Fractional executives provide specialized leadership on a part-time basis, offering companies strategic expertise without the commitment of a full-time hire. Gig workers, on the other hand, perform short-term tasks or projects, often through digital platforms, delivering flexibility without long-term employment obligations. Explore the distinct benefits and challenges of each to determine the best fit for your organization's workforce needs.
Why it is important
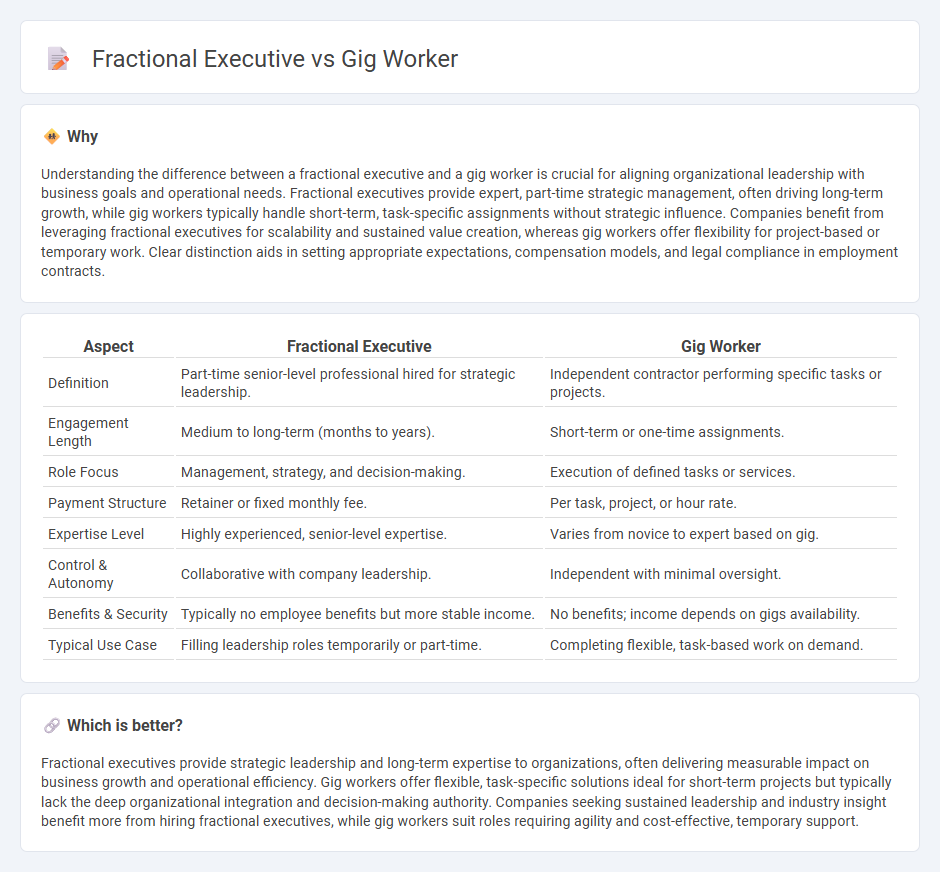
Understanding the difference between a fractional executive and a gig worker is crucial for aligning organizational leadership with business goals and operational needs. Fractional executives provide expert, part-time strategic management, often driving long-term growth, while gig workers typically handle short-term, task-specific assignments without strategic influence. Companies benefit from leveraging fractional executives for scalability and sustained value creation, whereas gig workers offer flexibility for project-based or temporary work. Clear distinction aids in setting appropriate expectations, compensation models, and legal compliance in employment contracts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Executive | Gig Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time senior-level professional hired for strategic leadership. | Independent contractor performing specific tasks or projects. |
| Engagement Length | Medium to long-term (months to years). | Short-term or one-time assignments. |
| Role Focus | Management, strategy, and decision-making. | Execution of defined tasks or services. |
| Payment Structure | Retainer or fixed monthly fee. | Per task, project, or hour rate. |
| Expertise Level | Highly experienced, senior-level expertise. | Varies from novice to expert based on gig. |
| Control & Autonomy | Collaborative with company leadership. | Independent with minimal oversight. |
| Benefits & Security | Typically no employee benefits but more stable income. | No benefits; income depends on gigs availability. |
| Typical Use Case | Filling leadership roles temporarily or part-time. | Completing flexible, task-based work on demand. |
Which is better?
Fractional executives provide strategic leadership and long-term expertise to organizations, often delivering measurable impact on business growth and operational efficiency. Gig workers offer flexible, task-specific solutions ideal for short-term projects but typically lack the deep organizational integration and decision-making authority. Companies seeking sustained leadership and industry insight benefit more from hiring fractional executives, while gig workers suit roles requiring agility and cost-effective, temporary support.
Connection
Fractional executives and gig workers share a flexible employment model that allows organizations to access specialized skills on a project or part-time basis without long-term commitments. This trend supports businesses in managing costs while benefiting from expert leadership or expertise tailored to specific initiatives. The rise of the gig economy has significantly contributed to the growth of fractional executive roles by emphasizing agility and adaptive workforce strategies.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Gig workers offer unparalleled flexibility by taking on short-term projects or tasks, enabling businesses to scale their workforce quickly without long-term commitments. Fractional executives provide strategic leadership on a part-time basis, balancing expert guidance with adaptable time commitment tailored to company needs. Explore how these flexible workforce options can optimize your business performance and agility.
Compensation structure
Gig workers typically receive payment per task or project, often lacking benefits and long-term incentives, while fractional executives engage on part-time retainer contracts with fixed monthly fees and potential performance bonuses. Gig worker compensation is variable and transactional, whereas fractional executive remuneration aligns with strategic contributions to company growth, providing more predictable income. Explore the nuances of compensation structures to determine which model fits your business or career goals best.
Scope of responsibility
Gig workers typically handle specific, short-term tasks with limited scope and accountability, often focused on execution rather than strategy. Fractional executives assume broader responsibilities, overseeing strategic decision-making, managing teams, and driving company growth on a part-time basis. Explore further to understand how these distinct roles align with your organizational needs.
Source and External Links
What is a gig worker vs. independent contractor? Employer Guide - Gig workers are independent contractors performing short-term, flexible jobs for various clients or platforms, including freelancers, rideshare drivers, and self-employed individuals who pick their projects, hours, and work location freely.
What Is a Gig Worker? Meaning and How To Find Gig Work - Upwork - Gig workers take on short-term or project-based jobs for multiple clients rather than being employed by a single company, with many finding gigs through online platforms in the gig economy.
Gig worker - Wikipedia - Gig workers are independent contractors or on-demand workers who enter formal agreements with companies for services; legal classification varies globally, with debates around employee benefits and rights.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com