AI ethics evaluation focuses on identifying and mitigating moral risks and biases within artificial intelligence systems to ensure responsible and fair technology deployment. Societal impact assessment analyzes broader consequences of AI on communities, economies, and social structures to promote sustainable and inclusive development. Explore detailed methodologies and case studies to understand the nuanced differences and applications in consulting contexts.
Why it is important
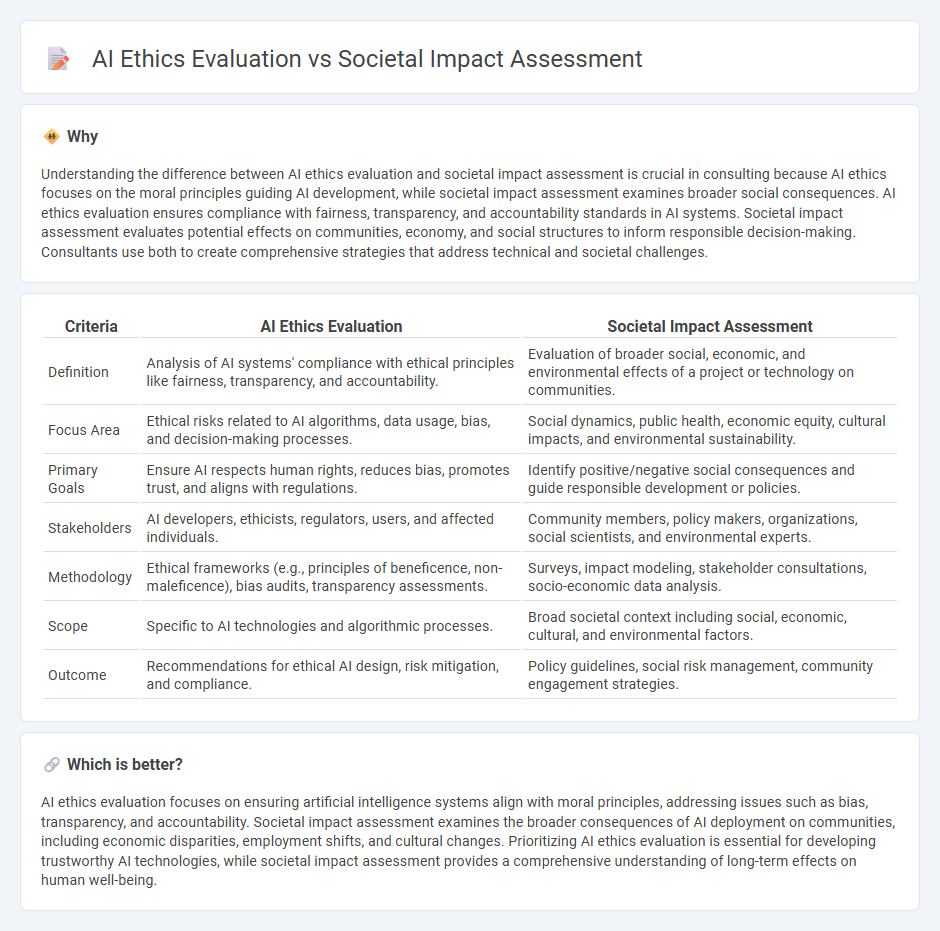
Understanding the difference between AI ethics evaluation and societal impact assessment is crucial in consulting because AI ethics focuses on the moral principles guiding AI development, while societal impact assessment examines broader social consequences. AI ethics evaluation ensures compliance with fairness, transparency, and accountability standards in AI systems. Societal impact assessment evaluates potential effects on communities, economy, and social structures to inform responsible decision-making. Consultants use both to create comprehensive strategies that address technical and societal challenges.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | AI Ethics Evaluation | Societal Impact Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analysis of AI systems' compliance with ethical principles like fairness, transparency, and accountability. | Evaluation of broader social, economic, and environmental effects of a project or technology on communities. |
| Focus Area | Ethical risks related to AI algorithms, data usage, bias, and decision-making processes. | Social dynamics, public health, economic equity, cultural impacts, and environmental sustainability. |
| Primary Goals | Ensure AI respects human rights, reduces bias, promotes trust, and aligns with regulations. | Identify positive/negative social consequences and guide responsible development or policies. |
| Stakeholders | AI developers, ethicists, regulators, users, and affected individuals. | Community members, policy makers, organizations, social scientists, and environmental experts. |
| Methodology | Ethical frameworks (e.g., principles of beneficence, non-maleficence), bias audits, transparency assessments. | Surveys, impact modeling, stakeholder consultations, socio-economic data analysis. |
| Scope | Specific to AI technologies and algorithmic processes. | Broad societal context including social, economic, cultural, and environmental factors. |
| Outcome | Recommendations for ethical AI design, risk mitigation, and compliance. | Policy guidelines, social risk management, community engagement strategies. |
Which is better?
AI ethics evaluation focuses on ensuring artificial intelligence systems align with moral principles, addressing issues such as bias, transparency, and accountability. Societal impact assessment examines the broader consequences of AI deployment on communities, including economic disparities, employment shifts, and cultural changes. Prioritizing AI ethics evaluation is essential for developing trustworthy AI technologies, while societal impact assessment provides a comprehensive understanding of long-term effects on human well-being.
Connection
AI ethics evaluation ensures that artificial intelligence systems align with core moral principles such as fairness, transparency, and accountability, which directly influences the outcome of societal impact assessments focused on the technology's effects on communities and social structures. Consulting firms integrate these processes to guide organizations in developing AI solutions that mitigate risks like bias, privacy invasion, and inequality, thereby promoting socially responsible innovation. This connection strengthens decision-making frameworks by embedding ethical considerations into the assessment of AI's broader societal consequences.
Key Terms
Stakeholder Engagement
Societal impact assessment emphasizes inclusive stakeholder engagement by actively involving diverse community groups, policymakers, and affected populations to identify social risks and benefits of AI technologies. AI ethics evaluation prioritizes ethical frameworks and principles, integrating stakeholder voices to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems. Explore further to understand best practices for balancing stakeholder input in both methodologies.
Bias Mitigation
Societal impact assessment examines the broader effects of AI systems on communities, highlighting potential biases in access, representation, and outcomes. AI ethics evaluation focuses on the principles of fairness, accountability, and transparency to mitigate algorithmic bias at the design and deployment stages. Discover more about effective strategies for bias mitigation and ethical AI governance.
Social Justice
Societal impact assessment prioritizes evaluating how AI technologies affect social equity, aiming to identify and mitigate disparities in access, outcomes, and representation for marginalized groups. AI ethics evaluation encompasses broader principles including fairness, transparency, and accountability, while emphasizing social justice to ensure AI systems promote inclusivity and protect human rights. Explore deeper insights on how integrating these frameworks advances equitable AI development.
Source and External Links
Social impact assessment (SIA) | EBSCO Research Starters - Social impact assessment (SIA) is a systematic approach used to evaluate social interventions' effects on populations, focusing on their everyday lives, well-being, and addressing both positive and negative impacts to maximize social return on investments.
Social impact assessment - SIA is a process including identification, analysis, management, and monitoring of potential social impacts of projects throughout their lifecycle, addressing key matters like community engagement, workforce management, and health to inform regulatory decisions.
Understanding Social Impact Assessments: Why They Matter and How to Conduct Them Effectively - A Social Impact Assessment is a proactive process analyzing and managing intended and unintended consequences of projects or policies on local livelihoods, social cohesion, cultural heritage, and community infrastructure to protect communities and promote positive contributions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com