Corporate venturing involves companies investing in external startups to foster innovation and access new markets, while intrapreneurship empowers employees to develop new ideas and projects within the organization. Both strategies drive growth, but corporate venturing leverages external partnerships, and intrapreneurship focuses on internal capabilities. Discover how these approaches can transform business innovation and competitive advantage.
Why it is important
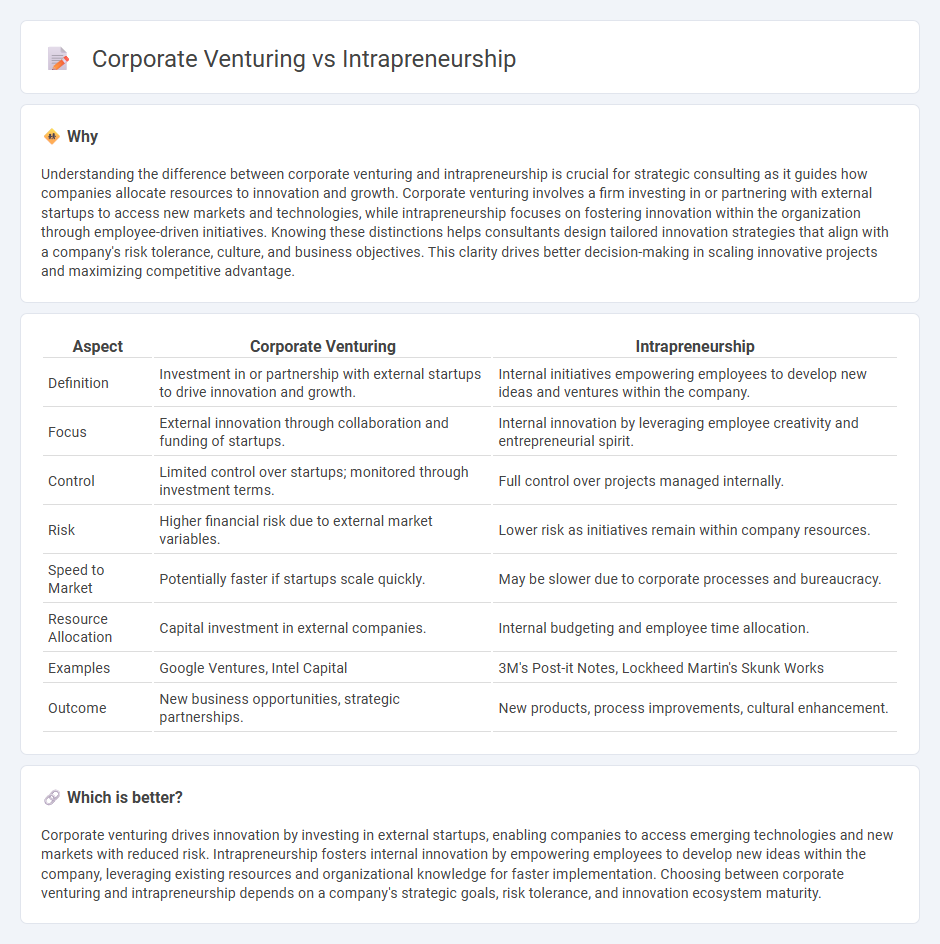
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and intrapreneurship is crucial for strategic consulting as it guides how companies allocate resources to innovation and growth. Corporate venturing involves a firm investing in or partnering with external startups to access new markets and technologies, while intrapreneurship focuses on fostering innovation within the organization through employee-driven initiatives. Knowing these distinctions helps consultants design tailored innovation strategies that align with a company's risk tolerance, culture, and business objectives. This clarity drives better decision-making in scaling innovative projects and maximizing competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Intrapreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in or partnership with external startups to drive innovation and growth. | Internal initiatives empowering employees to develop new ideas and ventures within the company. |
| Focus | External innovation through collaboration and funding of startups. | Internal innovation by leveraging employee creativity and entrepreneurial spirit. |
| Control | Limited control over startups; monitored through investment terms. | Full control over projects managed internally. |
| Risk | Higher financial risk due to external market variables. | Lower risk as initiatives remain within company resources. |
| Speed to Market | Potentially faster if startups scale quickly. | May be slower due to corporate processes and bureaucracy. |
| Resource Allocation | Capital investment in external companies. | Internal budgeting and employee time allocation. |
| Examples | Google Ventures, Intel Capital | 3M's Post-it Notes, Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works |
| Outcome | New business opportunities, strategic partnerships. | New products, process improvements, cultural enhancement. |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing drives innovation by investing in external startups, enabling companies to access emerging technologies and new markets with reduced risk. Intrapreneurship fosters internal innovation by empowering employees to develop new ideas within the company, leveraging existing resources and organizational knowledge for faster implementation. Choosing between corporate venturing and intrapreneurship depends on a company's strategic goals, risk tolerance, and innovation ecosystem maturity.
Connection
Corporate venturing and intrapreneurship are interconnected through their shared goal of fostering innovation within established organizations by leveraging internal talent and resources. Corporate venturing often provides a strategic framework and funding for intrapreneurial initiatives that develop new products, services, or business models. This synergy accelerates growth and competitive advantage by combining entrepreneurial agility with corporate stability.
Key Terms
Innovation Management
Intrapreneurship involves empowering employees to develop innovative ideas within an existing organization, driving internal growth and agility. Corporate venturing refers to a company investing in or partnering with external startups to accelerate innovation and gain competitive advantage. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies transform innovation management and business growth.
Risk Allocation
Intrapreneurship involves employees driving innovation within an existing company, bearing minimal financial risk as resources are controlled by the parent organization. Corporate venturing allocates higher risk by investing corporate funds into external startups or new ventures, aiming for strategic growth and innovation. Explore detailed risk allocation strategies to understand which model best aligns with your business goals.
Strategic Autonomy
Intrapreneurship empowers employees to innovate within an existing company structure, fostering strategic autonomy by enabling internal development of new products or services. Corporate venturing involves a company investing in or acquiring external startups to accelerate innovation and gain competitive edges without disrupting core operations. Explore how balancing these approaches can maximize strategic autonomy and drive sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Intrapreneurship - Intrapreneurship is the act of behaving like an entrepreneur while working within a large organization, focusing on innovation and risk-taking to create profitable products or ideas internally.
What is intrapreneurship, and how can you cultivate it at your company? - Intrapreneurs are individuals within established companies who innovate and improve their work and organization, driving growth without bearing the financial risks typical of entrepreneurs.
What is Intrapreneurship: Definition, Strategies, and Examples - Intrapreneurship means applying entrepreneurial principles inside large organizations to foster innovation, with intrapreneurs empowered to take risks and leverage resources, thereby keeping companies competitive and adaptive.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com