Fractional hiring offers companies the flexibility to onboard specialized talent on a part-time or project basis, optimizing costs and expertise without long-term commitments. Internships provide valuable learning opportunities for students or recent graduates to gain hands-on experience while supporting basic operational tasks. Explore the distinct advantages of fractional hiring and internships to determine the best fit for your workforce strategy.
Why it is important
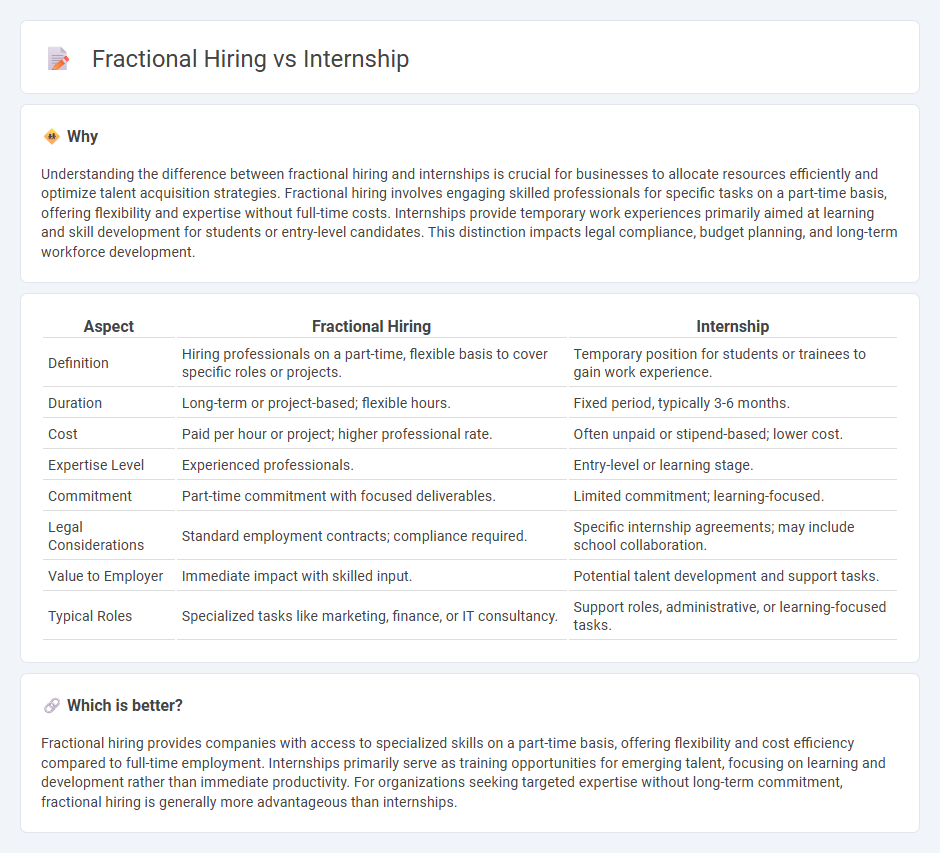
Understanding the difference between fractional hiring and internships is crucial for businesses to allocate resources efficiently and optimize talent acquisition strategies. Fractional hiring involves engaging skilled professionals for specific tasks on a part-time basis, offering flexibility and expertise without full-time costs. Internships provide temporary work experiences primarily aimed at learning and skill development for students or entry-level candidates. This distinction impacts legal compliance, budget planning, and long-term workforce development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Hiring | Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring professionals on a part-time, flexible basis to cover specific roles or projects. | Temporary position for students or trainees to gain work experience. |
| Duration | Long-term or project-based; flexible hours. | Fixed period, typically 3-6 months. |
| Cost | Paid per hour or project; higher professional rate. | Often unpaid or stipend-based; lower cost. |
| Expertise Level | Experienced professionals. | Entry-level or learning stage. |
| Commitment | Part-time commitment with focused deliverables. | Limited commitment; learning-focused. |
| Legal Considerations | Standard employment contracts; compliance required. | Specific internship agreements; may include school collaboration. |
| Value to Employer | Immediate impact with skilled input. | Potential talent development and support tasks. |
| Typical Roles | Specialized tasks like marketing, finance, or IT consultancy. | Support roles, administrative, or learning-focused tasks. |
Which is better?
Fractional hiring provides companies with access to specialized skills on a part-time basis, offering flexibility and cost efficiency compared to full-time employment. Internships primarily serve as training opportunities for emerging talent, focusing on learning and development rather than immediate productivity. For organizations seeking targeted expertise without long-term commitment, fractional hiring is generally more advantageous than internships.
Connection
Fractional hiring enables companies to engage skilled professionals on a part-time basis, providing flexible workforce solutions that complement internship programs by offering real-world experience alongside structured learning. Internships serve as a talent pipeline, allowing employers to evaluate potential fractional hires while interns gain industry-relevant skills and exposure to fractional work models. This synergy enhances workforce agility, reduces hiring risks, and accelerates professional development in dynamic employment landscapes.
Key Terms
Duration
Internships typically span from a few weeks to several months, offering temporary, project-based engagement primarily for learning and skill development. Fractional hiring involves part-time commitment over an extended period, where professionals contribute specialized expertise without full-time employment. Discover how choosing between internship and fractional hiring can align with your business duration needs.
Work Commitment
Internships typically involve a fixed short-term commitment where interns gain hands-on experience by working set hours over several weeks or months, often part-time or full-time. Fractional hiring entails engaging professionals who commit to a specific portion of their working time, usually on an ongoing basis, providing specialized skills without the need for full-time employment. Explore further to understand how work commitment influences the choice between internships and fractional hiring for your business needs.
Compensation
Internship compensation often includes stipends or academic credit with limited financial benefits, designed primarily for skill development and experience. Fractional hiring offers proportional salary based on hours worked, providing cost-effective access to specialized talent without full-time employment costs. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your hiring strategy effectively.
Source and External Links
Internship - Wikipedia - An internship is a limited period of work experience offered by organizations across various sectors for students or graduates to gain relevant skills and build professional networks, often serving as a pathway to full-time employment.
Internship Meaning and Definition: A NACE Guide - Internships integrate classroom knowledge with practical experience, helping students develop skills, explore careers, and connect professionally while serving as a key recruiting tool for employers to hire and retain talent.
Internships for students - Amazon.jobs - Amazon offers internships to rising seniors and recent graduates, providing impactful projects, mentorship, skill-building, and networking opportunities that contribute to career growth in various fields.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com