Consulting in stakeholder capitalism focuses on creating value for all parties affected by a company's operations, including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders, emphasizing long-term sustainable growth. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) centers on a company's commitments to ethical practices, environmental stewardship, and social impacts beyond profit generation. Explore how expert consulting bridges these models to drive responsible business strategies and measurable outcomes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between stakeholder capitalism and corporate social responsibility (CSR) is crucial for consulting because it shapes strategic decision-making and aligns business goals with societal impact. Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes long-term value creation for all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and communities, while CSR focuses on specific ethical practices and philanthropic efforts. Consultants need to tailor their recommendations based on whether a company prioritizes broad stakeholder engagement or targeted social initiatives. This insight drives sustainable growth and enhances corporate reputation in competitive markets.
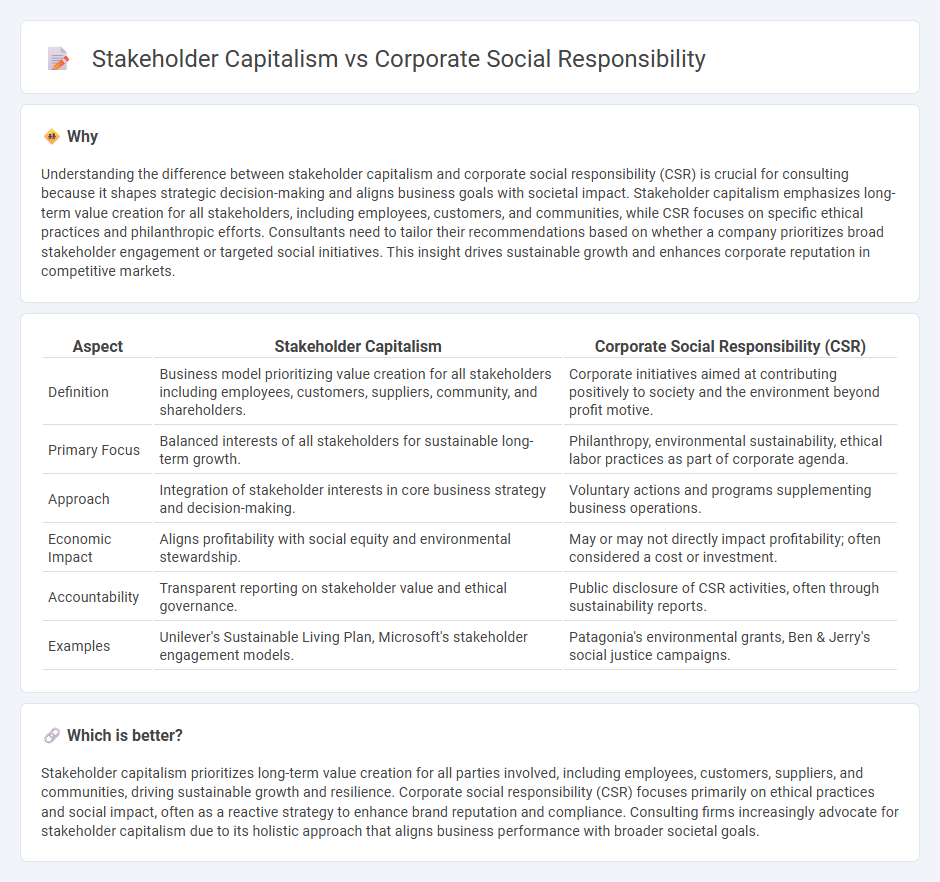
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Stakeholder Capitalism | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model prioritizing value creation for all stakeholders including employees, customers, suppliers, community, and shareholders. | Corporate initiatives aimed at contributing positively to society and the environment beyond profit motive. |
| Primary Focus | Balanced interests of all stakeholders for sustainable long-term growth. | Philanthropy, environmental sustainability, ethical labor practices as part of corporate agenda. |
| Approach | Integration of stakeholder interests in core business strategy and decision-making. | Voluntary actions and programs supplementing business operations. |
| Economic Impact | Aligns profitability with social equity and environmental stewardship. | May or may not directly impact profitability; often considered a cost or investment. |
| Accountability | Transparent reporting on stakeholder value and ethical governance. | Public disclosure of CSR activities, often through sustainability reports. |
| Examples | Unilever's Sustainable Living Plan, Microsoft's stakeholder engagement models. | Patagonia's environmental grants, Ben & Jerry's social justice campaigns. |
Which is better?
Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes long-term value creation for all parties involved, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, driving sustainable growth and resilience. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) focuses primarily on ethical practices and social impact, often as a reactive strategy to enhance brand reputation and compliance. Consulting firms increasingly advocate for stakeholder capitalism due to its holistic approach that aligns business performance with broader societal goals.
Connection
Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes the interests of all parties impacted by business operations, aligning closely with corporate social responsibility (CSR) principles that emphasize ethical practices and social impact. Both concepts drive companies to integrate sustainable strategies that benefit employees, customers, communities, and shareholders simultaneously. Effective consulting helps organizations implement stakeholder-focused CSR initiatives to enhance reputation, compliance, and long-term value creation.
Key Terms
Triple Bottom Line
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes ethical business practices and sustainability, focusing on the Triple Bottom Line of people, planet, and profit to balance social, environmental, and economic impacts. Stakeholder capitalism extends this concept by integrating the interests of all stakeholders--including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and investors--into core business strategies to drive long-term value creation. Explore how these frameworks reshape corporate accountability and promote sustainable growth.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes voluntary ethical practices and community engagement, while stakeholder capitalism integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria into core business strategies to create long-term value for all stakeholders. ESG metrics drive accountability and transparency, influencing investment decisions and corporate performance in a way CSR initiatives alone often do not. Explore how integrating ESG within stakeholder capitalism transforms sustainable business practices and stakeholder trust.
Shared Value
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes a company's commitment to ethical practices and philanthropy as separate from profit-making, while stakeholder capitalism integrates the interests of employees, customers, suppliers, and communities directly into business strategy. Shared Value drives this integration by creating economic value in a way that also produces value for society, aligning business success with social progress. Explore how Shared Value reshapes conventional business models to foster sustainable growth and community development.
Source and External Links
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? - IBM - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the principle that businesses should operate ethically and sustainably to positively impact society and the environment, balancing financial goals with people, planet, and profit considerations to foster corporate citizenship beyond legal obligations.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? Guide & Examples - CSR represents a company's voluntary efforts to improve society through philanthropy, social justice, environmental actions, and ethical business, aiming to build community impact, employee engagement, and stronger brand trust beyond profit motives.
Corporate social responsibility - Wikipedia - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a form of business self-regulation with a social or environmental mission, evolving from voluntary initiatives to more mandated or incentivized frameworks globally, supporting philanthropy, ethical business practices, and shared value creation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com