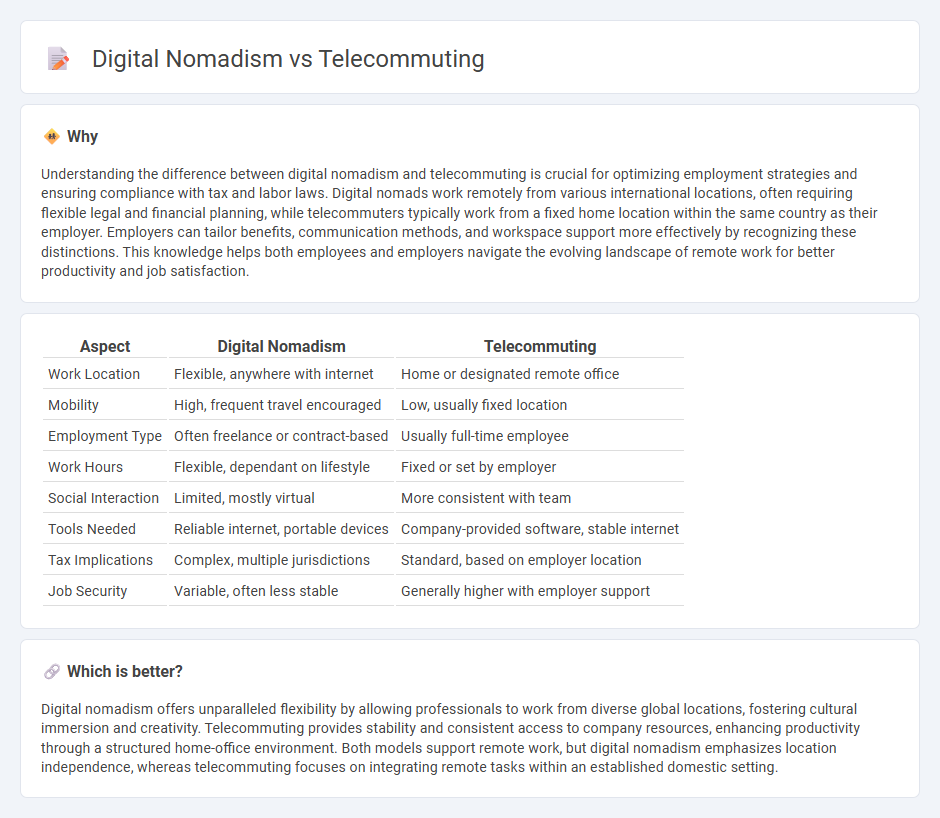
Understanding the difference between digital nomadism and telecommuting is crucial for optimizing employment strategies and ensuring compliance with tax and labor laws. Digital nomads work remotely from various international locations, often requiring flexible legal and financial planning, while telecommuters typically work from a fixed home location within the same country as their employer. Employers can tailor benefits, communication methods, and workspace support more effectively by recognizing these distinctions. This knowledge helps both employees and employers navigate the evolving landscape of remote work for better productivity and job satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Nomadism | Telecommuting |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Flexible, anywhere with internet | Home or designated remote office |
| Mobility | High, frequent travel encouraged | Low, usually fixed location |
| Employment Type | Often freelance or contract-based | Usually full-time employee |
| Work Hours | Flexible, dependant on lifestyle | Fixed or set by employer |
| Social Interaction | Limited, mostly virtual | More consistent with team |
| Tools Needed | Reliable internet, portable devices | Company-provided software, stable internet |
| Tax Implications | Complex, multiple jurisdictions | Standard, based on employer location |
| Job Security | Variable, often less stable | Generally higher with employer support |
Which is better?
Digital nomadism offers unparalleled flexibility by allowing professionals to work from diverse global locations, fostering cultural immersion and creativity. Telecommuting provides stability and consistent access to company resources, enhancing productivity through a structured home-office environment. Both models support remote work, but digital nomadism emphasizes location independence, whereas telecommuting focuses on integrating remote tasks within an established domestic setting.
Connection
Digital nomadism and telecommuting are interconnected through their reliance on remote work technologies, allowing employees to perform job duties from any location with internet access. This shift towards location-independent employment models enhances flexibility, reduces the need for physical office spaces, and supports a global workforce. The rise of cloud computing, collaboration tools, and high-speed internet has been instrumental in enabling both digital nomads and telecommuters to maintain productivity without geographical constraints.
Key Terms
Remote Work
Remote work encompasses telecommuting and digital nomadism, both enabling employees to work outside traditional office settings but differing in lifestyle flexibility and mobility. Telecommuting typically involves working from a fixed home location with consistent hours, while digital nomadism combines remote work with travel, allowing professionals to change locations frequently. Explore the advantages and challenges of each remote work style to find the best fit for your career goals.
Location Independence
Telecommuting allows employees to work remotely while maintaining ties to a specific employer, typically from a home office or fixed location, emphasizing flexibility within a structured environment. Digital nomadism extends location independence by enabling professionals to work from various global destinations, leveraging technology to sustain productivity without geographical constraints. Explore how these lifestyles transform work-life balance and productivity in the modern economy.
Work-Life Balance
Telecommuting allows employees to work from home or any fixed location, providing a structured environment that often enhances productivity and maintains traditional work-life boundaries. Digital nomadism embraces location independence, enabling individuals to travel frequently while working, which can blur the lines between personal life and work but offers unparalleled lifestyle flexibility. Explore key strategies to optimize work-life balance for both telecommuters and digital nomads.
Source and External Links
What Is Telecommuting in Today's Work Environment? - Telecommuting is the practice of employees working remotely by connecting to their company's network via their own or company-provided devices and the internet, a trend accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and now widely adopted in many sectors.
What is telecommuting? | Definition from TechTarget - Telecommuting allows employees to work from outside the traditional office using telecommunications tools, with variations including full-time, part-time (hybrid), temporary, and freelance telecommuting depending on the worker's arrangement.
What is telecommuting? - Telecommuting means working from a location outside the traditional office, commonly from home, using digital technology to communicate and collaborate with colleagues without commuting to a central workplace.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com