Regenerative business models focus on restoring and revitalizing ecosystems while promoting long-term sustainability, contrasting with shared value creation which centers on generating economic value alongside societal benefits. Both approaches aim to redefine corporate success by integrating environmental and social impact into core strategies, ensuring resilience and community well-being. Explore how consulting experts tailor these models to drive innovation and responsible growth in diverse industries.
Why it is important
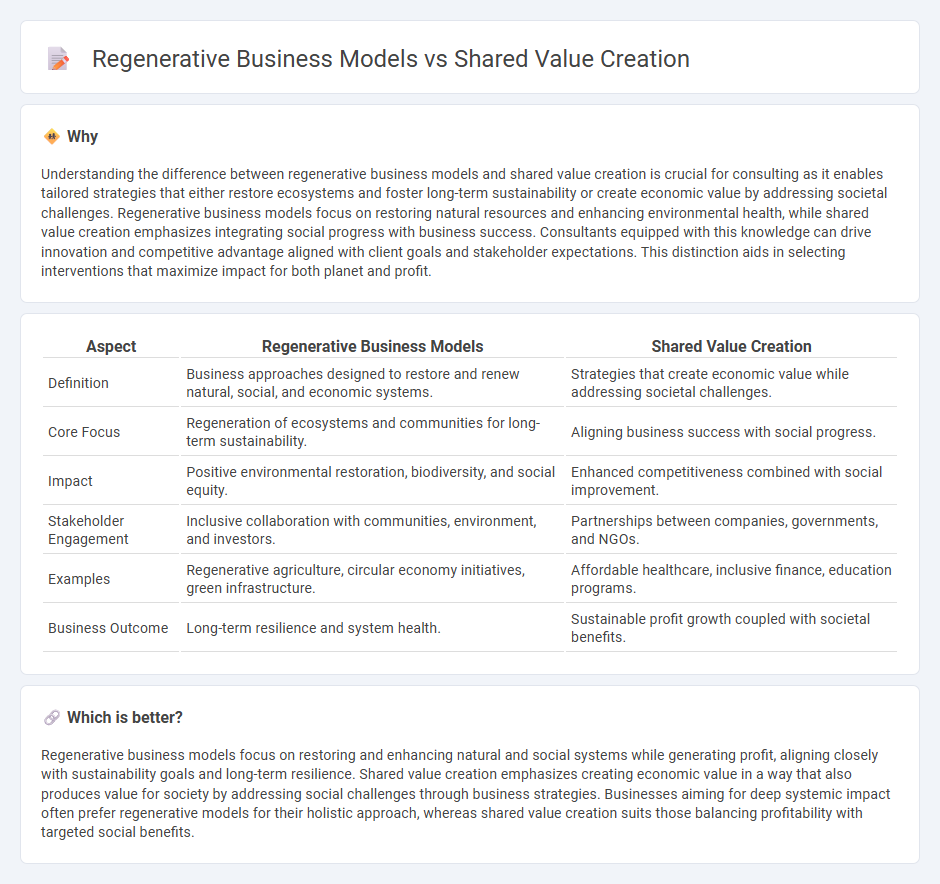
Understanding the difference between regenerative business models and shared value creation is crucial for consulting as it enables tailored strategies that either restore ecosystems and foster long-term sustainability or create economic value by addressing societal challenges. Regenerative business models focus on restoring natural resources and enhancing environmental health, while shared value creation emphasizes integrating social progress with business success. Consultants equipped with this knowledge can drive innovation and competitive advantage aligned with client goals and stakeholder expectations. This distinction aids in selecting interventions that maximize impact for both planet and profit.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Models | Shared Value Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business approaches designed to restore and renew natural, social, and economic systems. | Strategies that create economic value while addressing societal challenges. |
| Core Focus | Regeneration of ecosystems and communities for long-term sustainability. | Aligning business success with social progress. |
| Impact | Positive environmental restoration, biodiversity, and social equity. | Enhanced competitiveness combined with social improvement. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Inclusive collaboration with communities, environment, and investors. | Partnerships between companies, governments, and NGOs. |
| Examples | Regenerative agriculture, circular economy initiatives, green infrastructure. | Affordable healthcare, inclusive finance, education programs. |
| Business Outcome | Long-term resilience and system health. | Sustainable profit growth coupled with societal benefits. |
Which is better?
Regenerative business models focus on restoring and enhancing natural and social systems while generating profit, aligning closely with sustainability goals and long-term resilience. Shared value creation emphasizes creating economic value in a way that also produces value for society by addressing social challenges through business strategies. Businesses aiming for deep systemic impact often prefer regenerative models for their holistic approach, whereas shared value creation suits those balancing profitability with targeted social benefits.
Connection
Regenerative business models and shared value creation are connected through their focus on integrating environmental sustainability with economic growth to benefit both businesses and society. By adopting regenerative practices, companies enhance ecosystems and community well-being, which generates long-term value beyond traditional profit metrics. This alignment drives innovation, improves stakeholder engagement, and fosters resilient economies, demonstrating a holistic approach to sustainable consulting strategies.
Key Terms
Stakeholder Engagement
Shared value creation prioritizes aligning business success with social progress by engaging stakeholders in solving community challenges through innovative products and services. Regenerative business models extend this by fostering systems that restore and replenish environmental and social resources, thereby ensuring long-term resilience and stakeholder well-being. Explore how deep stakeholder engagement transforms value creation into regenerative impact for sustainable growth.
Systems Thinking
Shared value creation integrates social and economic goals by aligning company success with community well-being through collaborative initiatives, enhancing stakeholder engagement and long-term profitability. Regenerative business models emphasize restoring and revitalizing natural and social systems, adopting systems thinking to create resilient, circular, and adaptive enterprises that go beyond sustainability. Explore how systems thinking shapes these approaches to transform business impact comprehensively.
Circular Economy
Shared value creation integrates social and environmental benefits with economic gains, driving innovation in Circular Economy practices that reduce waste and optimize resource use. Regenerative business models go beyond sustainability, aiming to restore ecosystems and enhance social well-being through closed-loop systems and renewable inputs. Explore how these approaches transform industries by fostering resilience, profitability, and positive impact within Circular Economy frameworks.
Source and External Links
The Three Levels of CSV - Shared value creation involves companies generating economic value by meeting societal needs through three ways: reconceiving products and markets, redefining productivity in the value chain, and improving local and regional business environments.
What is shared value? | Ellis Jones - Shared value is a strategic approach where organizations achieve economic returns by addressing social problems, leveraging business strengths to innovate and solve societal issues while gaining competitive advantage and fostering partnerships.
Creating Shared Value: Explained with Examples - Creating Shared Value (CSV) is a management strategy applicable across industries that focuses on creating measurable business value by addressing social problems through innovations in products, processes, and community engagement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com