Anticipatory governance involves proactive strategies and foresight techniques to address potential challenges before they arise, leveraging data analytics and scenario planning to inform decision-making. Reactive governance, in contrast, focuses on responding to issues after they occur, often leading to quicker but less strategic interventions. Discover more about how consulting bridges these governance approaches to optimize organizational resilience and agility.
Why it is important
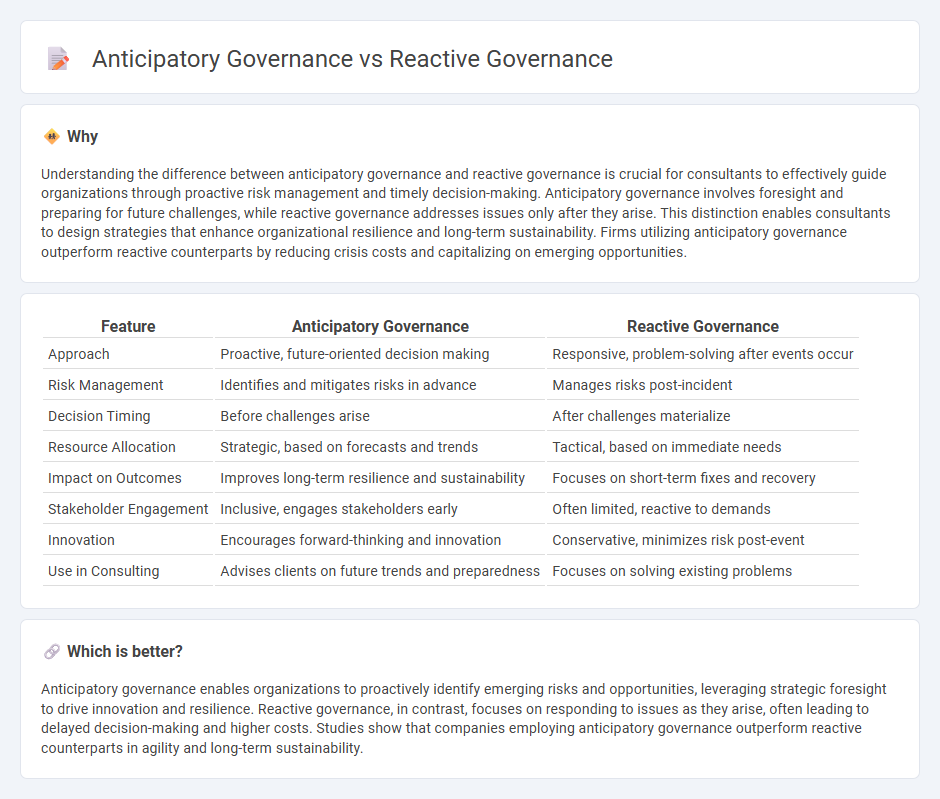
Understanding the difference between anticipatory governance and reactive governance is crucial for consultants to effectively guide organizations through proactive risk management and timely decision-making. Anticipatory governance involves foresight and preparing for future challenges, while reactive governance addresses issues only after they arise. This distinction enables consultants to design strategies that enhance organizational resilience and long-term sustainability. Firms utilizing anticipatory governance outperform reactive counterparts by reducing crisis costs and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Anticipatory Governance | Reactive Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Proactive, future-oriented decision making | Responsive, problem-solving after events occur |
| Risk Management | Identifies and mitigates risks in advance | Manages risks post-incident |
| Decision Timing | Before challenges arise | After challenges materialize |
| Resource Allocation | Strategic, based on forecasts and trends | Tactical, based on immediate needs |
| Impact on Outcomes | Improves long-term resilience and sustainability | Focuses on short-term fixes and recovery |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Inclusive, engages stakeholders early | Often limited, reactive to demands |
| Innovation | Encourages forward-thinking and innovation | Conservative, minimizes risk post-event |
| Use in Consulting | Advises clients on future trends and preparedness | Focuses on solving existing problems |
Which is better?
Anticipatory governance enables organizations to proactively identify emerging risks and opportunities, leveraging strategic foresight to drive innovation and resilience. Reactive governance, in contrast, focuses on responding to issues as they arise, often leading to delayed decision-making and higher costs. Studies show that companies employing anticipatory governance outperform reactive counterparts in agility and long-term sustainability.
Connection
Anticipatory governance and reactive governance are interconnected approaches within consulting that address organizational risk management and strategic planning. Anticipatory governance involves proactively identifying potential challenges and opportunities through data analysis and foresight methods, enabling consultants to design strategies that prevent risks before they materialize. Reactive governance complements this by providing frameworks to respond effectively when unforeseen issues arise, ensuring resilience and continuous improvement in consulting outcomes.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Reactive governance addresses risk management by responding to crises and issues after they have occurred, often relying on corrective measures and established protocols to mitigate damage. Anticipatory governance emphasizes proactive identification and management of potential risks through forecasting, scenario planning, and stakeholder engagement to prevent or minimize future threats. Explore further to understand how anticipatory strategies can transform risk governance in dynamic environments.
Scenario Planning
Reactive governance primarily addresses issues as they arise, relying on scenario planning to manage risks and uncertainties after events occur. Anticipatory governance integrates scenario planning proactively, aiming to predict and shape future developments by incorporating diverse possible futures into decision-making processes. Explore how leveraging scenario planning enhances the effectiveness of both governance models in navigating complex challenges.
Crisis Response
Reactive governance centers on addressing and managing crises after they occur, relying on established protocols and real-time data to mitigate damage. Anticipatory governance emphasizes foresight and preparedness, using predictive analytics and scenario planning to prevent or minimize crises before they unfold. Explore the distinct approaches of these governance models to enhance crisis response strategies.
Source and External Links
Proactive or Reactive Governance? - Reactive governance focuses on establishing governance processes and then using audits and controls to ensure compliance, addressing issues after they arise rather than preventing them upfront.
Compare and contrast: Proactive vs. reactive governance - Reactive governance means acting to address problems as they emerge, while proactive governance involves actions to prevent problems from occurring in the first place.
What are the differences between proactive and reactive ... - Reactive governance prioritizes responding to issues after they happen, often relying on post-incident analysis, whereas proactive governance emphasizes prevention through early design, automation, and monitoring.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com