Corporate venturing involves companies investing in or collaborating with startups to drive innovation and gain competitive advantages directly within their industry. Open innovation leverages external ideas, technologies, and partnerships beyond the organization's boundaries to accelerate growth and diversify innovation sources. Discover how these strategies can transform your business and fuel sustainable growth.
Why it is important
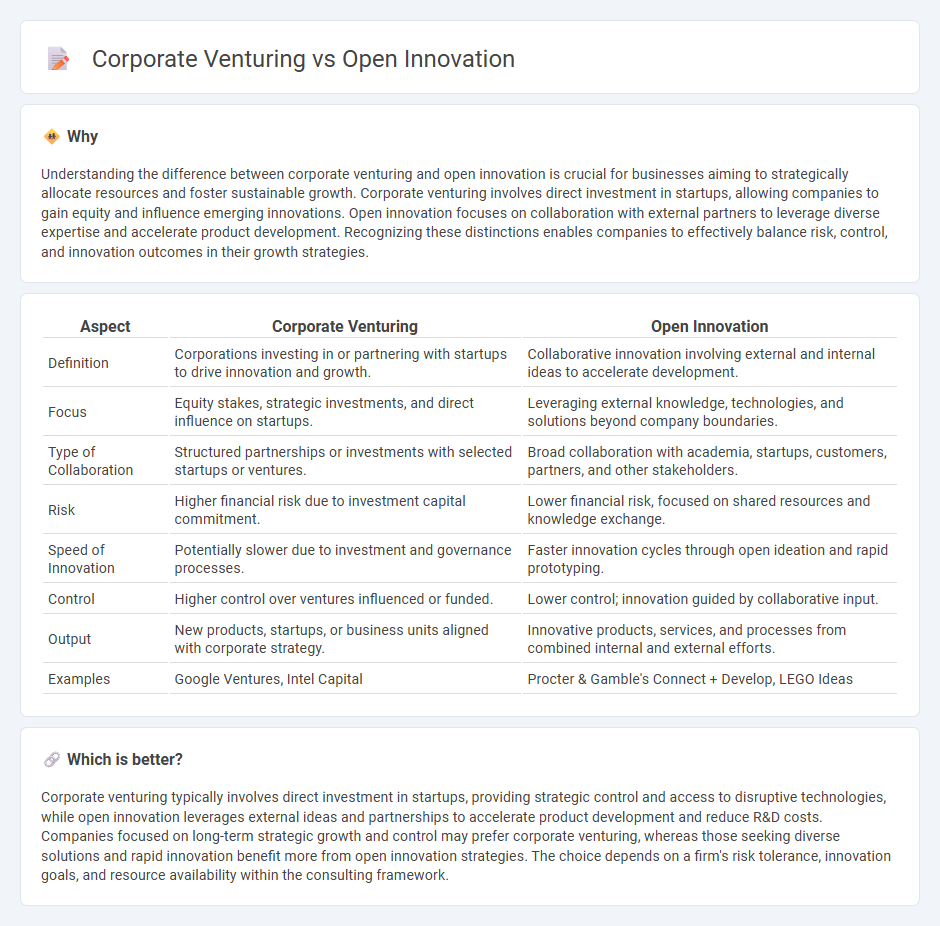
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and open innovation is crucial for businesses aiming to strategically allocate resources and foster sustainable growth. Corporate venturing involves direct investment in startups, allowing companies to gain equity and influence emerging innovations. Open innovation focuses on collaboration with external partners to leverage diverse expertise and accelerate product development. Recognizing these distinctions enables companies to effectively balance risk, control, and innovation outcomes in their growth strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Open Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Corporations investing in or partnering with startups to drive innovation and growth. | Collaborative innovation involving external and internal ideas to accelerate development. |
| Focus | Equity stakes, strategic investments, and direct influence on startups. | Leveraging external knowledge, technologies, and solutions beyond company boundaries. |
| Type of Collaboration | Structured partnerships or investments with selected startups or ventures. | Broad collaboration with academia, startups, customers, partners, and other stakeholders. |
| Risk | Higher financial risk due to investment capital commitment. | Lower financial risk, focused on shared resources and knowledge exchange. |
| Speed of Innovation | Potentially slower due to investment and governance processes. | Faster innovation cycles through open ideation and rapid prototyping. |
| Control | Higher control over ventures influenced or funded. | Lower control; innovation guided by collaborative input. |
| Output | New products, startups, or business units aligned with corporate strategy. | Innovative products, services, and processes from combined internal and external efforts. |
| Examples | Google Ventures, Intel Capital | Procter & Gamble's Connect + Develop, LEGO Ideas |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing typically involves direct investment in startups, providing strategic control and access to disruptive technologies, while open innovation leverages external ideas and partnerships to accelerate product development and reduce R&D costs. Companies focused on long-term strategic growth and control may prefer corporate venturing, whereas those seeking diverse solutions and rapid innovation benefit more from open innovation strategies. The choice depends on a firm's risk tolerance, innovation goals, and resource availability within the consulting framework.
Connection
Corporate venturing accelerates innovation by investing in or partnering with startups that offer novel technologies or business models. Open innovation leverages external ideas and pathways, enhancing corporate venturing initiatives through collaboration with diverse stakeholders. Together, they drive competitive advantage by integrating internal and external innovation ecosystems.
Key Terms
External Collaboration
Open innovation leverages external ideas and partnerships to accelerate business growth and foster creativity beyond internal R&D teams, while corporate venturing typically involves strategic investments in startups to gain competitive advantage and access to emerging technologies. Both strategies emphasize external collaboration, but open innovation encourages broad ecosystem integration, whereas corporate venturing centers on financial stakes and direct influence in portfolio companies. Explore the distinct benefits and implementation methods of each approach to optimize your organization's innovation strategy.
Corporate Spin-offs
Corporate spin-offs serve as a strategic tool within corporate venturing, enabling established companies to create independent entities that drive innovation and commercialize new technologies. Unlike open innovation, which often emphasizes external collaboration and idea sharing, corporate spin-offs focus on leveraging internal knowledge assets to accelerate growth and capture new market opportunities. Explore how corporate spin-offs transform innovation strategies and redefine competitive advantage by learning more about their practical applications and success stories.
Technology Scouting
Technology scouting in open innovation involves identifying external technological opportunities to accelerate internal R&D, enabling companies to remain competitive in fast-evolving markets. Corporate venturing focuses on investing in or partnering with startups to gain strategic access to emerging technologies and business models. Discover how leveraging these approaches can drive breakthrough innovations and sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
What is Open Innovation? Definition, Types, Model and Best Practices - This webpage provides a comprehensive overview of open innovation, including its definition, models, and best practices for collaborative innovation.
Open Innovation - Wikipedia - This Wikipedia article explains open innovation as a paradigm that encourages using external sources of innovation and managing intellectual property effectively.
What is Open Innovation? Benefits & Best Practices - Qmarkets - This article discusses the benefits of open innovation, including accelerated innovation processes, access to diverse ideas, and reduced R&D costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com