Regenerative business strategy focuses on creating systems that restore and renew natural resources, fostering long-term sustainability and resilience. Impact strategy aims to measure and enhance the social and environmental outcomes of business activities, ensuring positive contributions to communities and ecosystems. Explore how these approaches can transform your organization's purpose and performance.
Why it is important
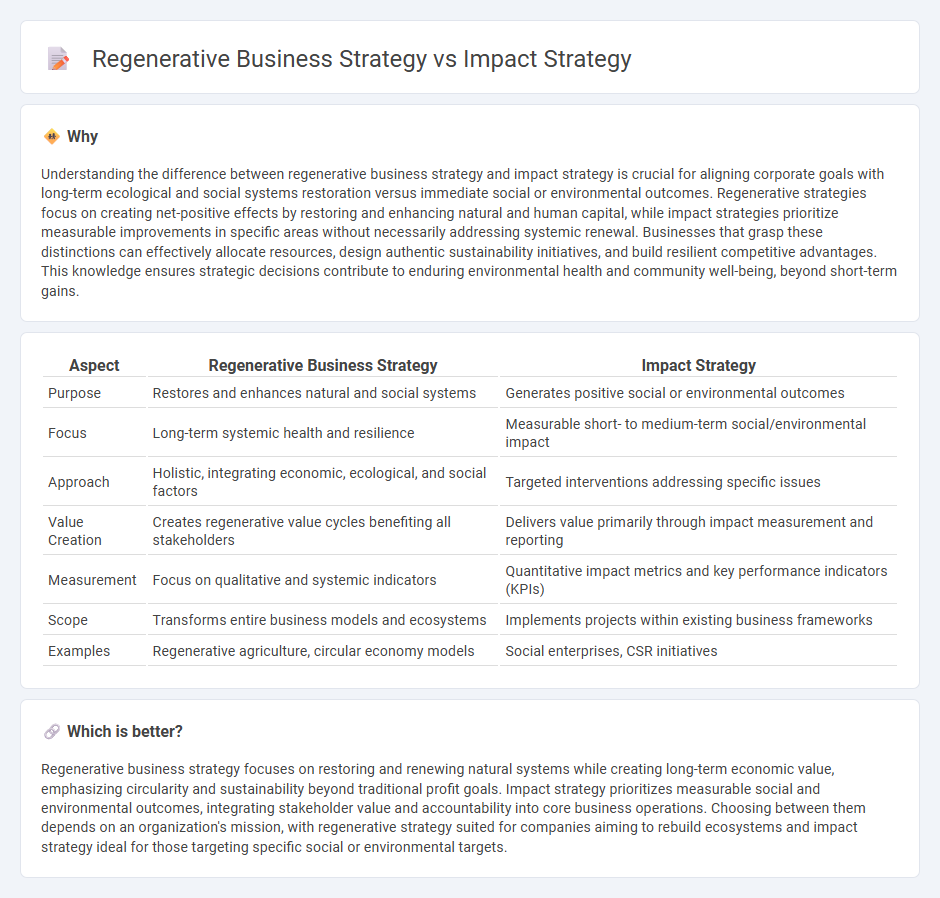
Understanding the difference between regenerative business strategy and impact strategy is crucial for aligning corporate goals with long-term ecological and social systems restoration versus immediate social or environmental outcomes. Regenerative strategies focus on creating net-positive effects by restoring and enhancing natural and human capital, while impact strategies prioritize measurable improvements in specific areas without necessarily addressing systemic renewal. Businesses that grasp these distinctions can effectively allocate resources, design authentic sustainability initiatives, and build resilient competitive advantages. This knowledge ensures strategic decisions contribute to enduring environmental health and community well-being, beyond short-term gains.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Strategy | Impact Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Restores and enhances natural and social systems | Generates positive social or environmental outcomes |
| Focus | Long-term systemic health and resilience | Measurable short- to medium-term social/environmental impact |
| Approach | Holistic, integrating economic, ecological, and social factors | Targeted interventions addressing specific issues |
| Value Creation | Creates regenerative value cycles benefiting all stakeholders | Delivers value primarily through impact measurement and reporting |
| Measurement | Focus on qualitative and systemic indicators | Quantitative impact metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) |
| Scope | Transforms entire business models and ecosystems | Implements projects within existing business frameworks |
| Examples | Regenerative agriculture, circular economy models | Social enterprises, CSR initiatives |
Which is better?
Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and renewing natural systems while creating long-term economic value, emphasizing circularity and sustainability beyond traditional profit goals. Impact strategy prioritizes measurable social and environmental outcomes, integrating stakeholder value and accountability into core business operations. Choosing between them depends on an organization's mission, with regenerative strategy suited for companies aiming to rebuild ecosystems and impact strategy ideal for those targeting specific social or environmental targets.
Connection
Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and enhancing ecological and social systems, aligning closely with impact strategy which aims to create measurable positive outcomes for society and the environment. Both approaches prioritize long-term value creation beyond financial performance, integrating sustainability metrics and stakeholder engagement to drive systemic change. Consulting services help organizations design and implement these interconnected strategies, utilizing frameworks such as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria and impact measurement tools to optimize business resilience and societal benefit.
Key Terms
Value Creation
Impact strategy targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, emphasizing accountability and stakeholder engagement to create shared value. Regenerative business strategy integrates ecological restoration and systemic resilience into core operations, fostering long-term sustainability and revitalizing natural and social systems. Explore how these approaches drive transformative value creation in modern enterprises.
Systems Thinking
Impact strategy emphasizes measurable social and environmental outcomes within existing business models, while regenerative business strategy integrates Systems Thinking to create self-sustaining processes that restore ecosystems and communities. Regenerative strategies leverage circular economies, biomimicry, and stakeholder collaboration to drive long-term resilience and adaptability. Discover how adopting Systems Thinking transforms traditional impact efforts into regenerative business models.
Stakeholder Engagement
Impact strategy emphasizes measuring and managing social and environmental outcomes to create positive change, prioritizing transparent communication and accountability with stakeholders. Regenerative business strategy fosters continuous stakeholder collaboration to restore and enhance ecosystems and communities, embedding long-term resilience into corporate practices. Explore how deepening stakeholder engagement transforms sustainable business models into regenerative ventures.
Source and External Links
A Short Guide: How to Develop an Impact Strategy - An impact strategy outlines the purpose of an investment with a detailed roadmap and long-term vision to achieve specific sector or stakeholder impact, measure it, and ensure an equitable return on investment.
Social Impact Strategy - A well-crafted impact strategy starts with a clear problem statement, identifies critical activities and outcomes, uses data-driven questions, and leverages tools to communicate impact effectively.
Creating an Impact Strategy: Examples & Key Insights - An impact strategy clarifies organizational direction by defining long-term outcomes that show the intended community changes, helping ensure focused progress toward meaningful impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com