Employment trends increasingly favor digital nomadism and outsourcing as flexible work models that boost global productivity and talent acquisition. Digital nomads leverage technology to work remotely across international locations, while outsourcing enables companies to delegate tasks to specialized external teams, optimizing costs and efficiency. Discover more about how these dynamic employment strategies are reshaping the future of work.
Why it is important
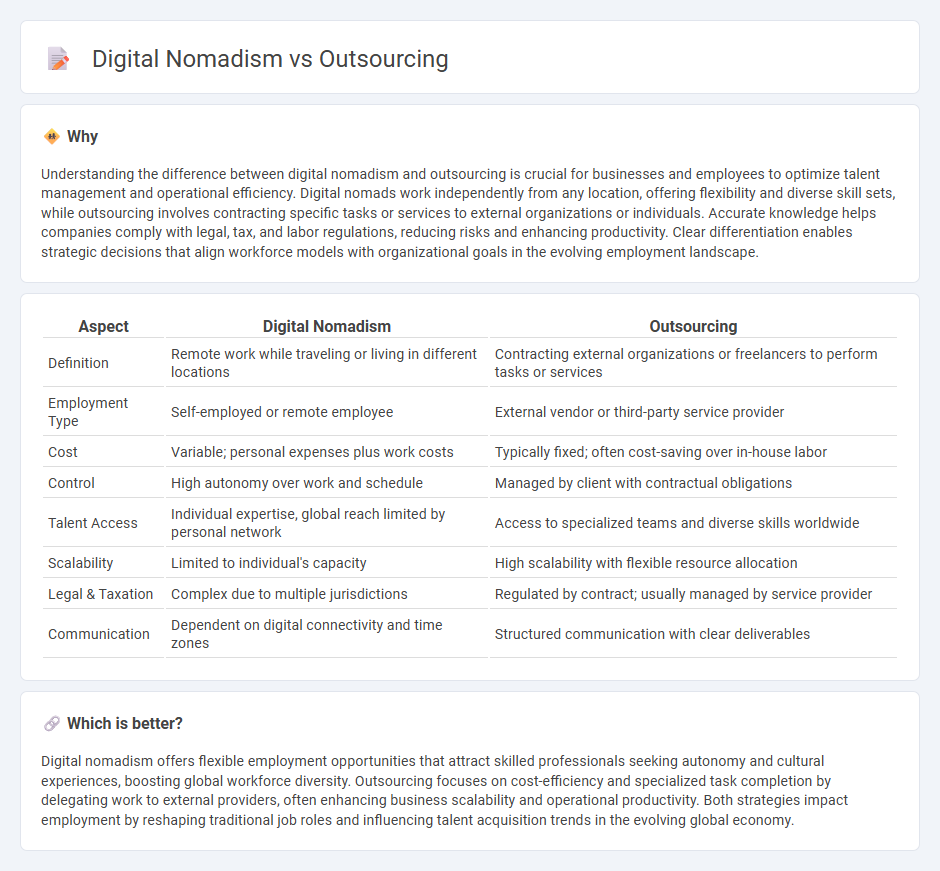
Understanding the difference between digital nomadism and outsourcing is crucial for businesses and employees to optimize talent management and operational efficiency. Digital nomads work independently from any location, offering flexibility and diverse skill sets, while outsourcing involves contracting specific tasks or services to external organizations or individuals. Accurate knowledge helps companies comply with legal, tax, and labor regulations, reducing risks and enhancing productivity. Clear differentiation enables strategic decisions that align workforce models with organizational goals in the evolving employment landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Nomadism | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote work while traveling or living in different locations | Contracting external organizations or freelancers to perform tasks or services |
| Employment Type | Self-employed or remote employee | External vendor or third-party service provider |
| Cost | Variable; personal expenses plus work costs | Typically fixed; often cost-saving over in-house labor |
| Control | High autonomy over work and schedule | Managed by client with contractual obligations |
| Talent Access | Individual expertise, global reach limited by personal network | Access to specialized teams and diverse skills worldwide |
| Scalability | Limited to individual's capacity | High scalability with flexible resource allocation |
| Legal & Taxation | Complex due to multiple jurisdictions | Regulated by contract; usually managed by service provider |
| Communication | Dependent on digital connectivity and time zones | Structured communication with clear deliverables |
Which is better?
Digital nomadism offers flexible employment opportunities that attract skilled professionals seeking autonomy and cultural experiences, boosting global workforce diversity. Outsourcing focuses on cost-efficiency and specialized task completion by delegating work to external providers, often enhancing business scalability and operational productivity. Both strategies impact employment by reshaping traditional job roles and influencing talent acquisition trends in the evolving global economy.
Connection
Digital nomadism and outsourcing are connected through the rise of remote work technologies that enable professionals to perform tasks from anywhere, facilitating global talent acquisition. Companies leverage outsourcing platforms to hire skilled digital nomads, reducing operational costs while accessing diverse expertise. This synergy enhances workforce flexibility and drives economic globalization by breaking geographical barriers.
Key Terms
Remote Work
Outsourcing leverages external teams or freelancers to optimize project execution and reduce operational costs, often enhancing scalability and access to specialized skills. Digital nomadism emphasizes the flexibility of remote work, allowing individuals to operate from various locations while maintaining productivity through digital tools and communication platforms. Explore deeper insights into how these remote work models transform business dynamics and employee lifestyle choices.
Flexibility
Outsourcing offers businesses flexibility by allowing tasks to be delegated to specialized professionals across different time zones, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Digital nomadism provides individuals unparalleled personal and professional flexibility, enabling work from any location served by reliable internet, fostering a dynamic lifestyle. Explore the unique advantages of each approach to understand which flexibility model best suits your needs.
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing significantly reduces operational costs by leveraging lower labor expenses in global markets, while digital nomadism optimizes personal expenses through location-independent work, often in affordable regions. Companies benefit from outsourcing to cut overhead and focus on core competencies, whereas digital nomads prioritize cost efficiency by choosing low-cost living destinations and remote job opportunities. Explore the advantages and cost dynamics of both models to determine the best strategy for your financial goals.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing is the practice where companies hire external contractors or companies to perform tasks or create goods to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency, including types like onshore, offshore, and nearshore outsourcing.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves contracting a third-party provider to perform tasks or services either onsite or remotely, often focusing on IT, customer service, manufacturing, or financial functions, and emphasizing the importance of managing the business relationship.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing allows businesses to lower costs, access specialized skills, and focus on core activities by contracting external providers for tasks like IT, accounting, and customer service, while also requiring good communication to ensure quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com