Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes creating long-term value for all parties involved, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, aligning business goals with social responsibility. Social entrepreneurship focuses on innovative solutions to social problems through sustainable business models that prioritize impact over profit maximization. Explore the distinctions between these approaches to understand their unique contributions to corporate strategy and societal change.
Why it is important
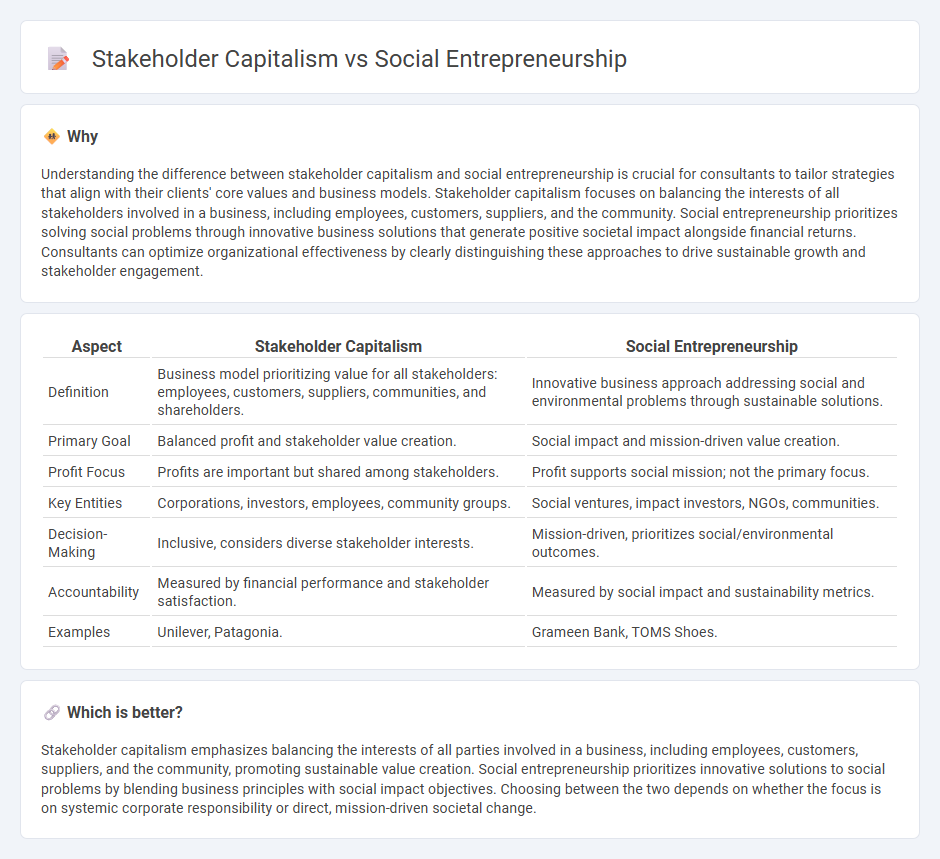
Understanding the difference between stakeholder capitalism and social entrepreneurship is crucial for consultants to tailor strategies that align with their clients' core values and business models. Stakeholder capitalism focuses on balancing the interests of all stakeholders involved in a business, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community. Social entrepreneurship prioritizes solving social problems through innovative business solutions that generate positive societal impact alongside financial returns. Consultants can optimize organizational effectiveness by clearly distinguishing these approaches to drive sustainable growth and stakeholder engagement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Stakeholder Capitalism | Social Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model prioritizing value for all stakeholders: employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders. | Innovative business approach addressing social and environmental problems through sustainable solutions. |
| Primary Goal | Balanced profit and stakeholder value creation. | Social impact and mission-driven value creation. |
| Profit Focus | Profits are important but shared among stakeholders. | Profit supports social mission; not the primary focus. |
| Key Entities | Corporations, investors, employees, community groups. | Social ventures, impact investors, NGOs, communities. |
| Decision-Making | Inclusive, considers diverse stakeholder interests. | Mission-driven, prioritizes social/environmental outcomes. |
| Accountability | Measured by financial performance and stakeholder satisfaction. | Measured by social impact and sustainability metrics. |
| Examples | Unilever, Patagonia. | Grameen Bank, TOMS Shoes. |
Which is better?
Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes balancing the interests of all parties involved in a business, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community, promoting sustainable value creation. Social entrepreneurship prioritizes innovative solutions to social problems by blending business principles with social impact objectives. Choosing between the two depends on whether the focus is on systemic corporate responsibility or direct, mission-driven societal change.
Connection
Stakeholder capitalism and social entrepreneurship both prioritize creating value beyond profit by addressing social, environmental, and economic challenges. Stakeholder capitalism focuses on balancing the interests of all parties involved, including employees, customers, communities, and shareholders, fostering sustainable business practices. Social entrepreneurship drives innovative solutions targeted at systemic problems, aligning with stakeholder-centric models to promote long-term societal benefits.
Key Terms
Impact Measurement
Social entrepreneurship emphasizes innovative solutions to social problems, prioritizing measurable social impact and community well-being as key performance indicators. Stakeholder capitalism integrates the interests of employees, customers, suppliers, and the environment into business decisions, using comprehensive impact measurement frameworks like ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria to assess long-term value creation. Explore further to understand the nuanced approaches to impact measurement and value creation within these models.
Value Creation
Social entrepreneurship drives value creation by addressing social and environmental challenges through innovative business models that prioritize positive societal impact alongside financial returns. Stakeholder capitalism expands the traditional profit-centric approach, integrating the interests of employees, customers, communities, and shareholders to foster sustainable and inclusive economic growth. Explore the nuanced distinctions between these approaches to understand how they shape responsible value creation in today's economy.
Stakeholder Engagement
Social entrepreneurship prioritizes creating positive social impact by addressing community needs through innovative solutions, while stakeholder capitalism emphasizes balancing the interests of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and investors, to achieve sustainable business growth. Stakeholder engagement in social entrepreneurship involves collaborative problem-solving with local communities, whereas in stakeholder capitalism it integrates systematic communication and accountability frameworks to align diverse stakeholder interests. Explore detailed strategies and real-world examples to deepen your understanding of how these models shape stakeholder engagement.
Source and External Links
Social entrepreneurship - Wikipedia - Social entrepreneurship involves developing and funding innovative solutions to social problems, prioritizing positive societal impact over profit maximization.
What Is Social Entrepreneurship? A Guide - Coursera - Social entrepreneurship applies business strategies to create lasting social change, with entrepreneurs motivated by addressing systemic social or cultural issues.
What is Social Entrepreneurship? - Social entrepreneurship aims to solve social problems through sustainable business models that reinvest profits to achieve social goals, focusing on impact rather than shareholder dividends.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com