Diagnostic mapping visually represents the relationships between problems and underlying causes, enabling clearer identification of root issues within consulting projects. Issue tree analysis breaks down complex problems into smaller, manageable components through a structured, hierarchical approach, facilitating targeted solutions. Explore deeper insights into how these methodologies enhance problem-solving efficiency in consulting.
Why it is important
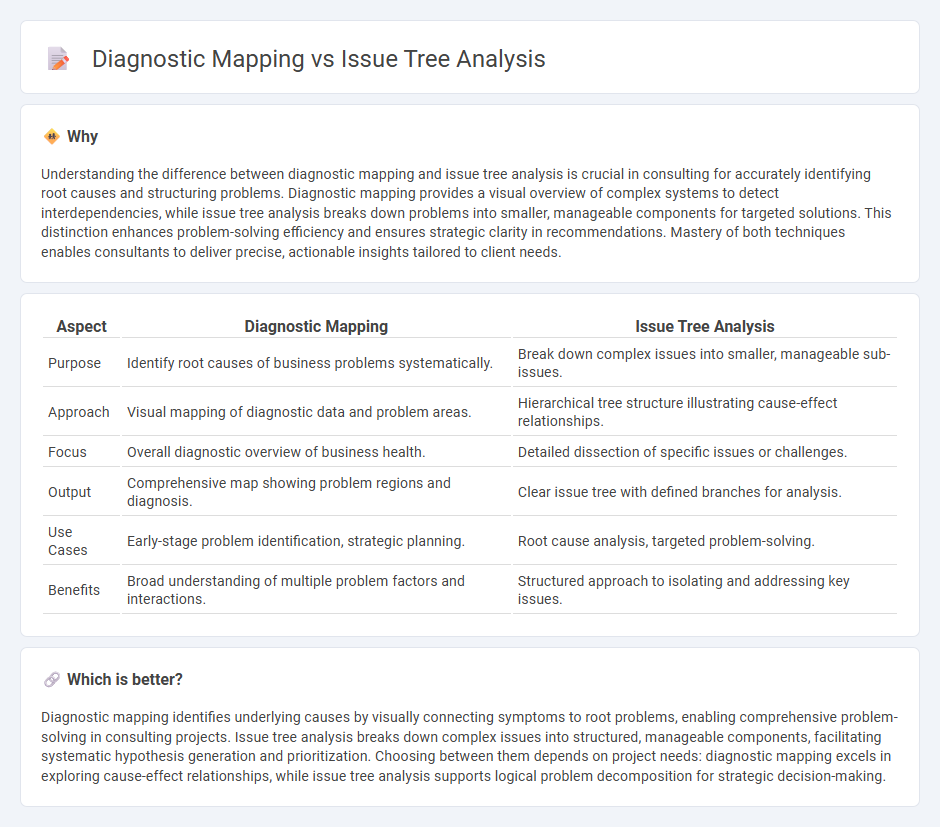
Understanding the difference between diagnostic mapping and issue tree analysis is crucial in consulting for accurately identifying root causes and structuring problems. Diagnostic mapping provides a visual overview of complex systems to detect interdependencies, while issue tree analysis breaks down problems into smaller, manageable components for targeted solutions. This distinction enhances problem-solving efficiency and ensures strategic clarity in recommendations. Mastery of both techniques enables consultants to deliver precise, actionable insights tailored to client needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Diagnostic Mapping | Issue Tree Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify root causes of business problems systematically. | Break down complex issues into smaller, manageable sub-issues. |
| Approach | Visual mapping of diagnostic data and problem areas. | Hierarchical tree structure illustrating cause-effect relationships. |
| Focus | Overall diagnostic overview of business health. | Detailed dissection of specific issues or challenges. |
| Output | Comprehensive map showing problem regions and diagnosis. | Clear issue tree with defined branches for analysis. |
| Use Cases | Early-stage problem identification, strategic planning. | Root cause analysis, targeted problem-solving. |
| Benefits | Broad understanding of multiple problem factors and interactions. | Structured approach to isolating and addressing key issues. |
Which is better?
Diagnostic mapping identifies underlying causes by visually connecting symptoms to root problems, enabling comprehensive problem-solving in consulting projects. Issue tree analysis breaks down complex issues into structured, manageable components, facilitating systematic hypothesis generation and prioritization. Choosing between them depends on project needs: diagnostic mapping excels in exploring cause-effect relationships, while issue tree analysis supports logical problem decomposition for strategic decision-making.
Connection
Diagnostic mapping and issue tree analysis are interconnected tools in consulting that systematically identify and break down complex business problems into manageable components. Diagnostic mapping outlines the overall structure and relationships of key issues, while issue tree analysis drills down into each element to explore root causes and potential solutions. Together, they enable consultants to develop targeted strategies based on a clear, data-driven understanding of the challenges faced by an organization.
Key Terms
Hypothesis-driven structure
Issue tree analysis uses a hypothesis-driven structure to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components, enabling targeted investigation of each branch for effective problem-solving. Diagnostic mapping systematically traces cause-and-effect relationships within a hypothesis framework, helping identify root causes through logical progression and validation of assumptions. Explore how combining these methods enhances strategic decision-making and problem resolution in business contexts.
Root cause identification
Issue tree analysis systematically breaks down complex problems into smaller, manageable components, enabling precise root cause identification through hierarchical decomposition. Diagnostic mapping visually represents relationships and causality between problem elements, offering a clear overview of underlying issues and their interdependencies. Explore these methodologies further to enhance your root cause identification process and problem-solving efficiency.
Logical sequencing
Issue tree analysis breaks down complex problems into hierarchical components, ensuring logical sequencing by decomposing issues into mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive branches. Diagnostic mapping systematically traces root causes and their interrelations, emphasizing causal pathways and logical order to identify underlying problems efficiently. Explore detailed methods and applications to enhance problem-solving precision.
Source and External Links
Issue Tree in Consulting: A Complete Guide (With Examples) - An issue tree is a structured method for breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable branches to isolate root causes and ensure all possibilities related to the problem are covered in a mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive (MECE) way for lasting solutions.
What are the differences between issue trees and hypothesis trees? - Issue trees, also called diagnostic trees, graphically break down the key question into WHY or HOW sub-questions and apply MECE principles to identify all possible causes or solutions, forming the core of problem-solving frameworks.
Issue Trees: Step-By-Step Guide with Examples (2025) - An issue tree starts with a top-level problem and systematically branches into major categories and further into sub-issues, helping simplify complex problems into smaller, solvable components, such as breaking "increase profits" into "increase revenues" and "decrease costs."
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com