Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes balancing the interests of all parties affected by business decisions, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, fostering long-term value beyond shareholder profits. Sustainable business integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into core operations to reduce ecological impact and promote ethical practices, driving resilience and innovation. Discover how consulting bridges these approaches to align purpose with performance for strategic growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between stakeholder capitalism and sustainable business is crucial for consultants to tailor strategies that align with a client's long-term goals and social responsibilities. Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes creating value for all stakeholders including employees, customers, and communities, while sustainable business focuses specifically on environmental and social impact alongside profitability. Clear differentiation enables consultants to drive ethical decision-making and competitive advantage in evolving markets. Mastery of these concepts enhances the ability to guide businesses toward responsible growth and stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
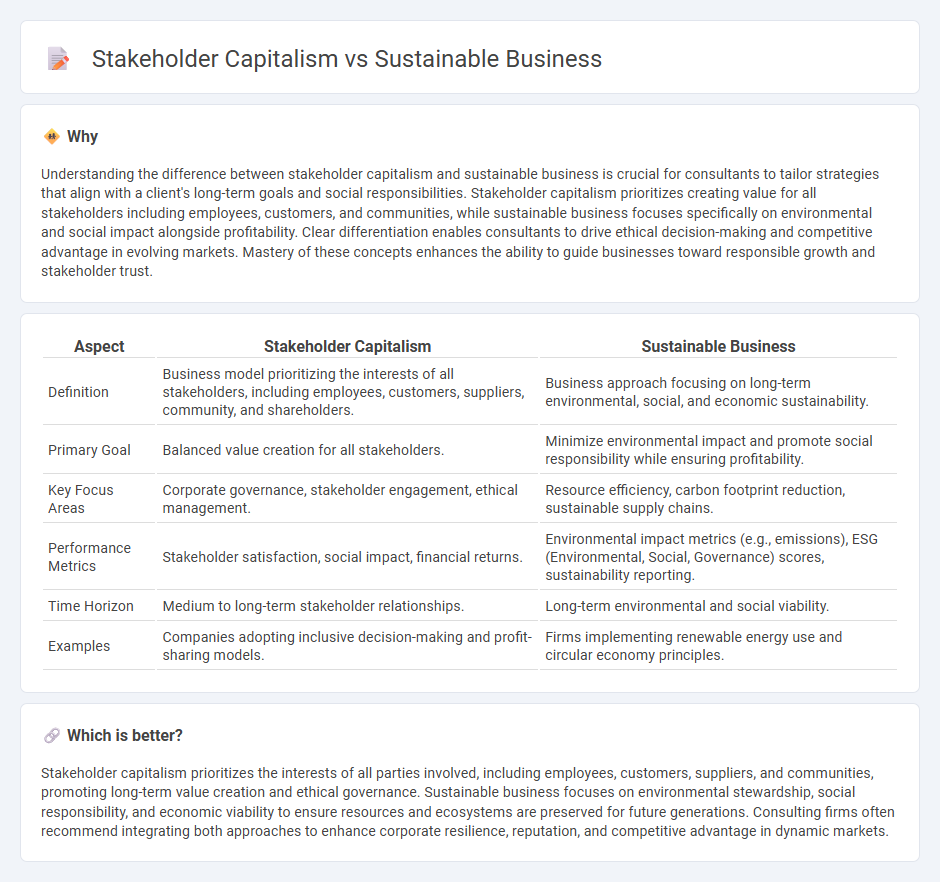
| Aspect | Stakeholder Capitalism | Sustainable Business |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model prioritizing the interests of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, community, and shareholders. | Business approach focusing on long-term environmental, social, and economic sustainability. |
| Primary Goal | Balanced value creation for all stakeholders. | Minimize environmental impact and promote social responsibility while ensuring profitability. |
| Key Focus Areas | Corporate governance, stakeholder engagement, ethical management. | Resource efficiency, carbon footprint reduction, sustainable supply chains. |
| Performance Metrics | Stakeholder satisfaction, social impact, financial returns. | Environmental impact metrics (e.g., emissions), ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) scores, sustainability reporting. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term stakeholder relationships. | Long-term environmental and social viability. |
| Examples | Companies adopting inclusive decision-making and profit-sharing models. | Firms implementing renewable energy use and circular economy principles. |
Which is better?
Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes the interests of all parties involved, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, promoting long-term value creation and ethical governance. Sustainable business focuses on environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability to ensure resources and ecosystems are preserved for future generations. Consulting firms often recommend integrating both approaches to enhance corporate resilience, reputation, and competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Connection
Stakeholder capitalism integrates sustainable business practices by prioritizing the interests of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, and the environment, over short-term shareholder profits. This approach drives long-term value creation through responsible governance, ethical supply chains, and reduced environmental impact. Consulting firms guide organizations in embedding these principles to enhance resilience, reputation, and competitive advantage in evolving markets.
Key Terms
Triple Bottom Line
Sustainable business emphasizes the Triple Bottom Line, integrating social, environmental, and economic impact to drive long-term value beyond profit. Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes balancing the interests of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, and investors, aligning corporate goals with broader societal needs. Explore in-depth how these models reshape corporate responsibility and impact global business strategies.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Sustainable business integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria to drive long-term value while minimizing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility. Stakeholder capitalism expands this approach by prioritizing the interests of all stakeholders--including employees, customers, communities, and shareholders--ensuring inclusive and ethical governance practices. Explore how adopting ESG strategies within stakeholder capitalism transforms corporate accountability and sustainability.
Shared Value
Sustainable business practices prioritize environmental stewardship and long-term resource management, aiming to reduce ecological impact while maintaining profitability. Stakeholder capitalism expands this focus by creating Shared Value that benefits not only shareholders but also employees, customers, communities, and the environment through inclusive decision-making and equitable growth. Explore how integrating these approaches can drive innovation and competitive advantage in today's economy.
Source and External Links
Sustainable business - Wikipedia - A sustainable business is an enterprise that aims to have minimal negative or potentially positive impact on the environment, community, society, or economy, often by integrating sustainability into all decisions and exceeding traditional environmental standards.
How to start a sustainable business - Wolters Kluwer - A sustainable business balances profit with environmental and community health by reducing or eliminating its negative impact through eco-friendly operations, sourcing, and production.
What Is Sustainability in Business? - IBM - Sustainability in business means adopting strategies to reduce negative environmental impacts, meeting regulatory requirements, and integrating responsible practices that also offer financial and brand benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com