Job ghosting occurs when employees abruptly stop responding to communication or fail to show up for work without notice, disrupting workforce planning and productivity. Quiet quitting involves employees fulfilling their job duties but disengaging emotionally and limiting effort beyond the minimum requirements, impacting overall organizational performance. Explore in-depth insights on these employment trends and their implications for modern workplaces.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between job ghosting and quiet quitting is crucial for employers to address employee engagement effectively and reduce turnover rates. Job ghosting involves employees abruptly leaving without notice, disrupting workflow, while quiet quitting refers to employees disengaging and doing minimum required work without formally resigning. Recognizing these behaviors helps organizations implement targeted retention strategies and improve workplace communication. Clear distinctions between these terms enable HR professionals to develop proactive interventions that enhance job satisfaction and productivity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Job Ghosting | Quiet Quitting |
|---|---|---|
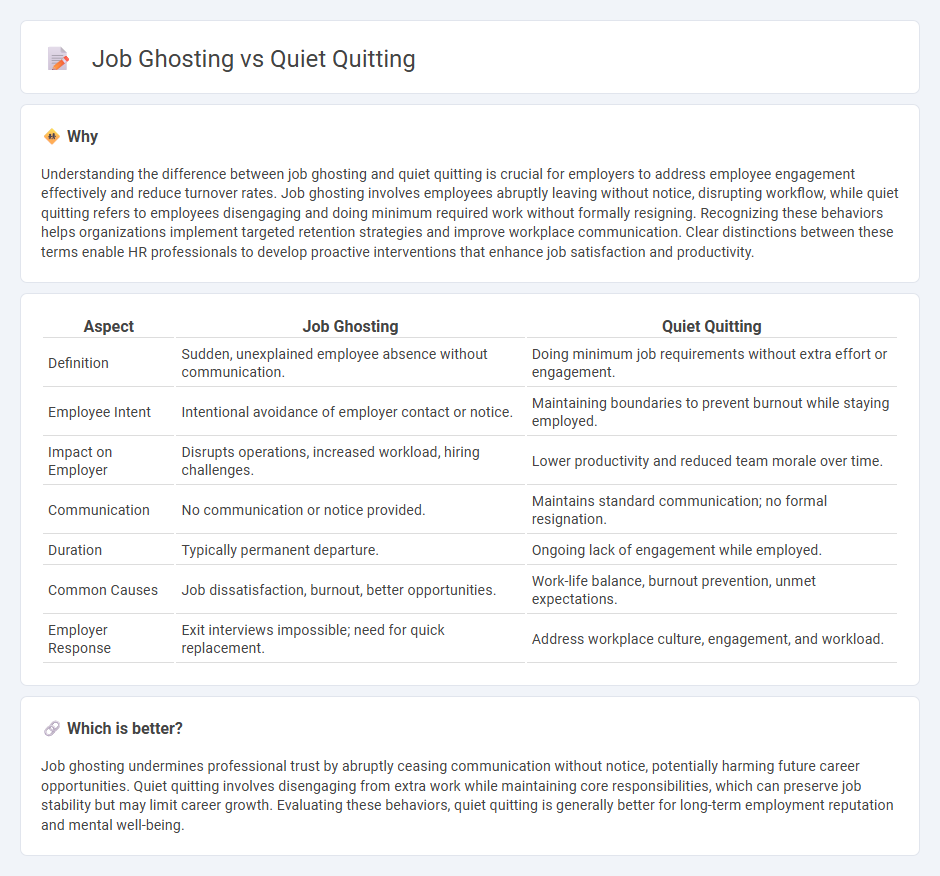
| Definition | Sudden, unexplained employee absence without communication. | Doing minimum job requirements without extra effort or engagement. |
| Employee Intent | Intentional avoidance of employer contact or notice. | Maintaining boundaries to prevent burnout while staying employed. |
| Impact on Employer | Disrupts operations, increased workload, hiring challenges. | Lower productivity and reduced team morale over time. |
| Communication | No communication or notice provided. | Maintains standard communication; no formal resignation. |
| Duration | Typically permanent departure. | Ongoing lack of engagement while employed. |
| Common Causes | Job dissatisfaction, burnout, better opportunities. | Work-life balance, burnout prevention, unmet expectations. |
| Employer Response | Exit interviews impossible; need for quick replacement. | Address workplace culture, engagement, and workload. |
Which is better?
Job ghosting undermines professional trust by abruptly ceasing communication without notice, potentially harming future career opportunities. Quiet quitting involves disengaging from extra work while maintaining core responsibilities, which can preserve job stability but may limit career growth. Evaluating these behaviors, quiet quitting is generally better for long-term employment reputation and mental well-being.
Connection
Job ghosting and quiet quitting both reflect disengagement in the workplace, where employees withdraw either by abruptly cutting off communication or by reducing effort and commitment. These behaviors signify deeper issues such as dissatisfaction, burnout, or lack of recognition, which can undermine productivity and morale. Addressing the root causes through transparent communication and supportive management improves retention and fosters a healthier work environment.
Key Terms
Employee engagement
Quiet quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum at work, driven by disengagement and lack of motivation, while job ghosting refers to employees abruptly disappearing without notice, reflecting deep dissatisfaction or distrust. Both behaviors signal significant challenges in employee engagement, resulting in reduced productivity and morale. Explore strategies to enhance engagement and prevent these issues for a healthier workplace culture.
Workplace communication
Quiet quitting occurs when employees reduce their effort and engagement without formally resigning, signaling disengagement through subdued communication and minimal interaction. Job ghosting involves employees abruptly cutting off all communication, leaving employers without notice and creating significant challenges in workforce planning and trust. Explore detailed strategies to manage and mitigate these communication breakdowns in the workplace.
Turnover
Quiet quitting refers to employees doing the bare minimum at work without formally resigning, which can lead to reduced productivity and increased turnover rates within organizations. Job ghosting occurs when employees abruptly stop responding to employers during hiring or after resignation, causing disruption in staffing and higher turnover management costs. Explore more insights on managing turnover challenges linked to quiet quitting and job ghosting.
Source and External Links
Quiet quitting explained: Everything you need to know - TechTarget - Quiet quitting means employees do only tasks strictly within their job description to avoid overtime, setting boundaries to improve work-life balance, often as a response to burnout or job dissatisfaction.
What Is Quiet Quitting and Can It Be Prevented? - Paychex - Quiet quitting involves employee disengagement manifesting as reduced work output, avoidance of extra tasks, and gradual withdrawal before leaving their roles, distinct from quiet firing by employers encouraging resignation.
Quiet Quitting: A Proper Guide to a Very Real Trend - Personio - Originating from TikTok in 2022, quiet quitting is employees meeting but not exceeding job duties by avoiding overtime, extra projects, or volunteering, which HR can address by fostering valued work culture and clear expectations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com